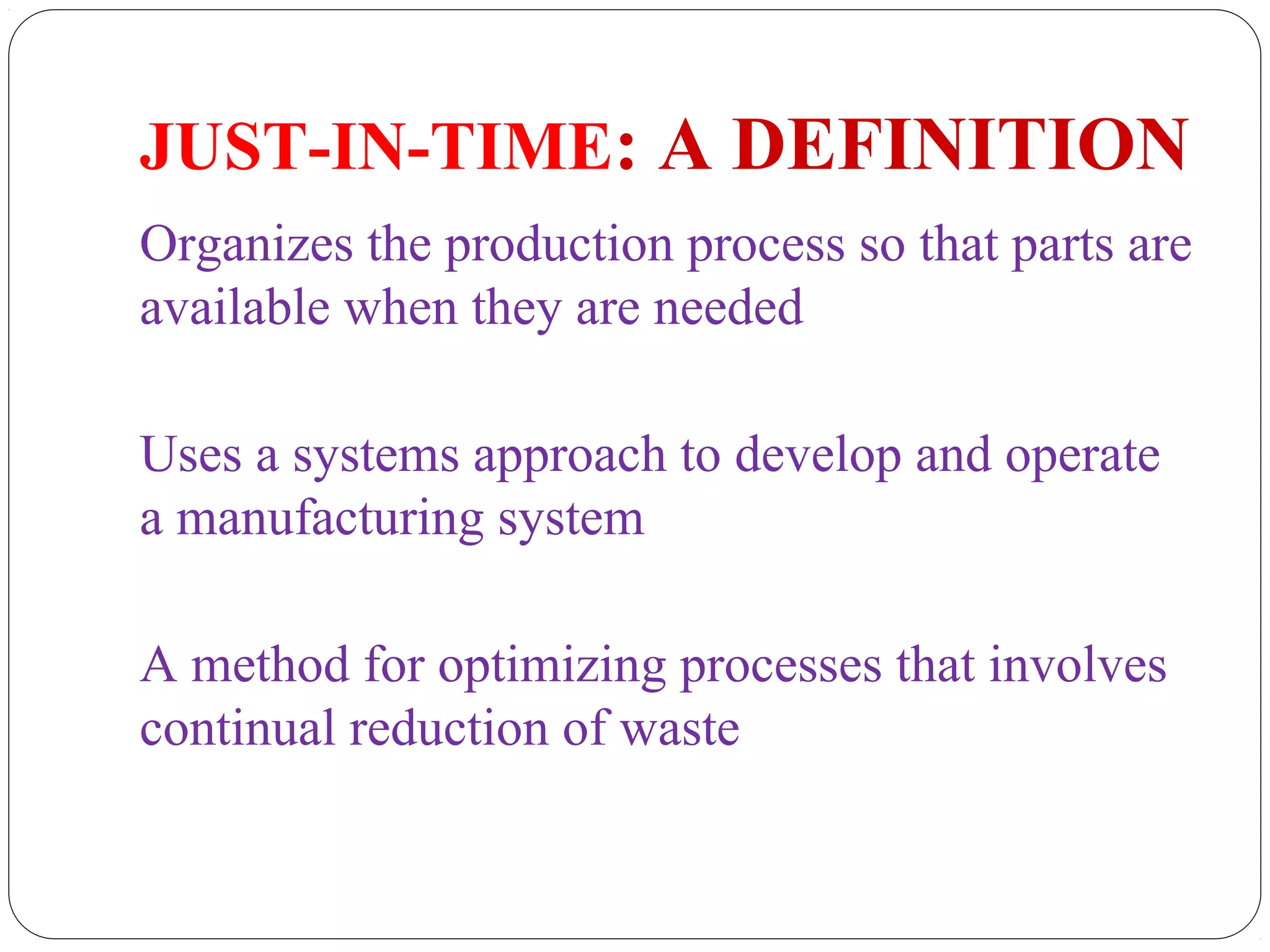
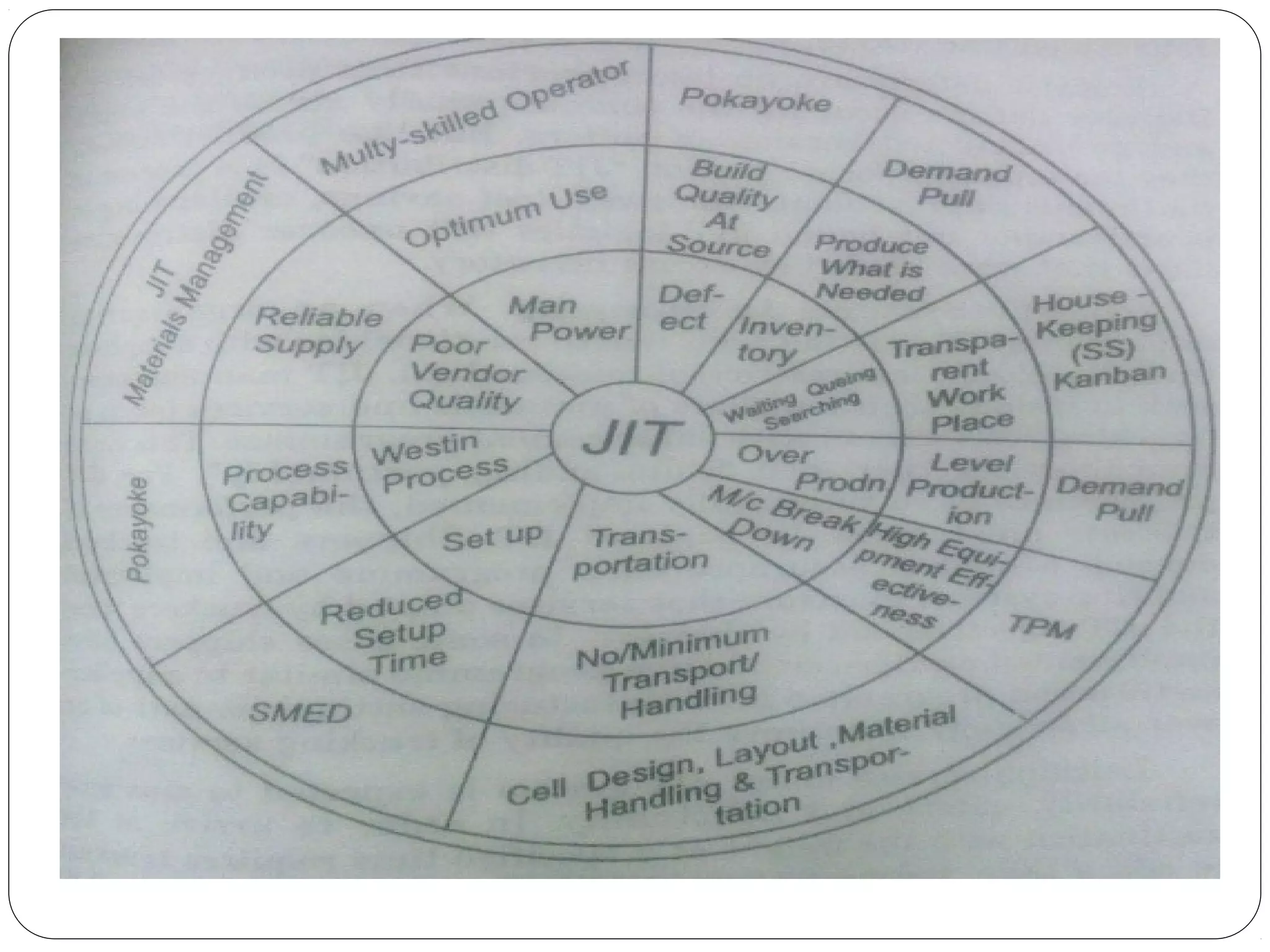
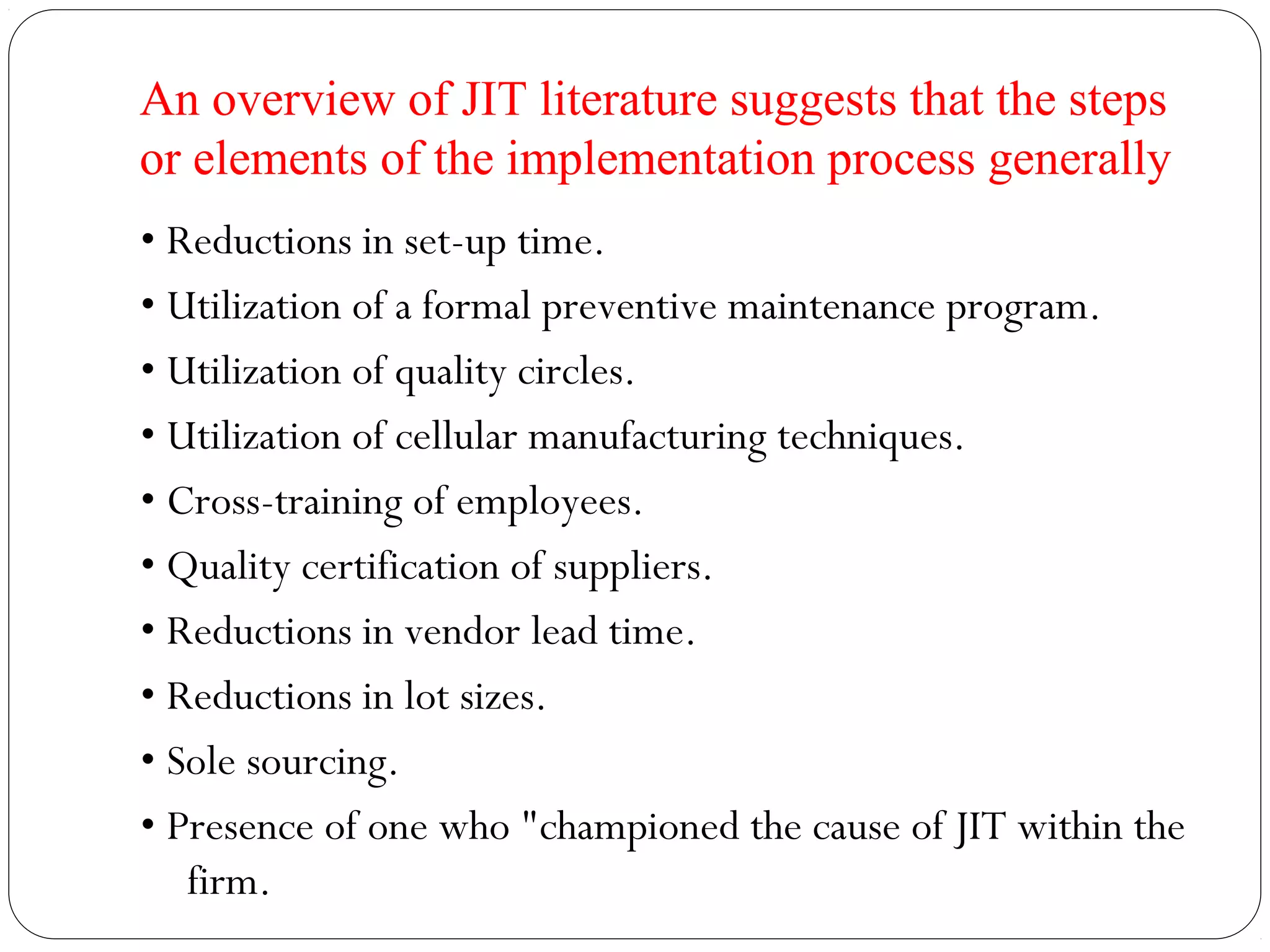
