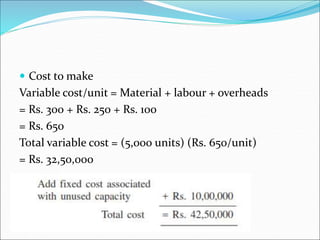
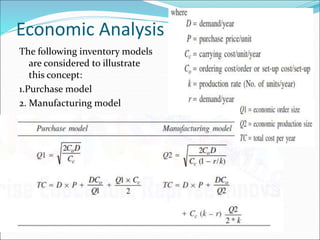
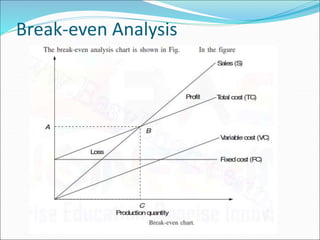
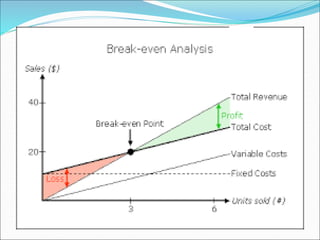
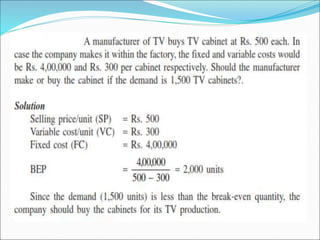
This document discusses factors to consider in a make or buy decision for an organization. It should evaluate the lowest cost alternative of making a product internally or purchasing it externally. The decision should be reviewed periodically as the business environment changes. Key criteria for making internally include lower cost, limited supplier capacity, and close quality control needs. Key criteria for buying externally include requiring existing supplier facilities, lacking internal production capabilities, and temporary or seasonal demand. Approaches to analyze the decision include simple cost analysis, economic analysis comparing purchase and manufacturing models, and break-even analysis.