This document discusses optimal capital structure and includes the following key points:
1. An optimal capital structure maximizes a company's market value while minimizing the cost of capital by striking a balance between risk and return. It occurs when the market price per share is at its maximum and cost of capital is at its minimum.
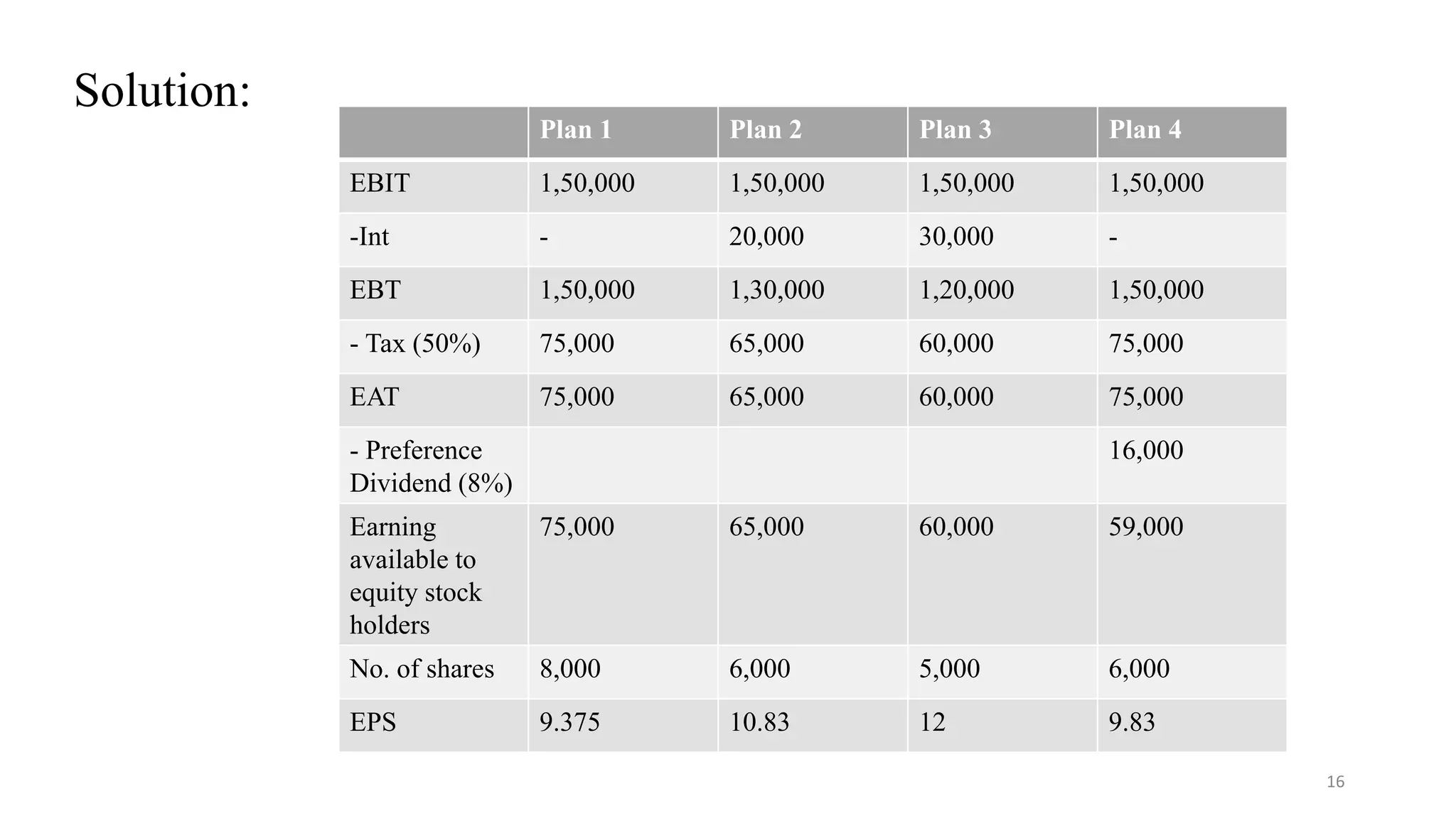
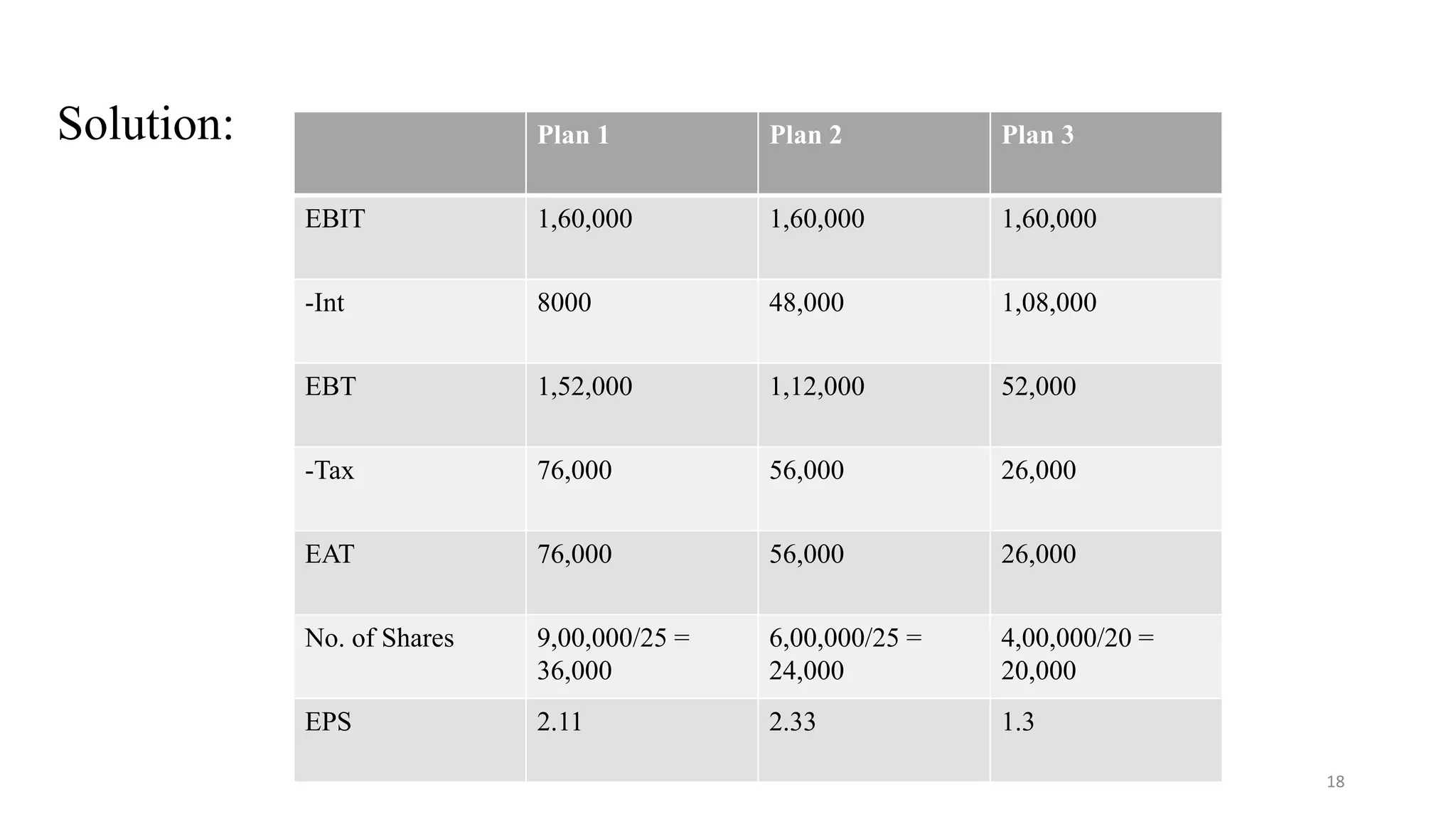
2. Several illustrations are provided to demonstrate how changes in the debt-equity mix impact total market value and overall cost of capital. Adding more debt initially increases value but can eventually increase costs if debt levels rise too high.