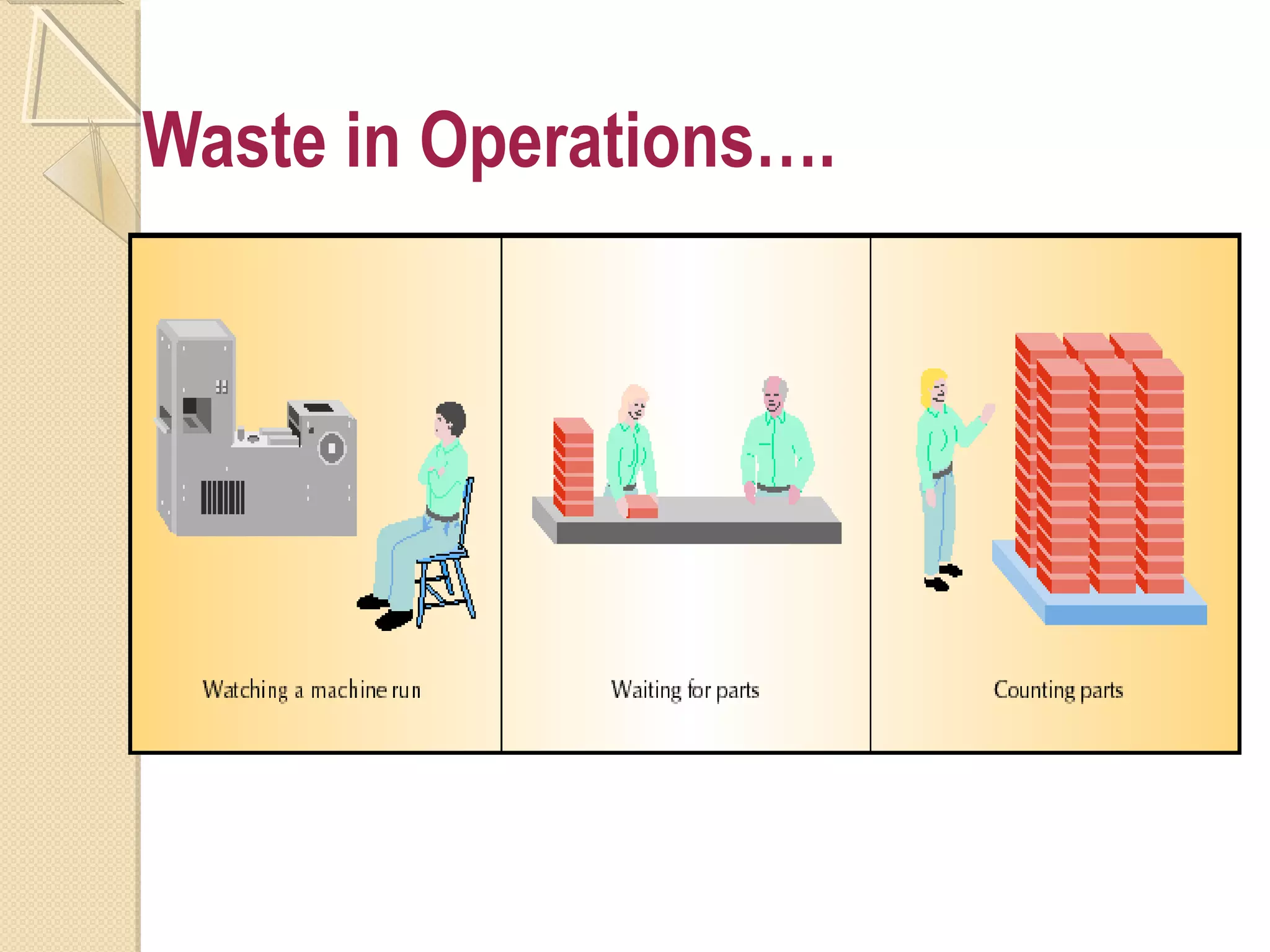
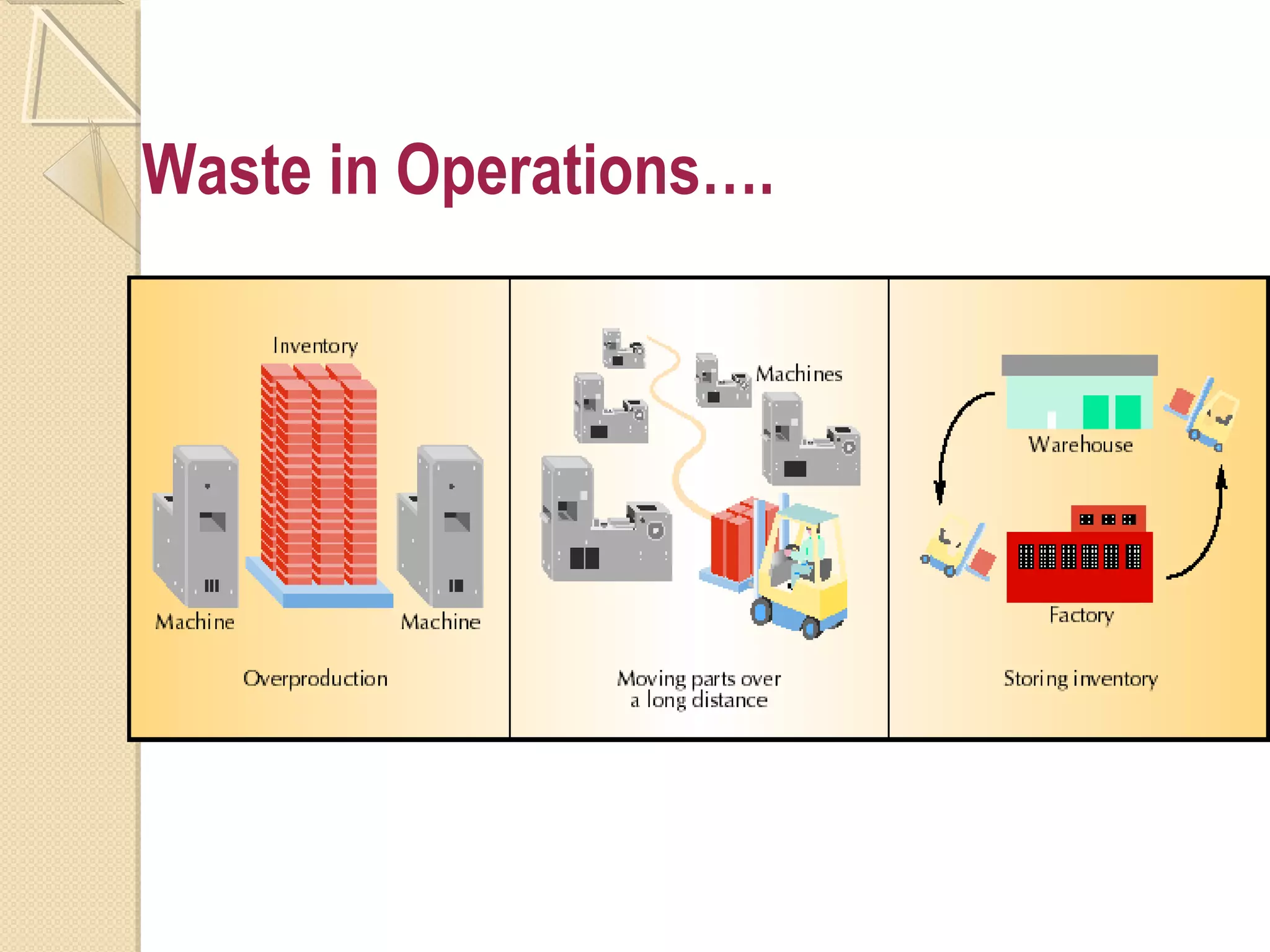
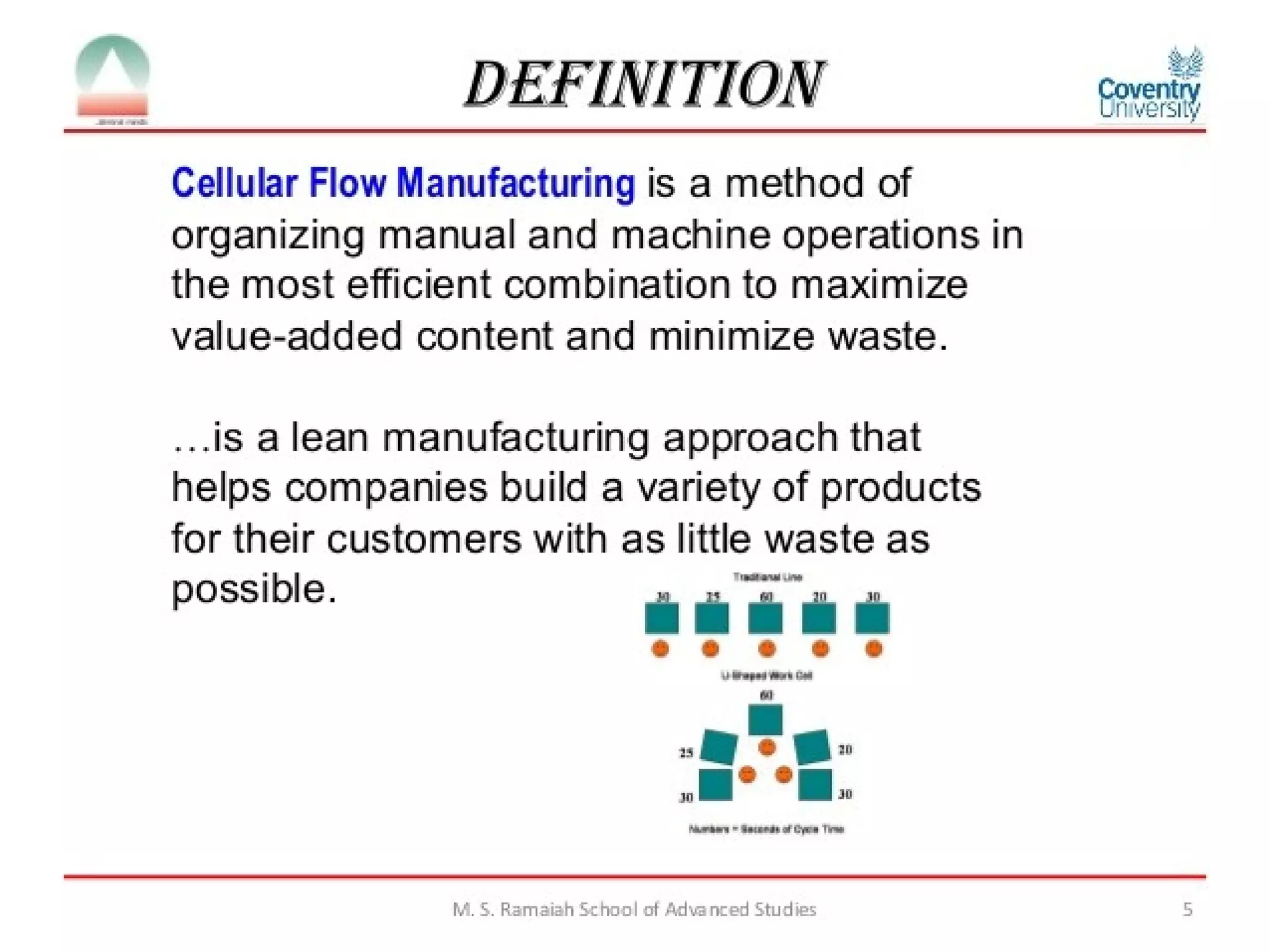
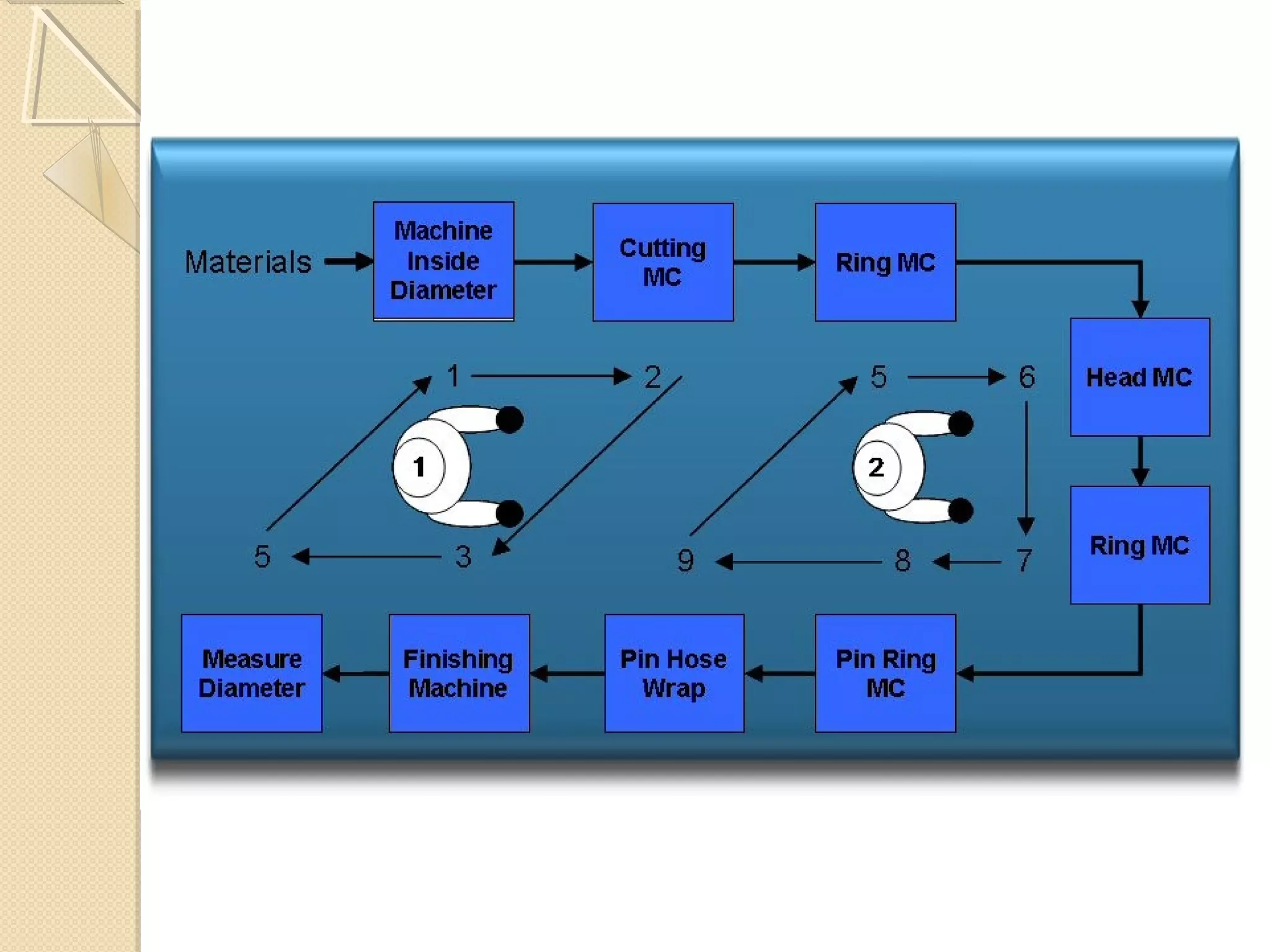
