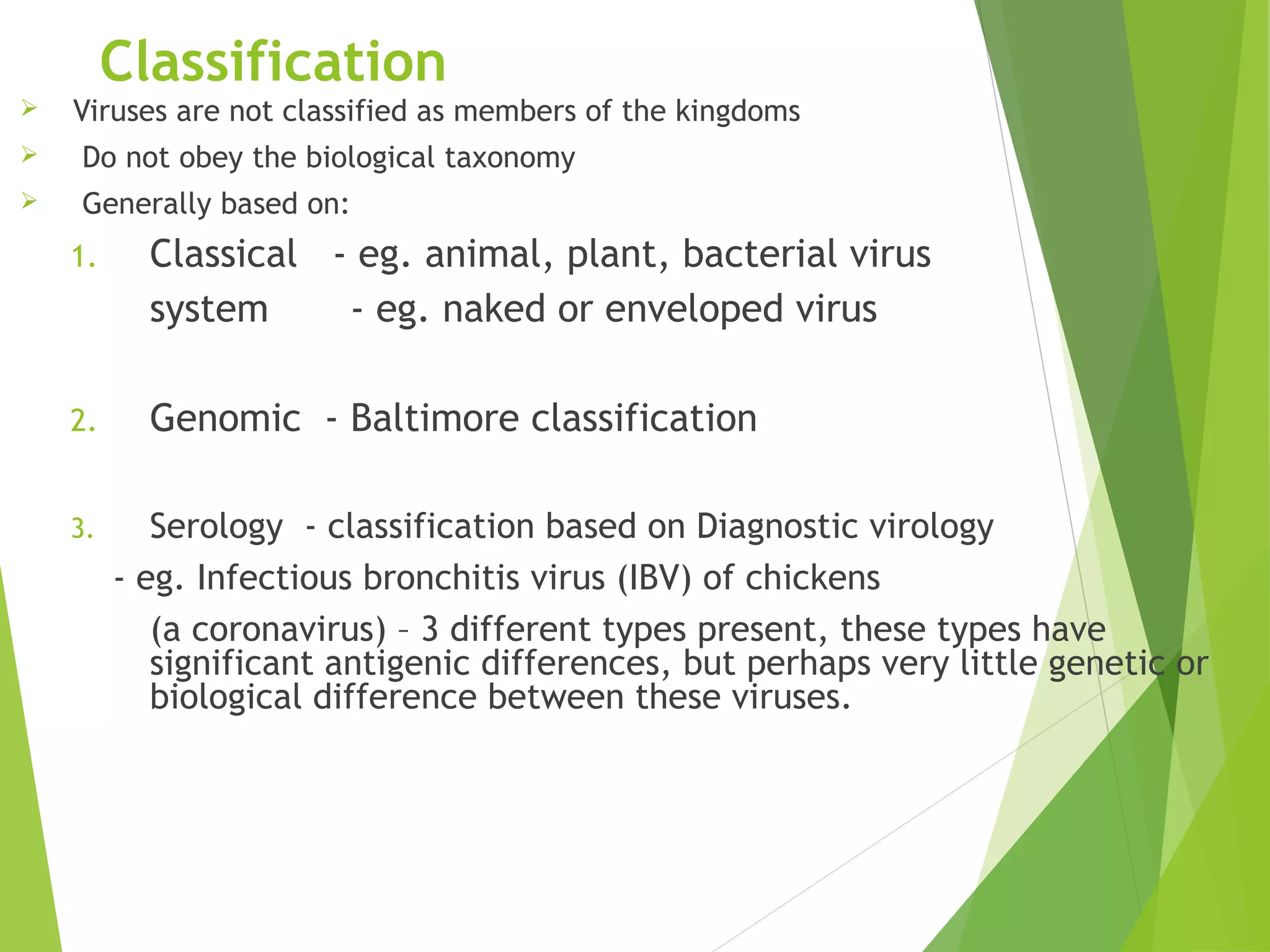
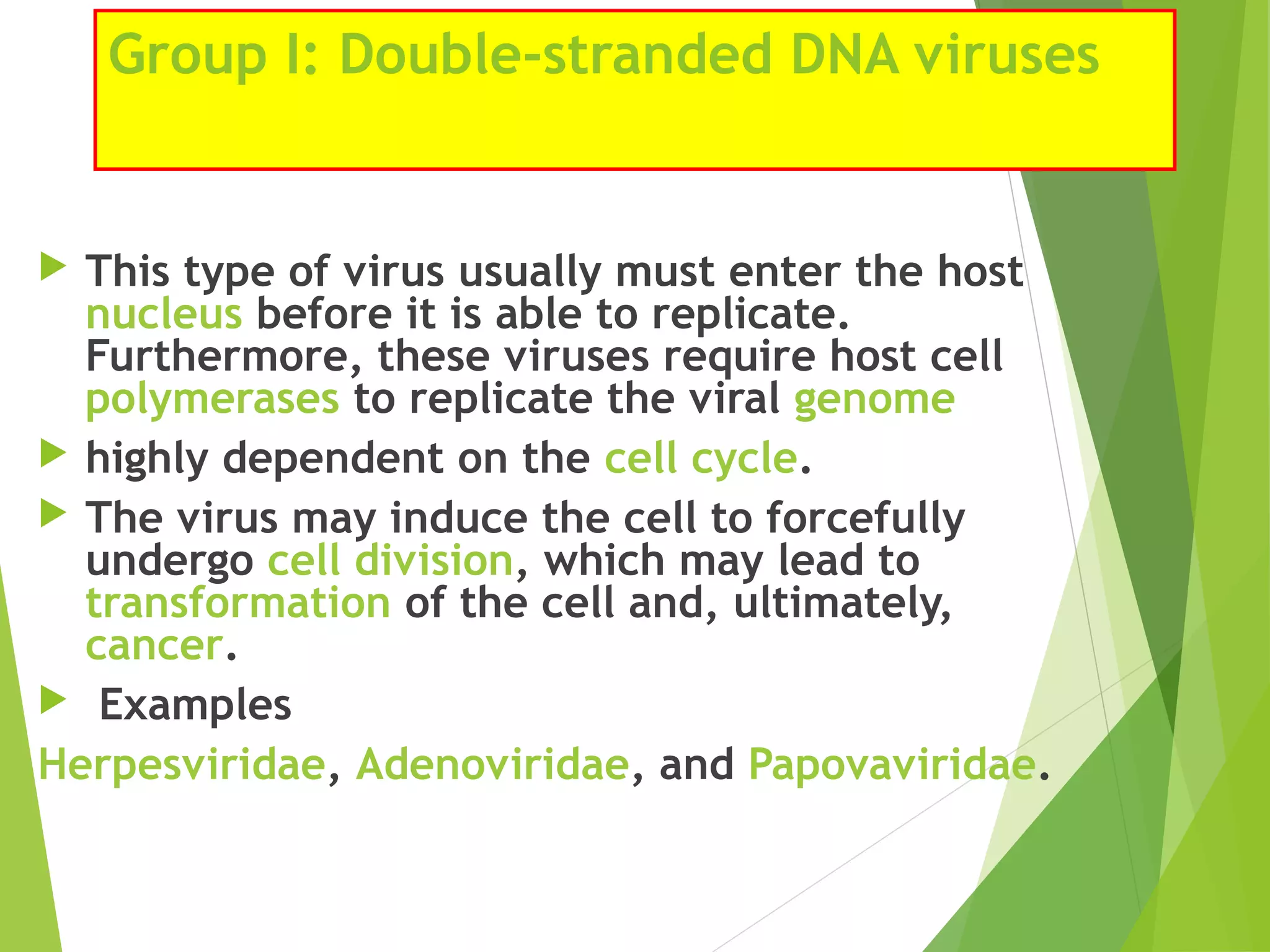
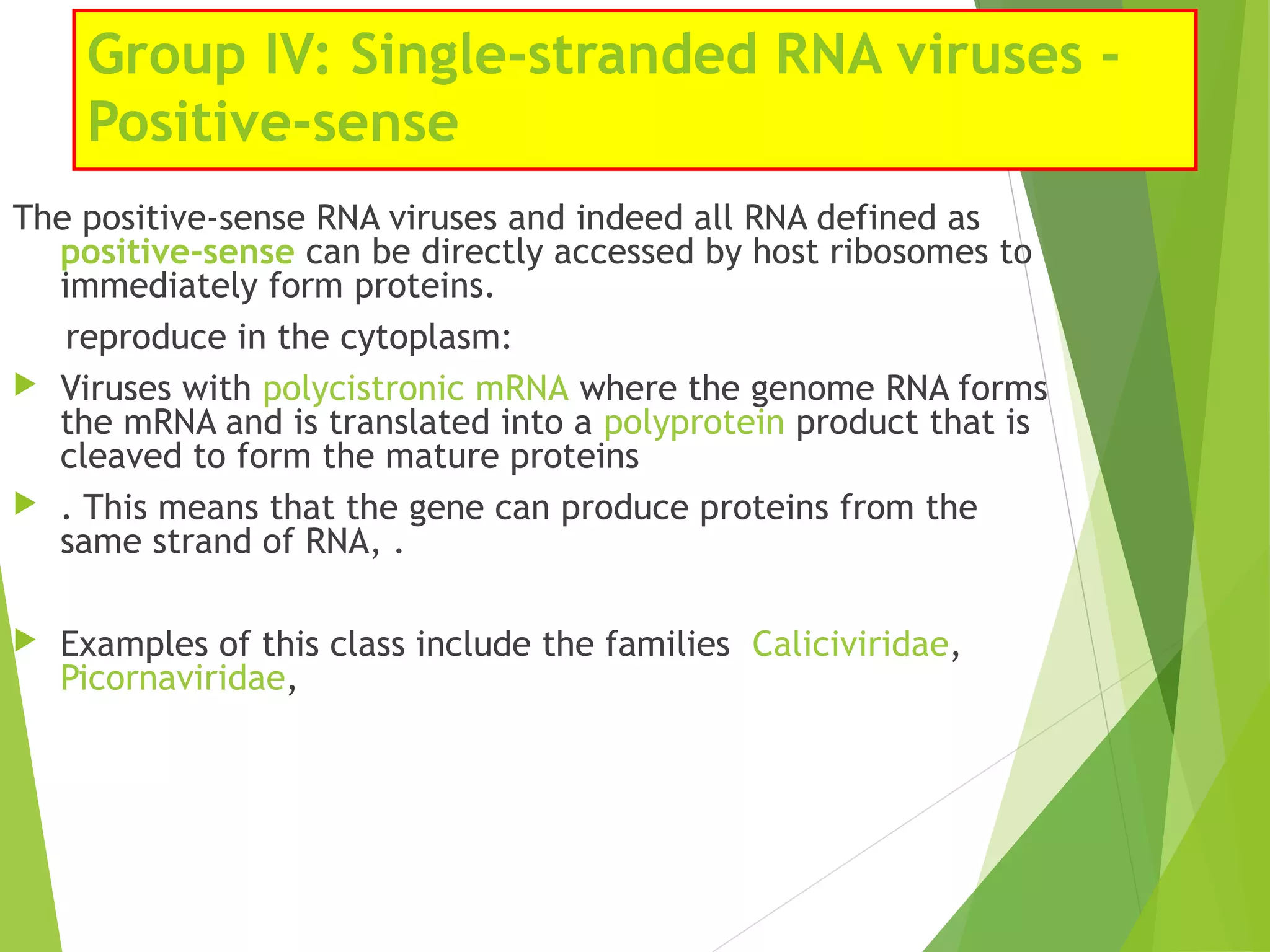
This document discusses the classification of viruses and viruses important to veterinary medicine. It begins by explaining different systems used to classify viruses, including the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses system and the Baltimore classification system, which categorizes viruses based on their genome and replication strategy. The document then discusses important viral families and genera that affect animals, such as rhabdoviruses, pestiviruses, arteriviruses, coronaviruses, influenza viruses, bluetongue virus, and circoviruses. It concludes by noting that viral diseases cannot be treated with antibiotics and vaccines are often the best prevention, though symptoms can be treated with over-the-counter medicines.