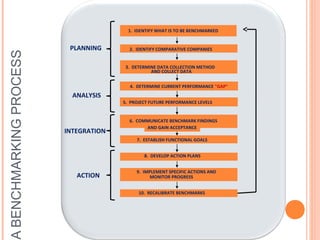
Benchmarking is the process of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry best practices in order to improve performance. It involves identifying top performers in other organizations, understanding what makes them successful, and adapting practices for one's own organization. The key advantages are improved processes and products, reduced costs and time, and a more competitive strategy. While benchmarking has helped many organizations, there are also risks if benchmarks are not well-defined or comparisons are incorrect. The typical benchmarking process involves planning, analysis, integration, action, and recalibrating benchmarks over time. There are different types of benchmarking based on what is compared (e.g. products, processes) and who is compared against (e.g. internal/external