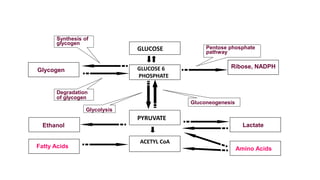
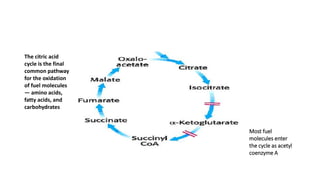
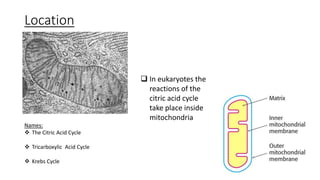
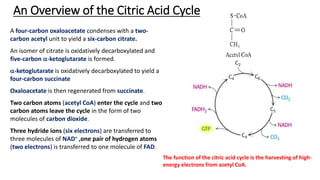
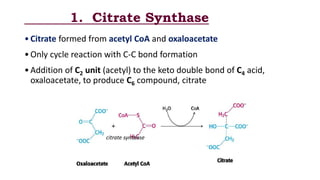
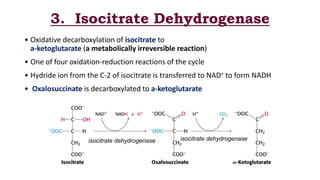
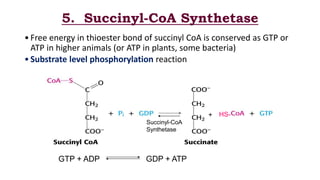
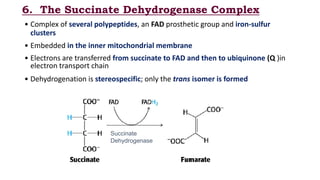
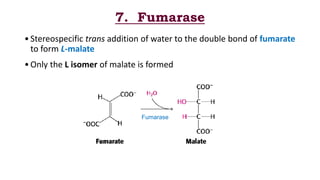
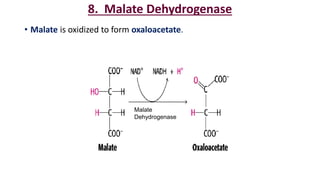
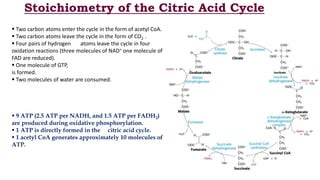
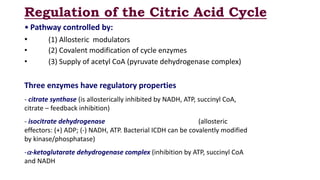
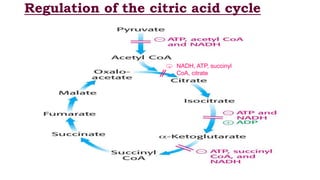
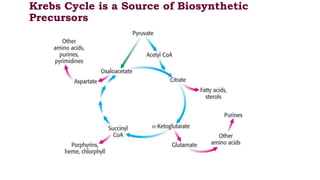
The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of molecules like amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. Most of these molecules enter the cycle as acetyl-CoA. The cycle was discovered in 1937 by Hans Krebs and involves 8 steps where acetyl-CoA condenses with oxaloacetate to form citrate and regenerate oxaloacetate. The cycle harvests energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and FADH2 and provides precursors for biosynthesis. Key enzymes in the cycle are regulated by factors like the levels of NADH and ATP.