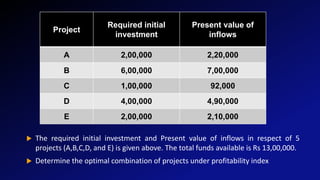
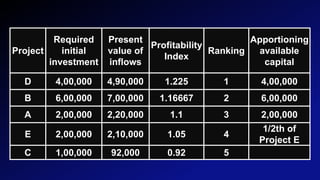
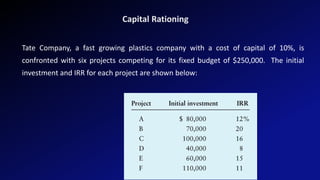
This document discusses capital rationing, which refers to choosing investment projects under financial constraints when there are more options available than funds. It outlines factors that can lead to capital rationing like management restrictions or imperfect capital markets. There are two types: soft rationing imposed by management, and hard rationing limited by external sources. Capital rationing involves ranking projects by profitability measures, selecting the highest ranked until funds are used up. The document provides an example of allocating $13 million between 5 projects ranked by profitability index.