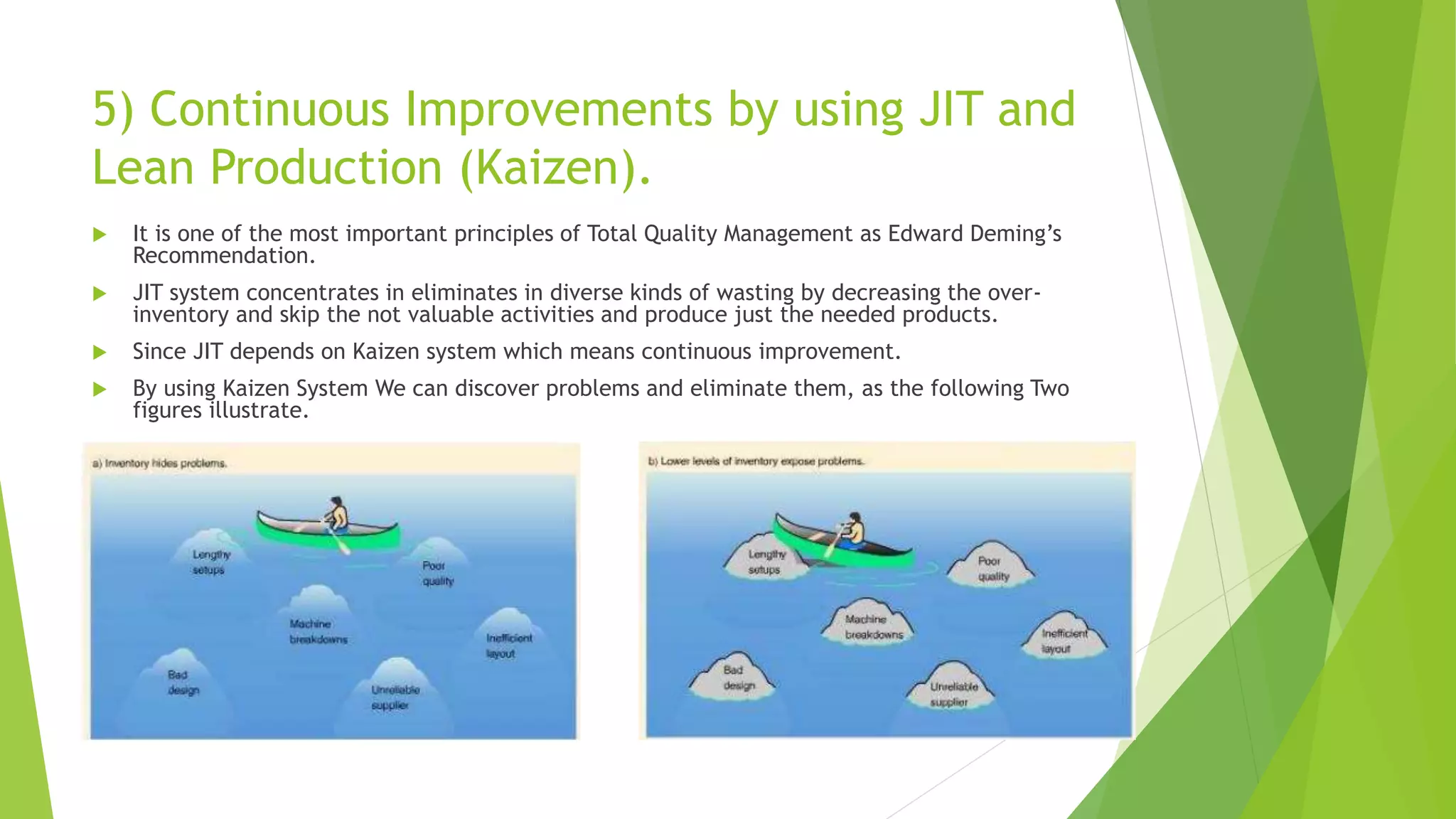
The document discusses Just-in-Time (JIT) and Lean Production methodologies aimed at reducing waste and improving efficiency in manufacturing. It covers objectives, definitions, key elements, the importance of continuous improvement (kaizen), types of waste, the 5S methodology, and the advantages and disadvantages of these systems. A case study on Harley-Davidson illustrates the successful implementation of JIT in response to competitive pressures.