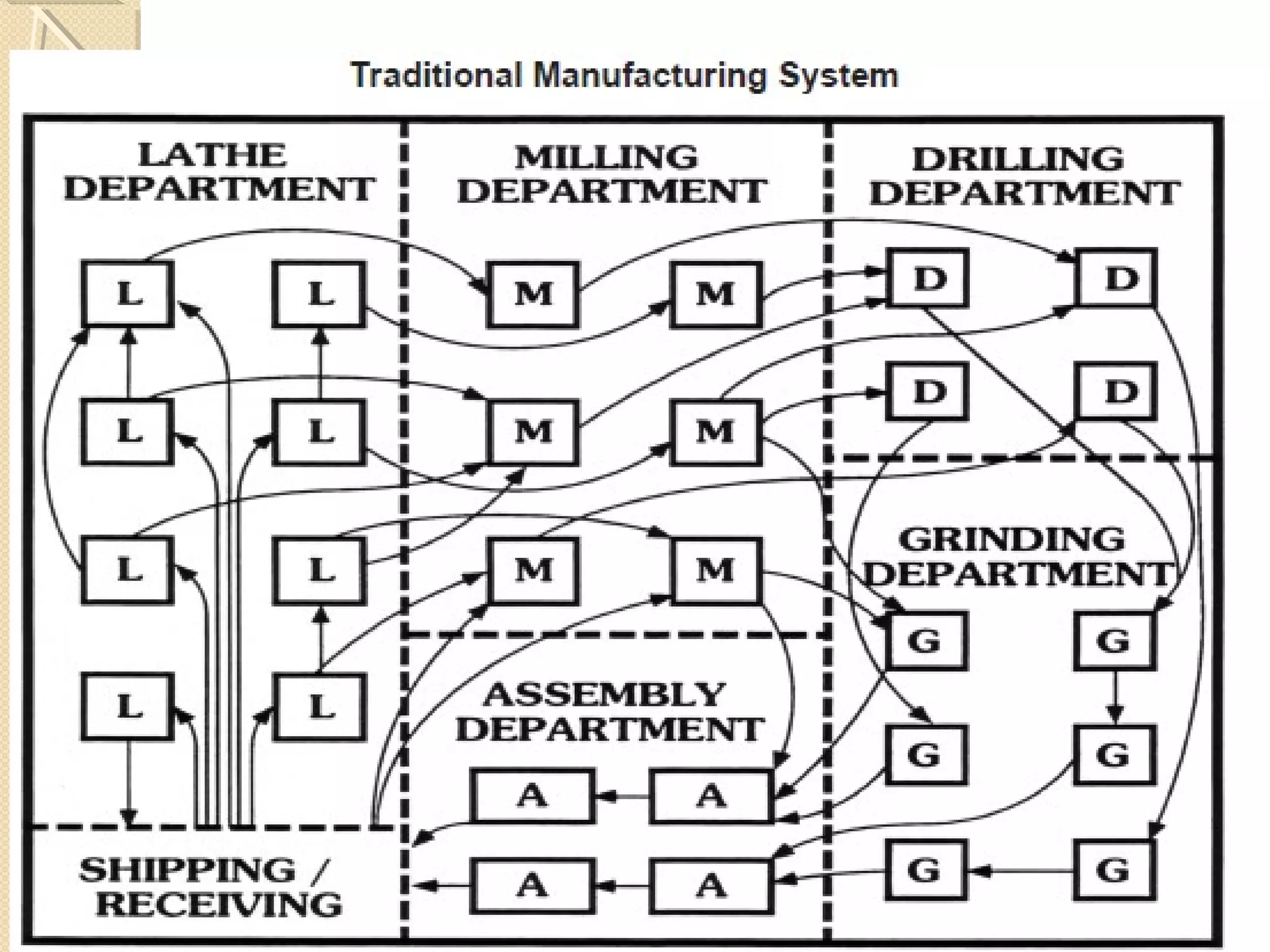
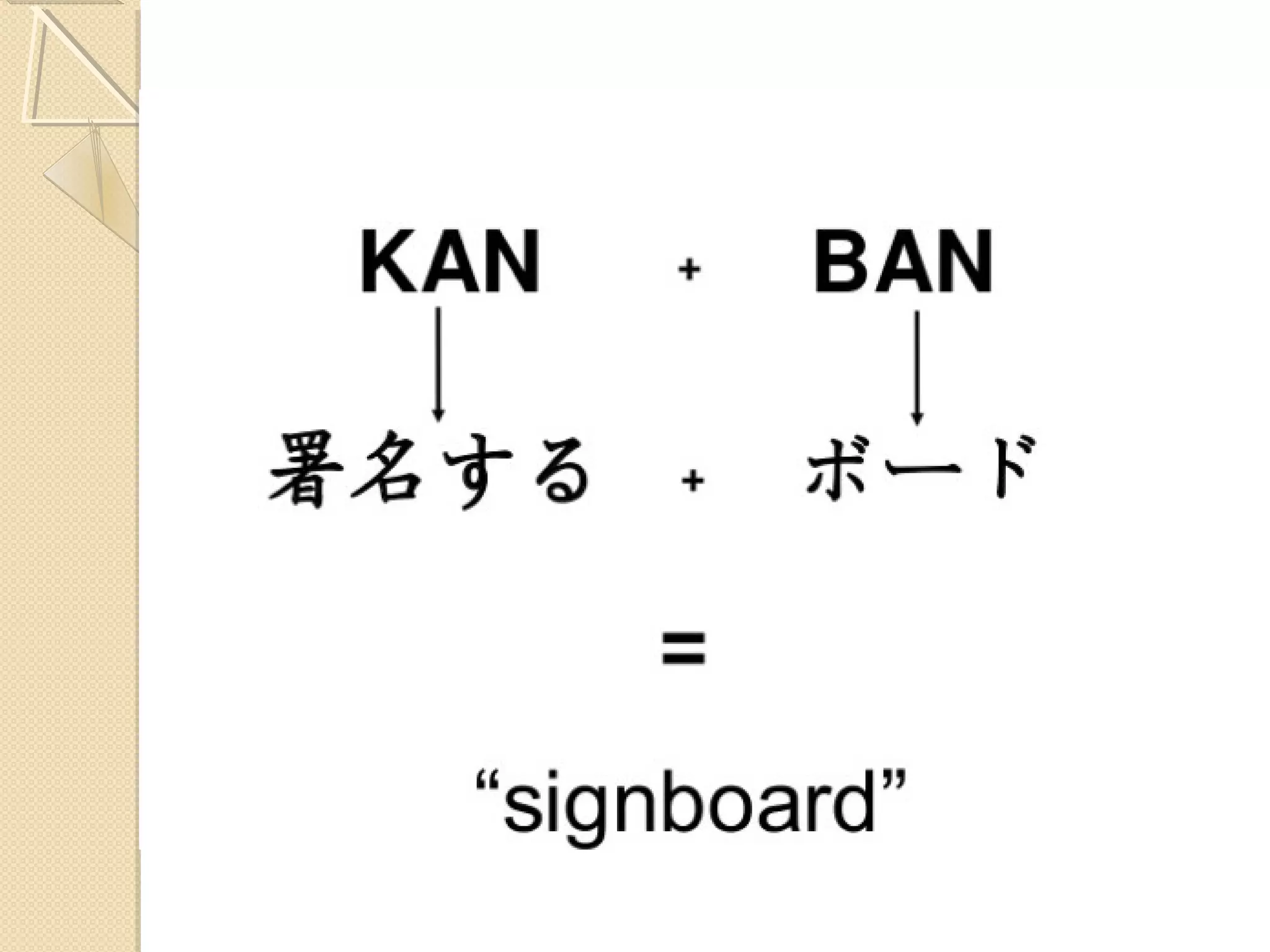
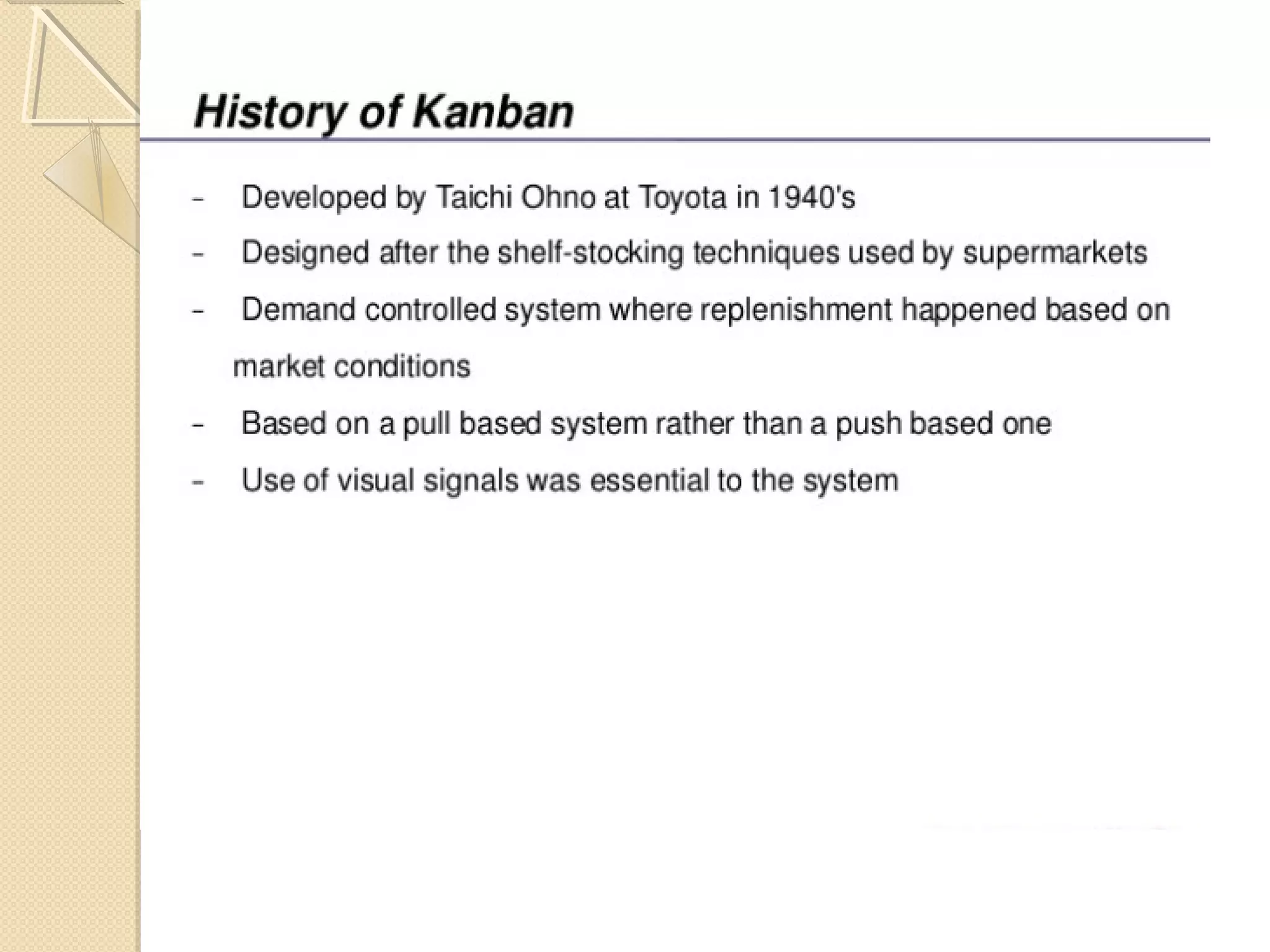
