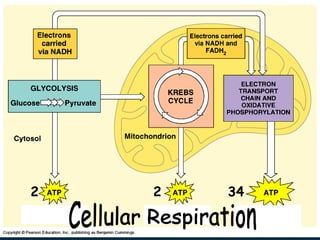
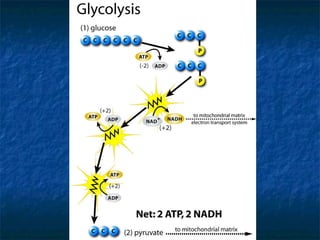
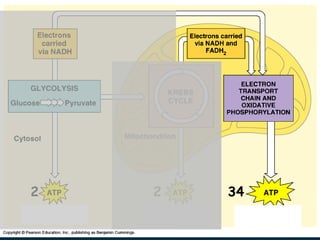
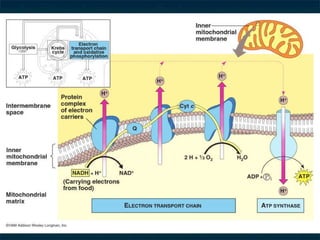
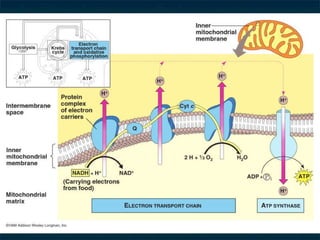
The document discusses cellular respiration, which is the process by which cells break down food molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP. It describes the three main stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and occurs in the cytoplasm, producing a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down molecules in the mitochondria, producing more ATP and electrons. The electron transport chain uses these electrons and oxygen to produce the most ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen through fermentation.