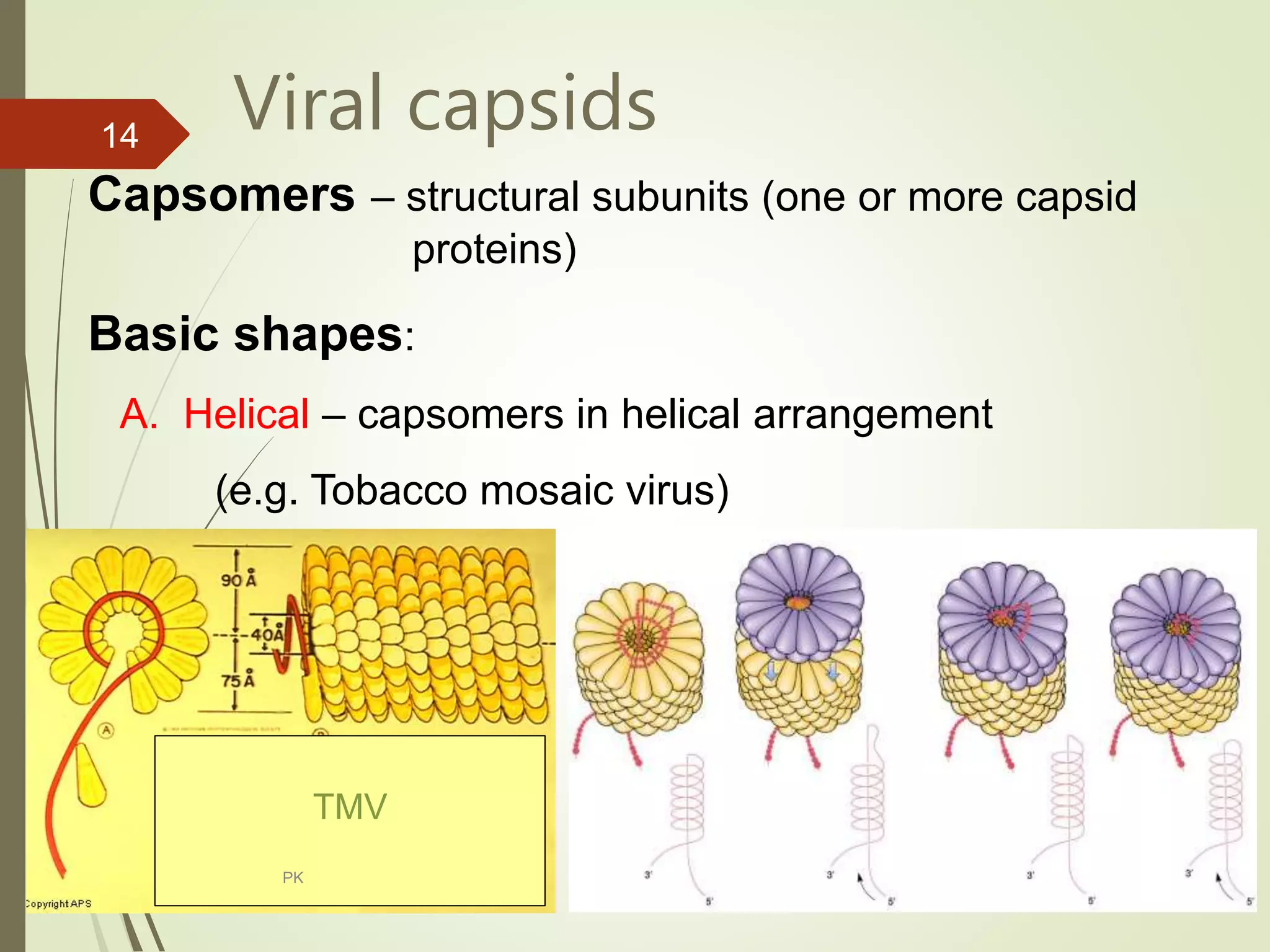
The document discusses plant viruses. It begins by outlining learning objectives about plant virus infections, life cycles, transmission, structures, classification, replication, symptoms, identification, and control. It then provides details on the characteristics of plant viruses, including their non-cellular nature and dependence on host cells. The document discusses plant virus transmission methods, proteins, capsids, classifications, replication cycles for different types of viruses, symptoms, and methods of detection, identification, and control.