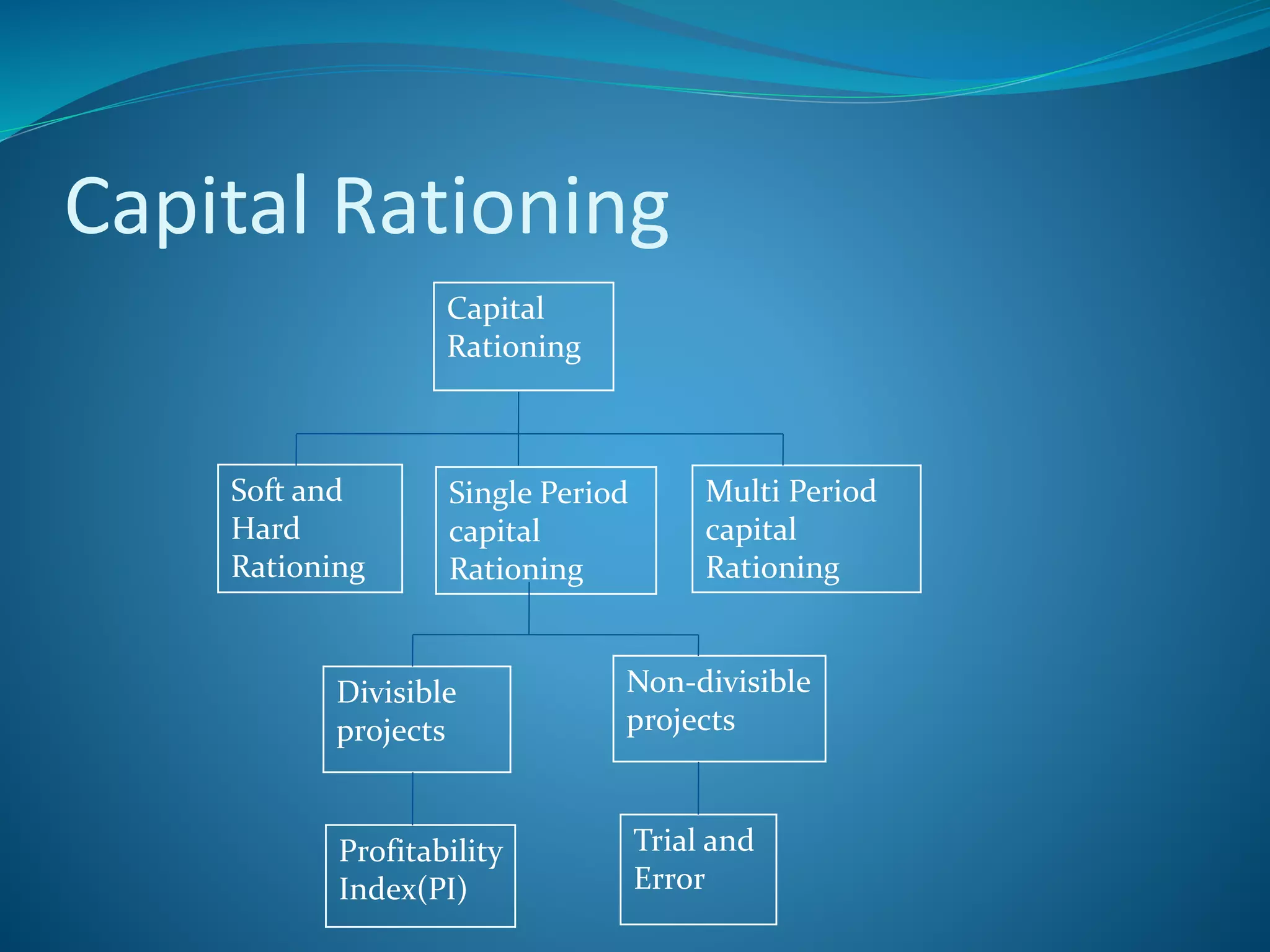
Capital rationing occurs when a company has a limited budget to allocate towards new investment projects, forcing it to reject some profitable projects. There are two types: hard rationing imposed by external restrictions on raising funds, and soft rationing when management imposes internal limits. When selecting projects under capital rationing, management must determine the optimal combination of projects that yields the highest net present value within budget constraints. This involves ranking projects by their profitability index and either choosing divisible portions of each or determining the highest net present value combination of indivisible whole projects.