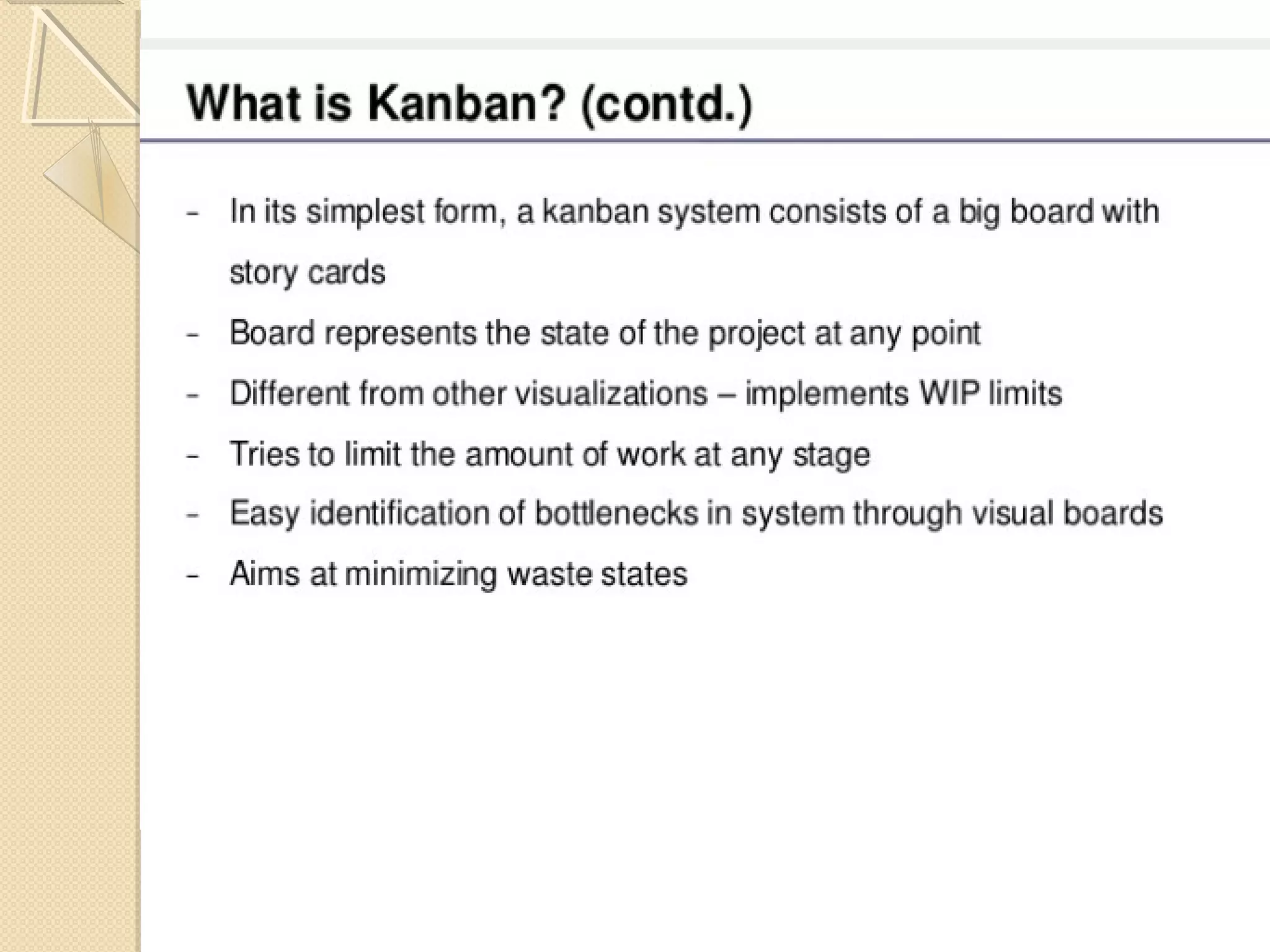
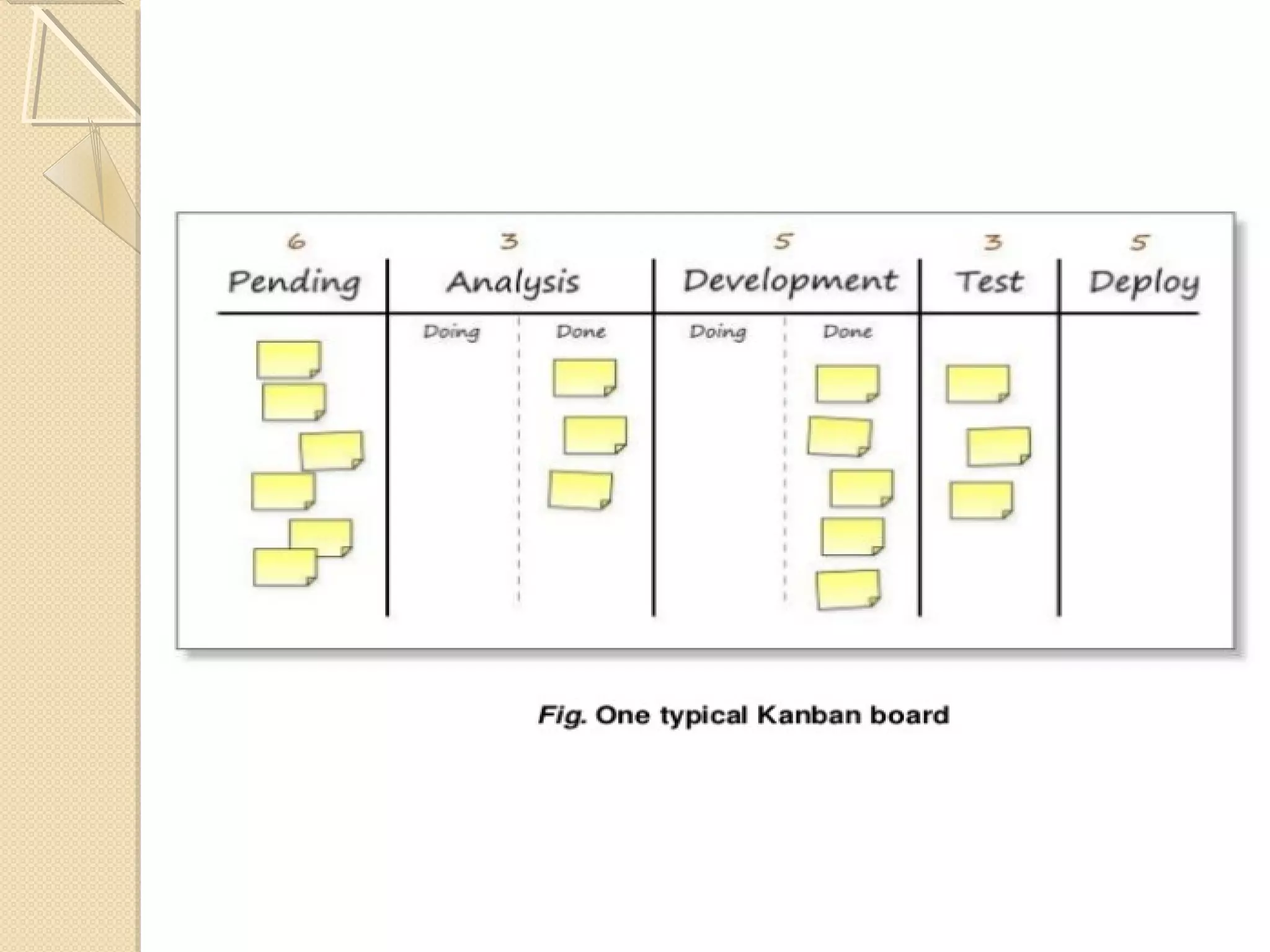
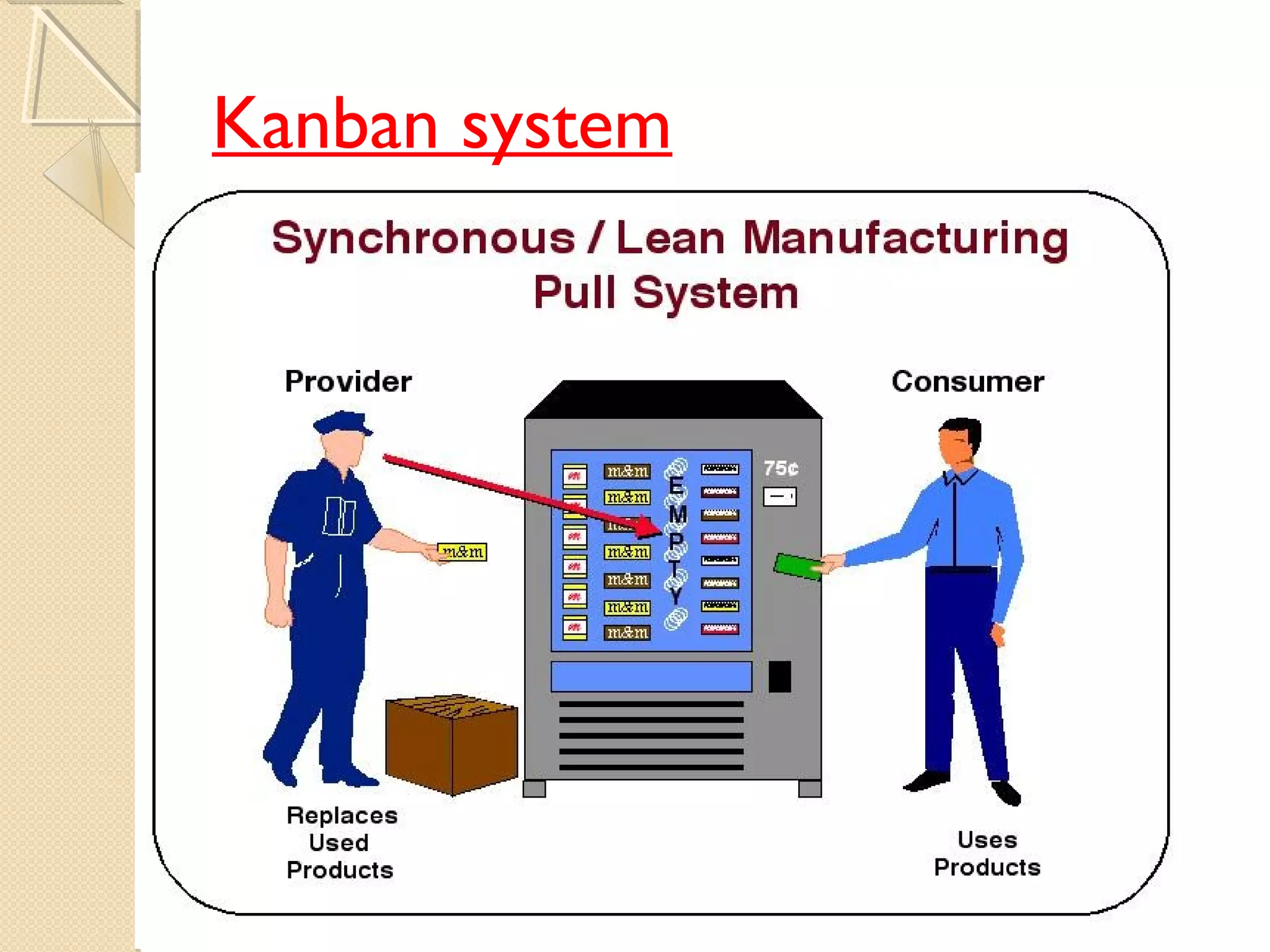
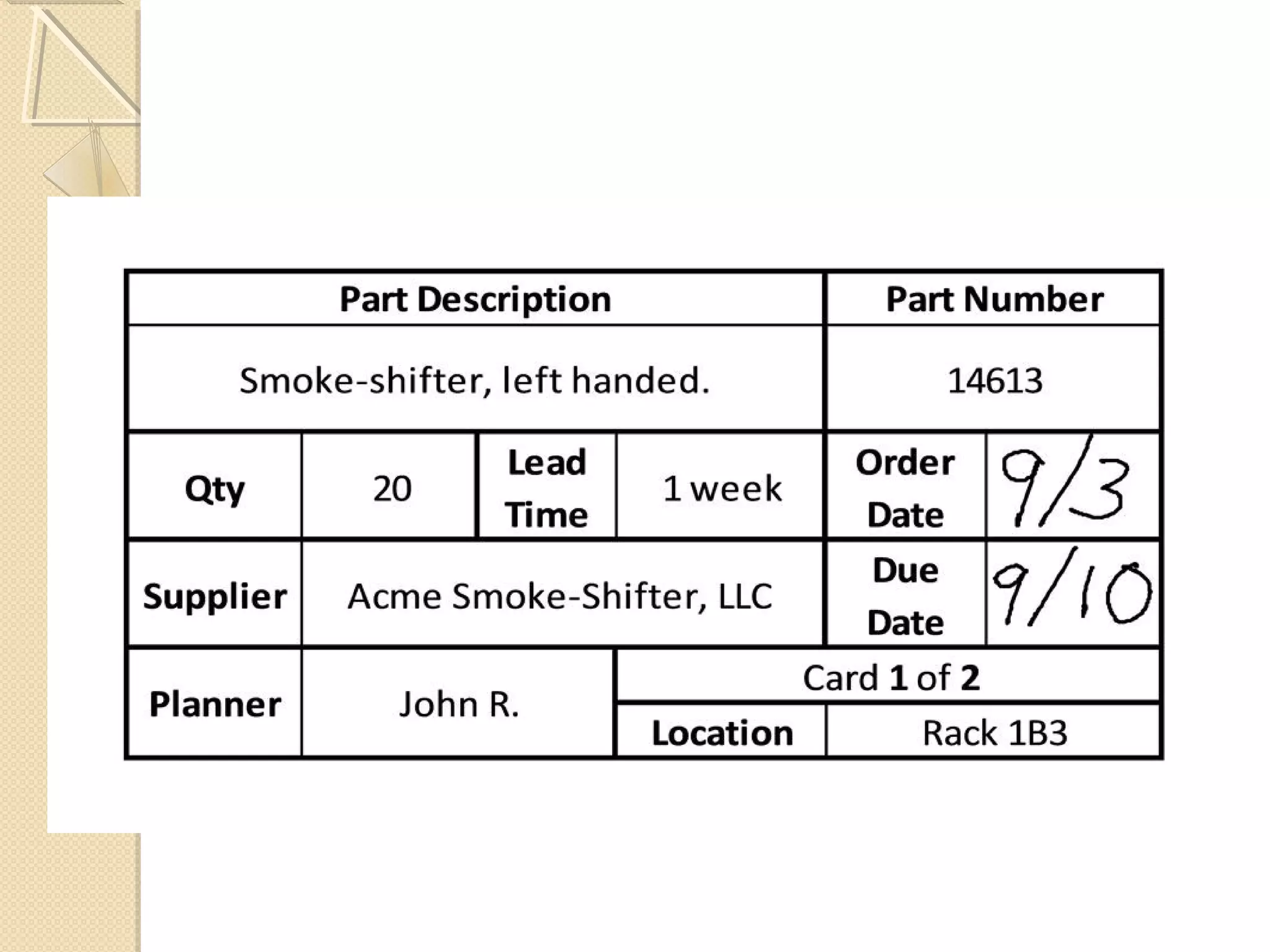
