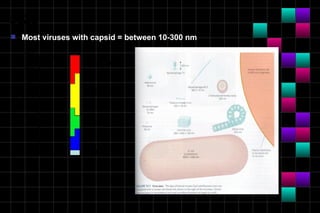
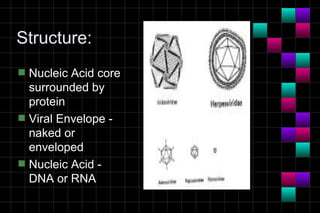
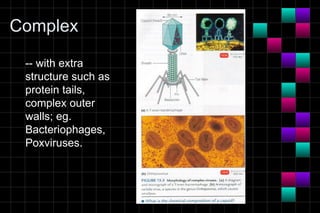
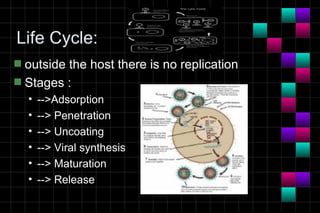
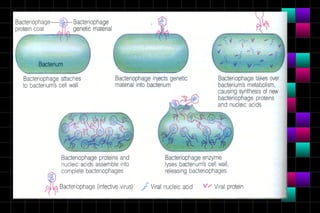
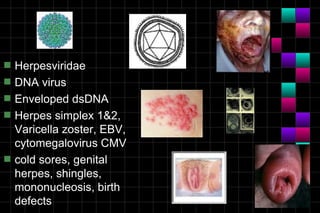
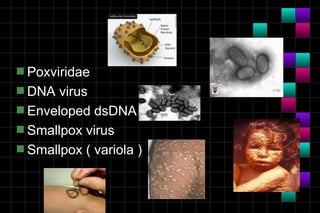
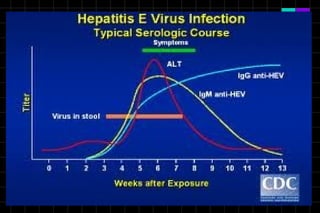
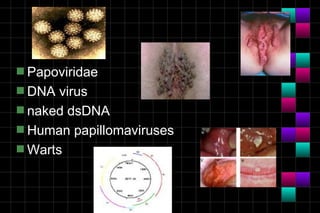
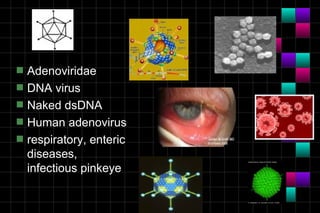
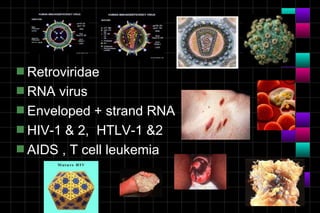
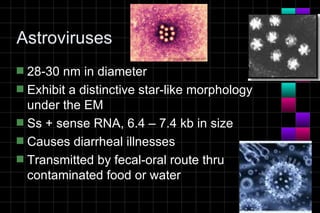
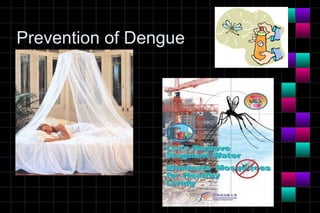
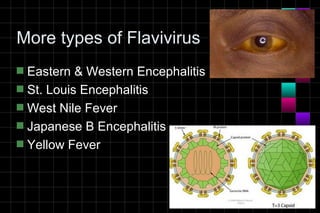
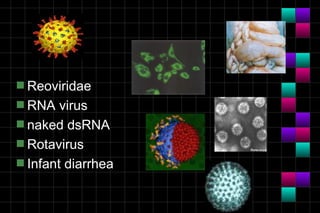
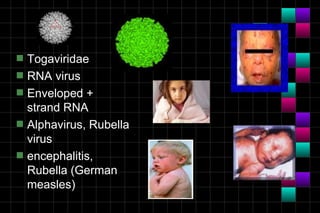
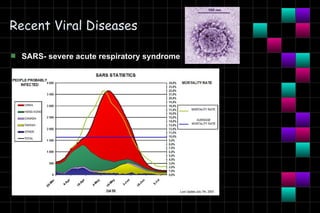
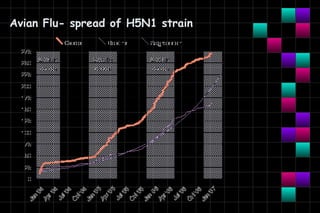
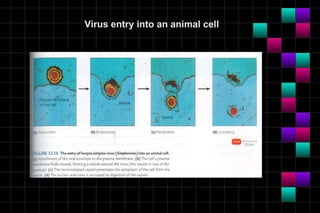
This document provides information on viruses including their structure, classification, life cycle, and diseases they cause. It defines key terms like capsids, genomes, and envelopes. It describes the four main types of viral structures and how viruses are classified based on attributes like morphology, genome, and host. Common animal viruses are outlined including families like Adenoviridae, Flaviviridae, and Picornaviridae. Public health issues like influenza, SARS, Ebola, and dengue are also summarized.