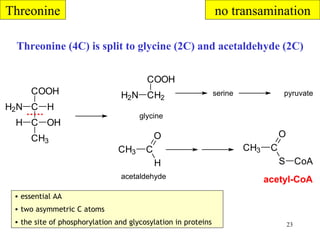
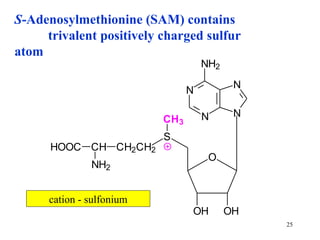
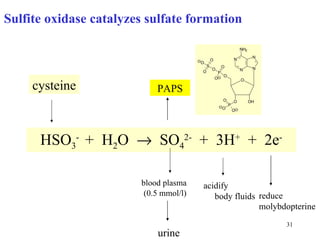
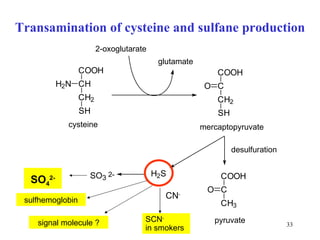
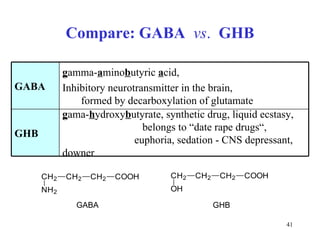
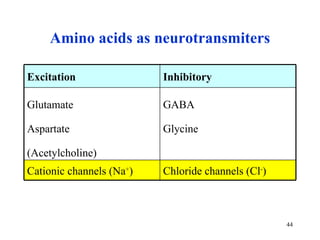
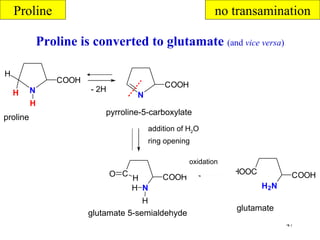
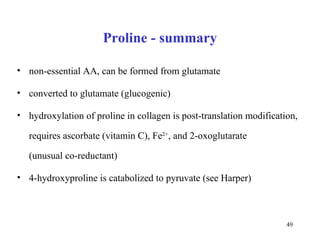
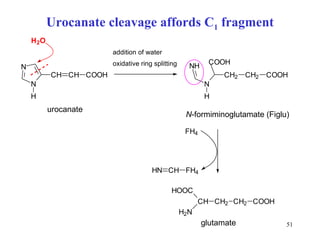
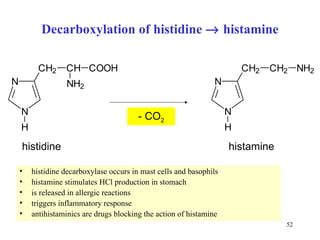
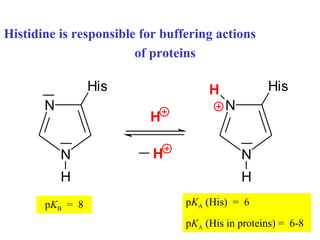
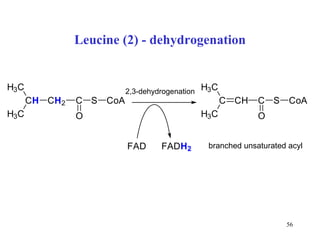
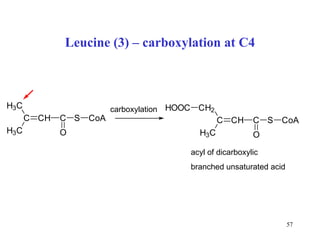
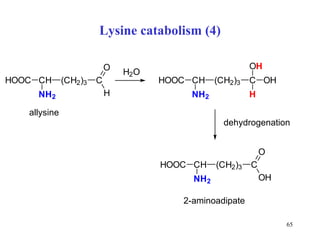
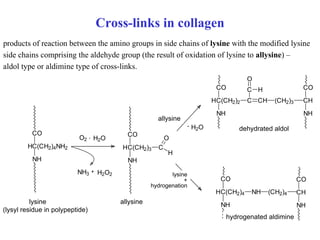
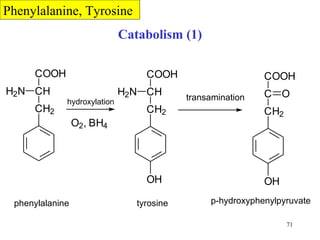
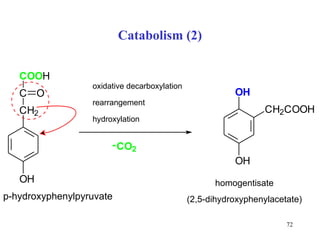
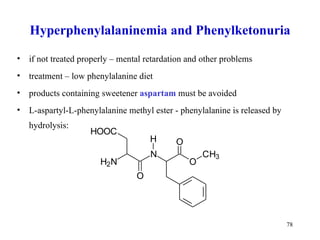
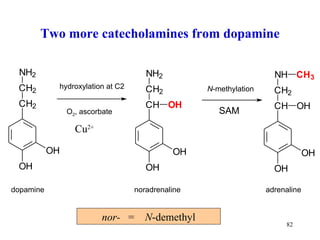
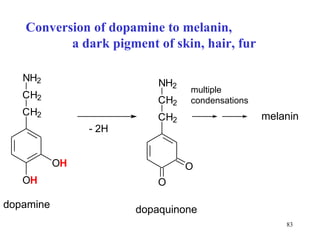
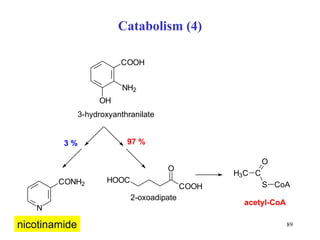
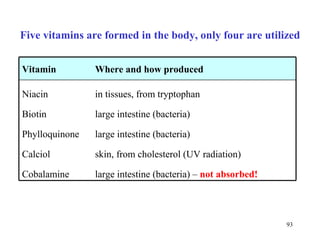
