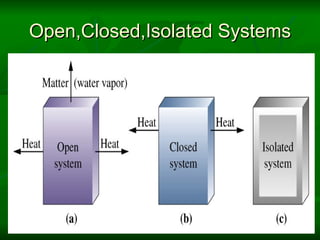
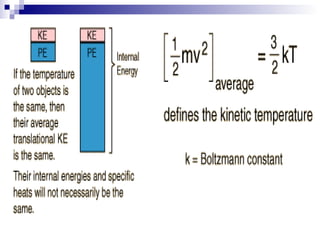
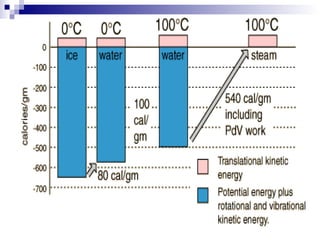
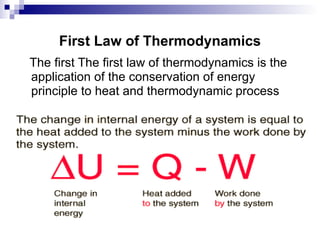
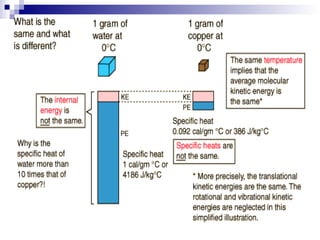
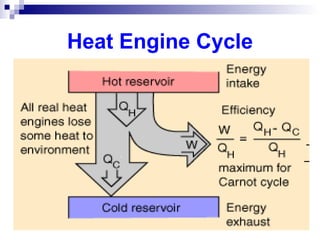
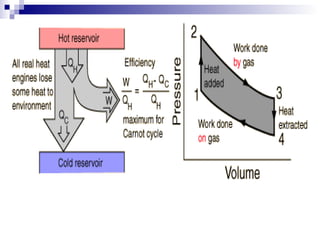
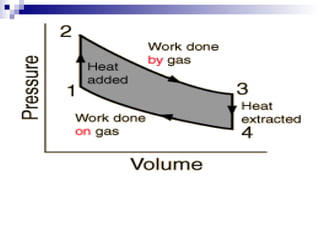
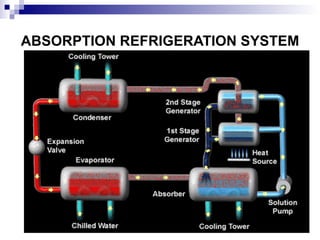
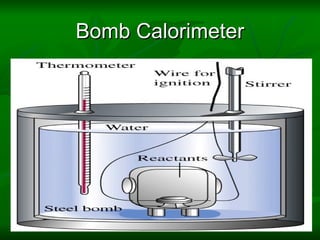
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to thermodynamics, defining key concepts such as thermodynamic systems, system boundaries, and classifications like open, closed, and isolated systems. It discusses properties of substances, equilibrium states, and the laws of thermodynamics, including the zeroth and first laws. Additionally, it touches on specific applications like heat engines and absorption refrigeration systems.