3. The document also defines capital structure, lists some features of an optimal structure, and outlines several theories of capital structure, including the Net Income Approach and Modigl





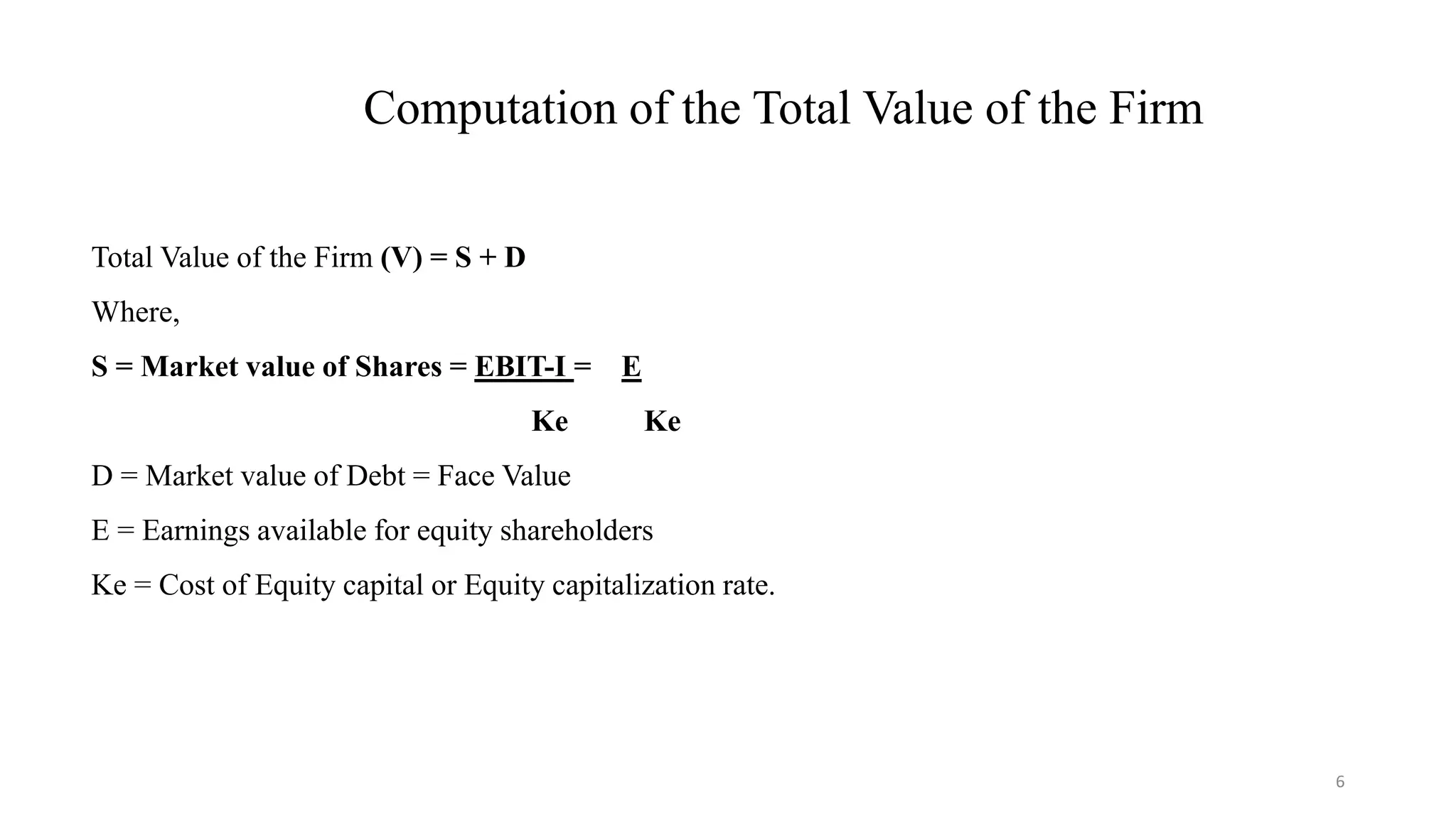


![A) Calculation of Existing total market value of the company
(EBIT) 400000
Interest — 100000
Equity Earnings (E) 300000
Cost of Equity (Ke) 15%
Cost of Debt (Kd) 10%
Market Value of Equity(S)=E/Ke 20,00,000
Market Value of Debt(D)=I/Kd 10,00,000
Total Value of the Firm (V)=[S+D] 30,00,000
Overall cost of capital (K0)=EBIT *100
V
13.33%
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmppt1-191011034752/75/optimal-capital-structure-10-2048.jpg)
![B) Increase in Debentures in Total Capitalization
(EBIT) 400000
Interest — 160000
Equity Earnings (E) 240000
Cost of Equity (Ke) 15%
Cost of Debt (Kd) 10%
Market Value of Equity(S)=E/Ke 16,00,000
Market Value of Debt(D)=I/Kd 16,00,000
Total Value of the Firm (V)=[S+D] 32,00,000
Overall cost of capital (K0)=EBIT *100
V
12.50%
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmppt1-191011034752/75/optimal-capital-structure-11-2048.jpg)
![C) Decrease in Debentures in Total Capitalization
(EBIT) 400000
Interest — 40000
Equity Earnings (E) 360000
Cost of Equity (Ke) 15%
Cost of Debt (Kd) 10%
Market Value of Equity(S)=E/Ke 24,00,000
Market Value of Debt(D)=I/Kd 4,00,000
Total Value of the Firm (V)=[S+D] 28,00,000
Overall cost of capital (K0)=EBIT *100
V
14.29%
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmppt1-191011034752/75/optimal-capital-structure-12-2048.jpg)