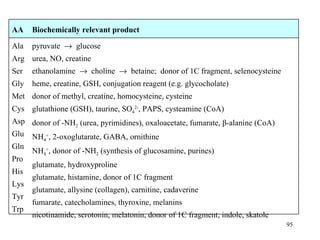
The document summarizes the metabolism of various amino acids. It notes that some amino acids are glucogenic, producing pyruvate or TCA cycle intermediates, while others are ketogenic, producing acetyl-CoA or acetoacetate. Key points include:
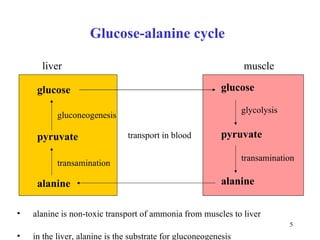
- Alanine can be readily formed from pyruvate via transamination and is important for gluconeogenesis.
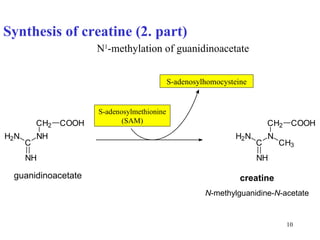
- Arginine produces ornithine and urea and is the precursor for nitric oxide and creatine synthesis.
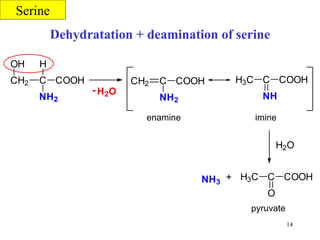
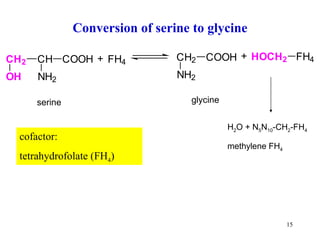
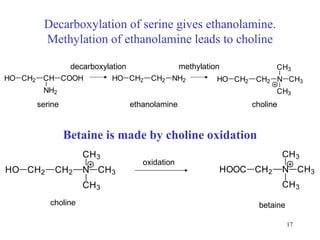
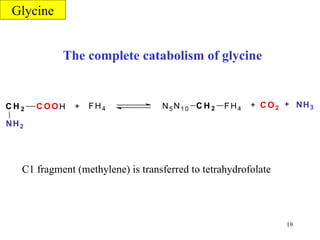
- Serine can be converted to glycine and provides one-carbon units via tetrahydrofolate. Its carbon skeleton feeds into other amino acids.
- Glutamate is central to amino acid