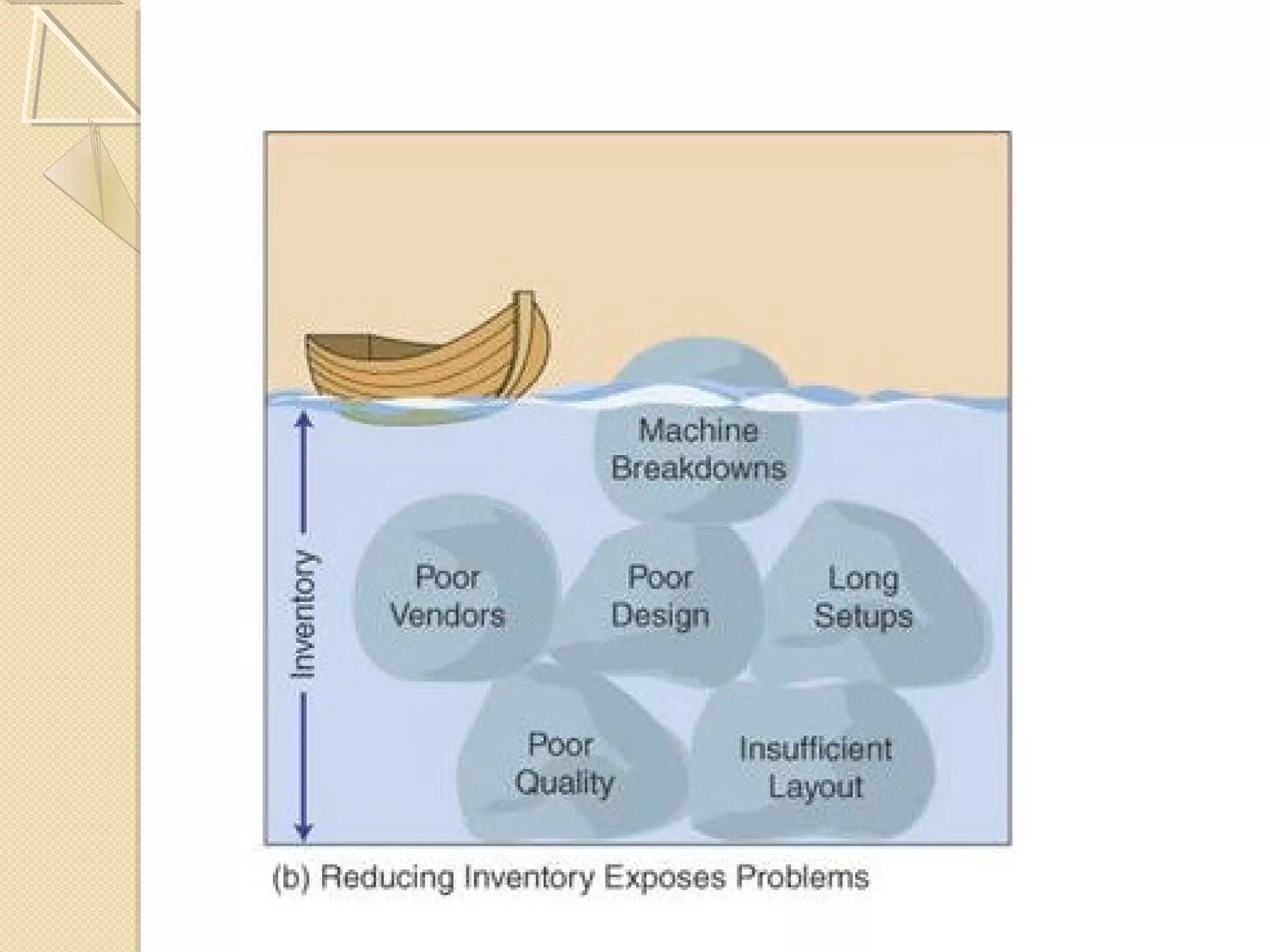
This document provides an overview of Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing. It defines JIT as a method that organizes production so that parts are available when needed. The key aspects of JIT discussed include: eliminating waste through continuous improvement, leveling production using a pull system like Kanban, setting up cells/modules, reducing setup times, and ensuring quality from suppliers. JIT aims to provide customers what they want, when they want it, with no excess inventory or waste.