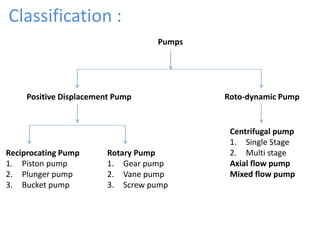
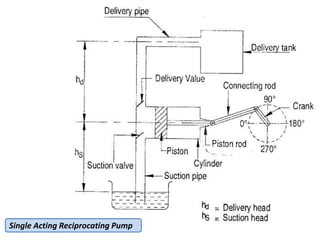
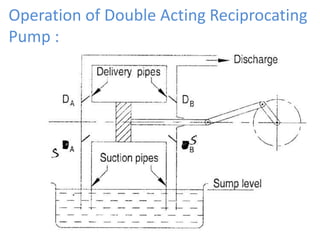
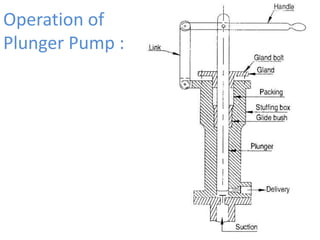
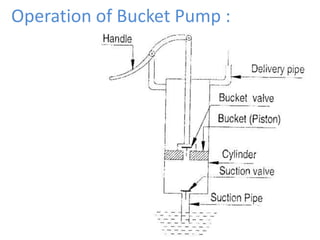
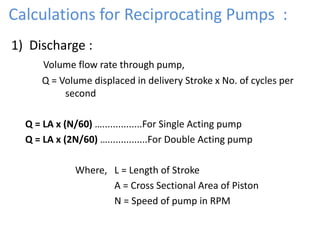
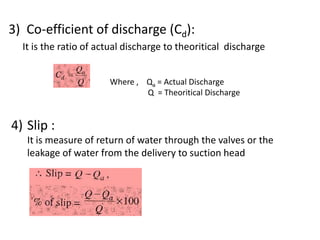
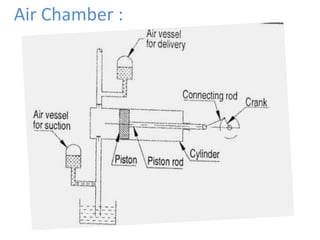
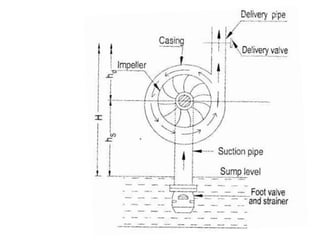
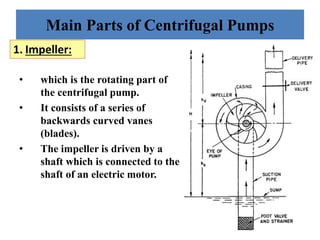
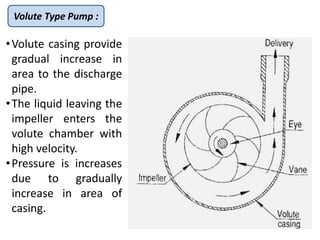
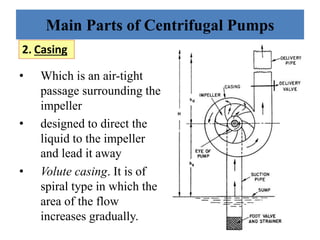
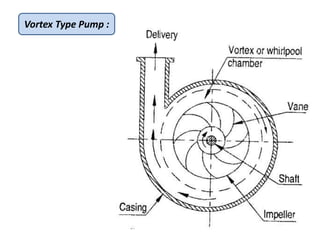
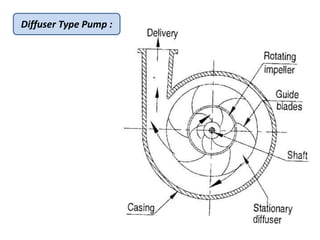
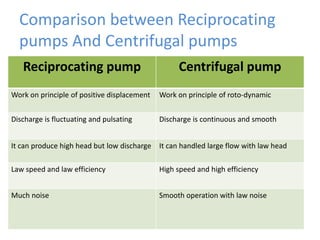
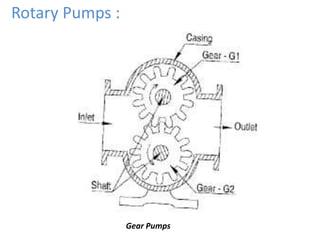
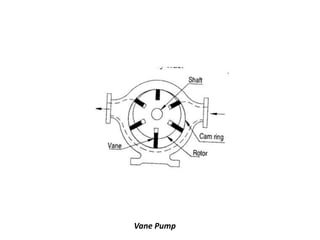
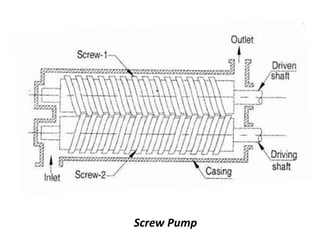
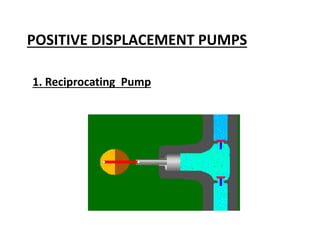
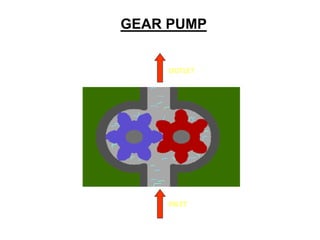
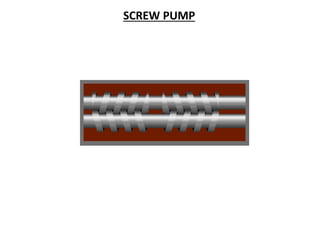
This document provides an overview of different types of pumps. It begins by defining a pump as a mechanical device that conveys liquid from one place to another by adding energy. Pumps are classified as either positive displacement pumps, which include reciprocating, gear, vane and screw pumps, or centrifugal pumps, which include single-stage, multi-stage, axial and mixed flow pumps. Key concepts discussed include pump components, classifications, operating principles, calculations and comparisons between reciprocating and centrifugal pumps. Terminology such as head, discharge and efficiency are also defined.