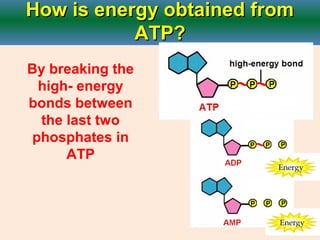
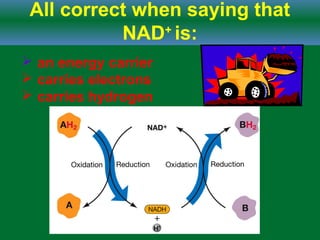
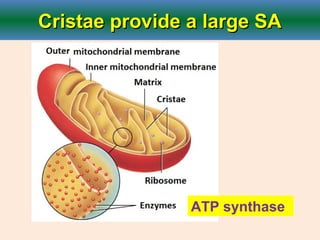
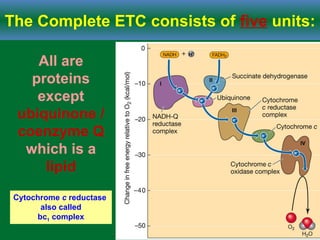
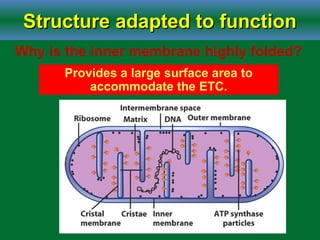
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to obtain energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down to form pyruvate in the cytoplasm. In the citric acid cycle, pyruvate enters the mitochondria and is further oxidized, producing NADH, FADH2, and ATP. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through an electron transport chain in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Their energy is used to pump protons out of the matrix, establishing a proton gradient. ATP synthase uses this gradient to























































































![The Chemiosmotic TheoryThe Chemiosmotic Theory
Peter Mitchell (1961)
proposed the Chemiosmotic
Theory: the ETC energy is
used to move H+
(protons)
across the cristae
membrane, and
that ATP is generated as the
H+
diffuse back into the matrix
through [proton motive force]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicaloxidation-150226065613-conversion-gate02/85/Biological-oxidation-93-320.jpg)

