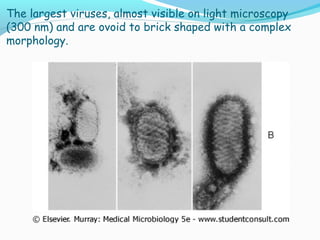
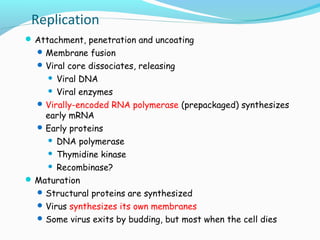
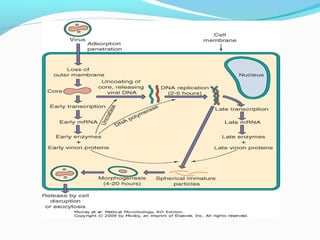
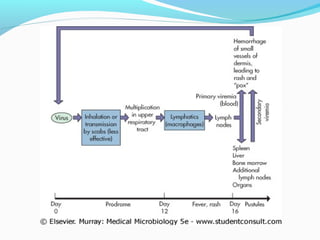
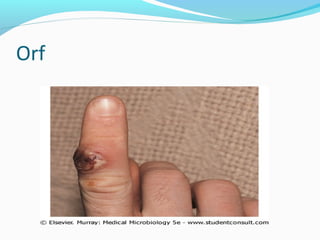
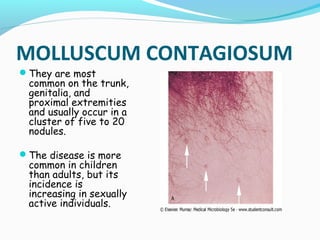
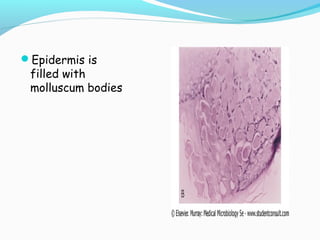
Poxviruses are a family of large, complex enveloped viruses that contain double-stranded DNA. They include viruses that infect humans and other vertebrates. Smallpox and molluscum contagiosum are human poxviruses, while viruses like vaccinia, cowpox and monkeypox can infect humans incidentally from animal hosts. Poxviruses replicate in the cytoplasm and have complex virion structures. Important human poxviruses include variola (smallpox virus), which was eradicated in the 1970s through vaccination, and molluscum contagiosum, which causes a generally mild skin infection.