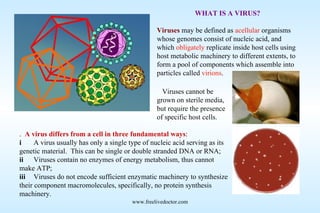
Viruses are acellular organisms that can only replicate inside host cells. They contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material but lack enzymes to synthesize proteins or metabolic machinery. A virus infects a host cell and uses the cell's machinery to produce copies of its genome and proteins which self-assemble into new virus particles. Viruses are distinguished from other parasites by their inability to grow outside of host cells and lack of cellular structure. They have played a major role in human diseases throughout history such as smallpox, measles, and influenza.