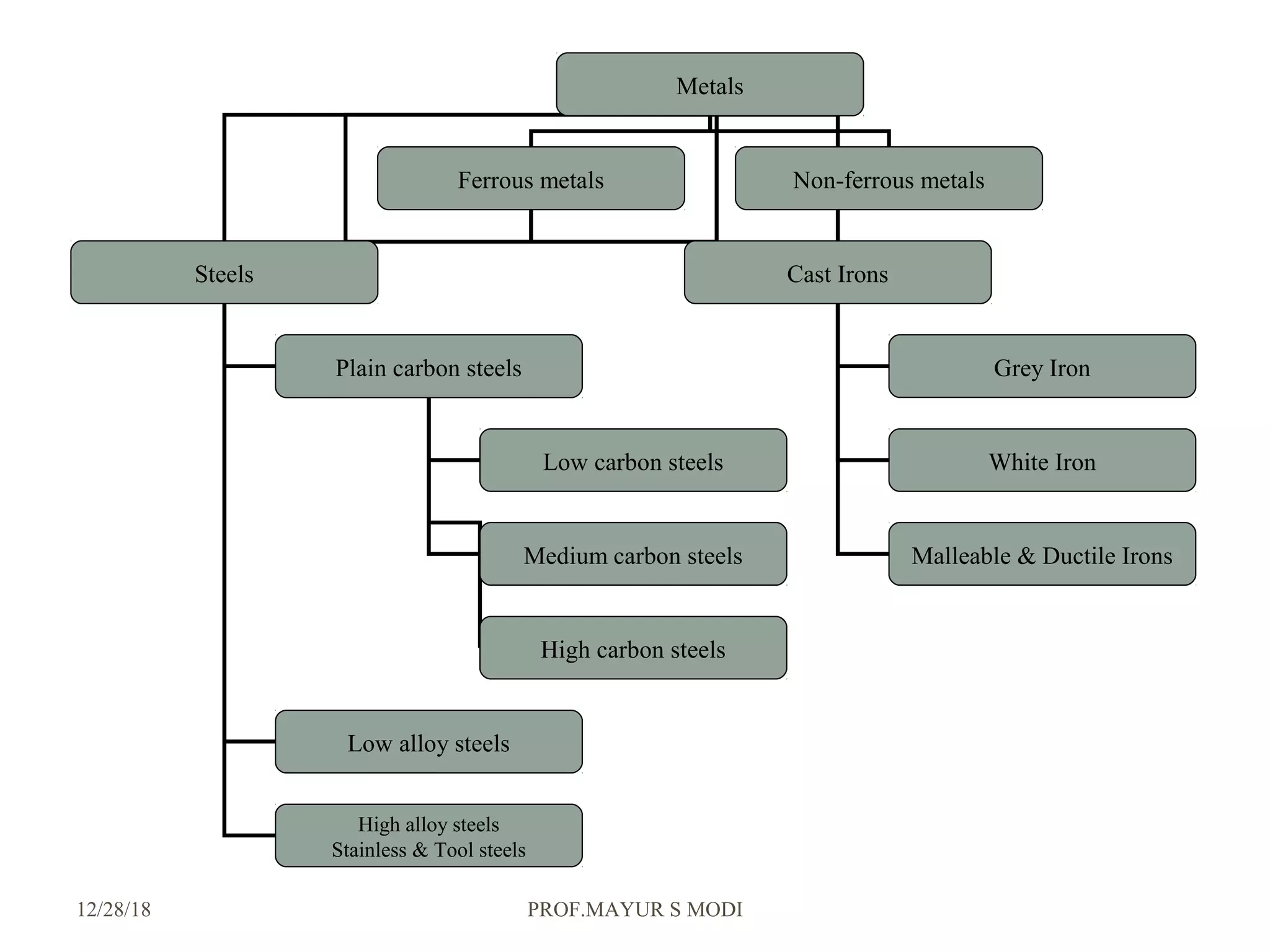
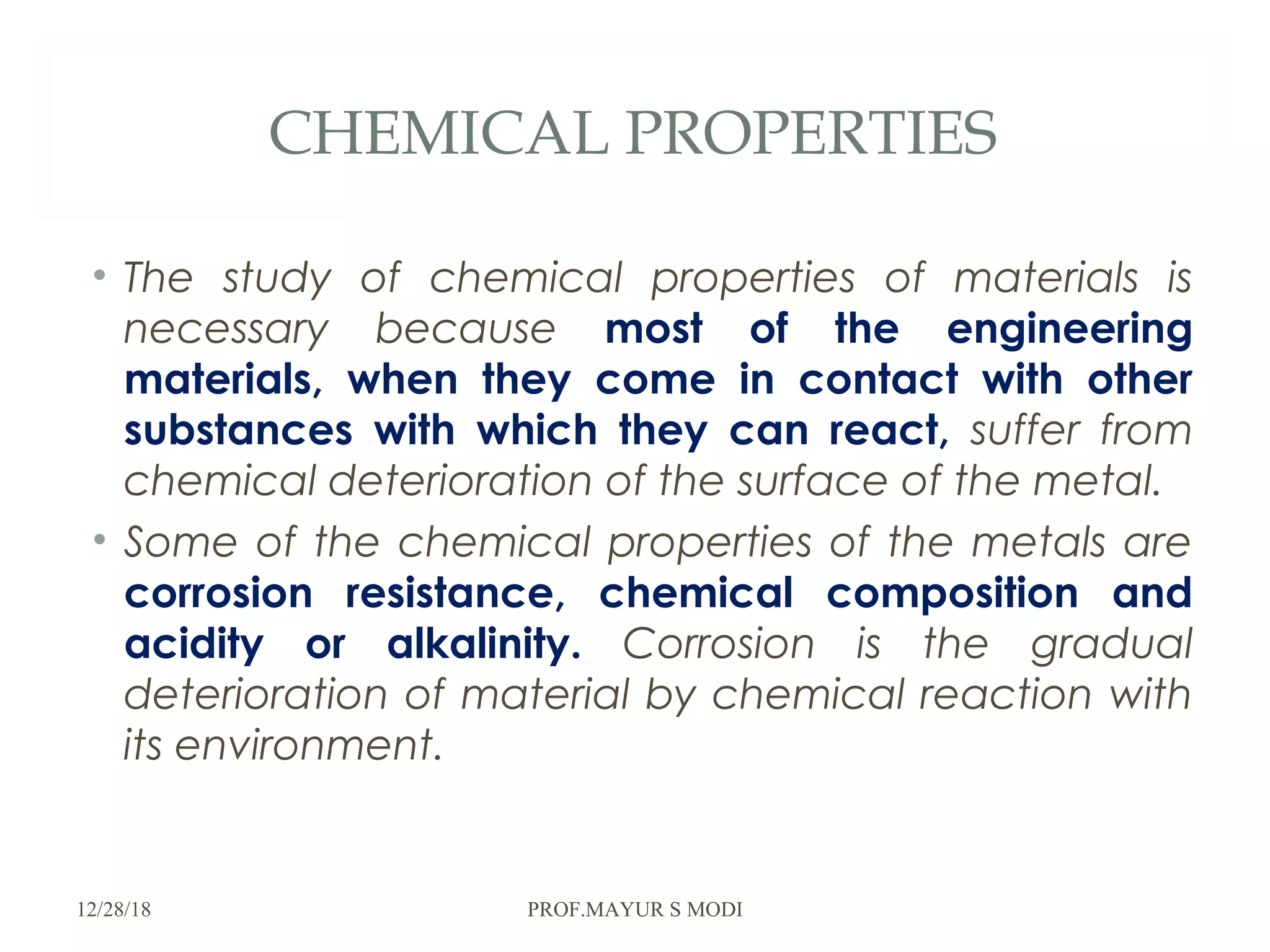
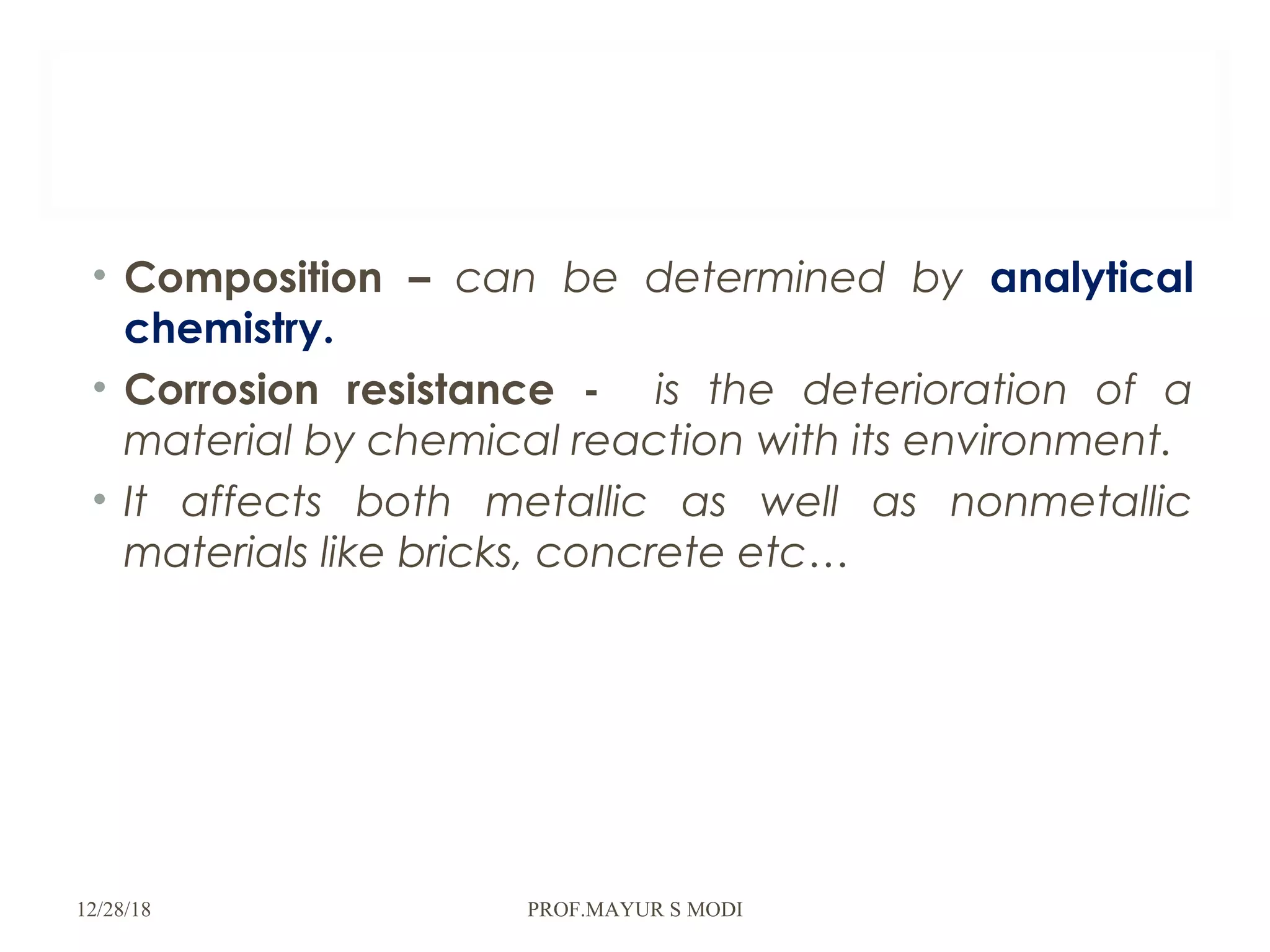
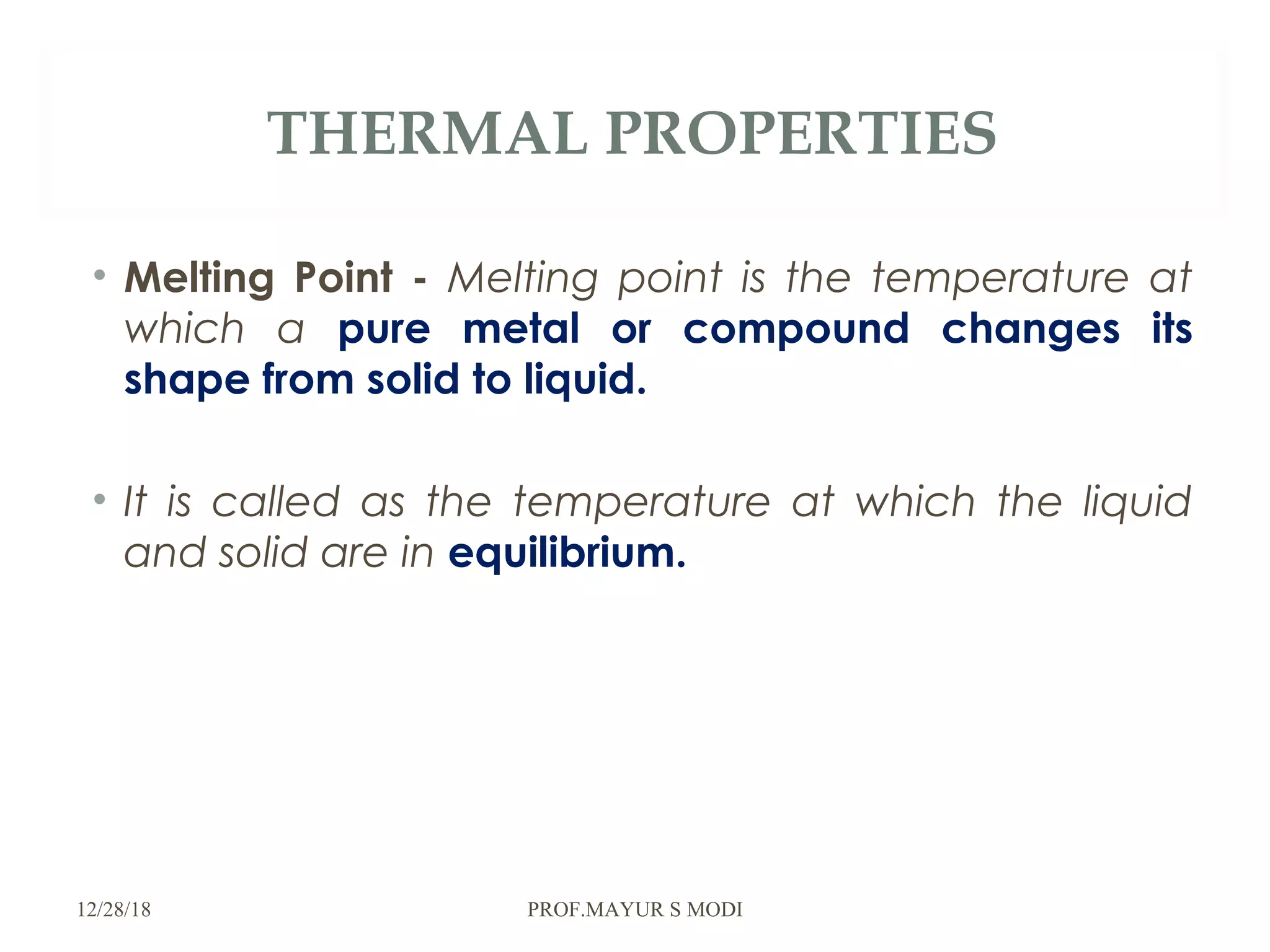
The document provides an overview of material science and metallurgy, focusing on the various properties of metals, including physical, chemical, thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties. It highlights the importance of understanding these properties for engineers in order to select appropriate materials for construction and manufacturing applications. Additionally, it discusses criteria for material selection based on performance, reliability, safety, and economic factors.