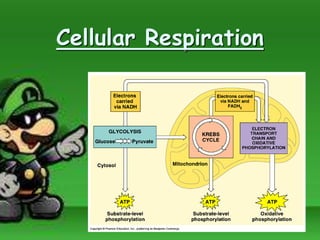
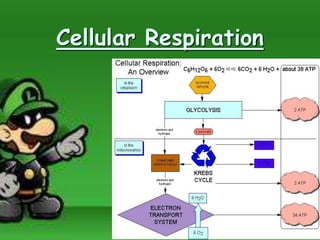
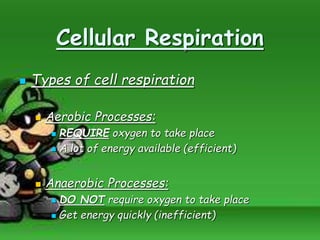
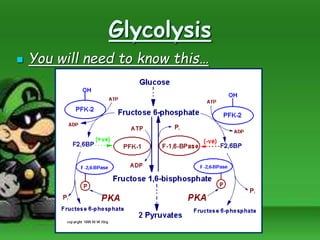
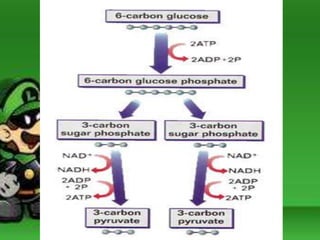
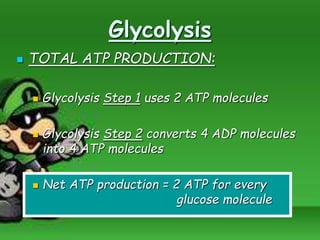
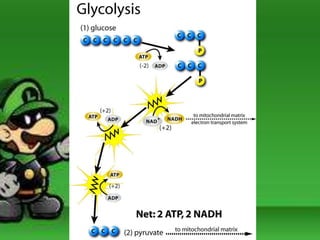
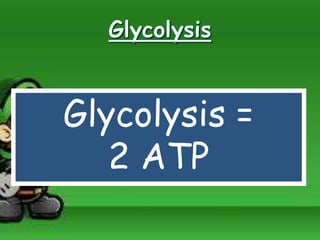
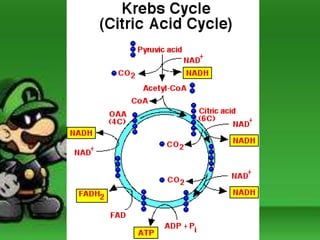
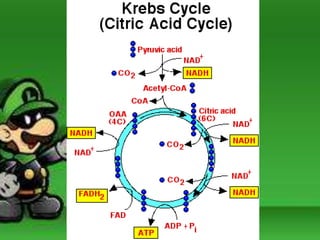
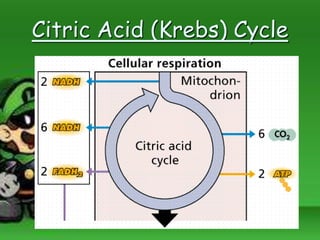
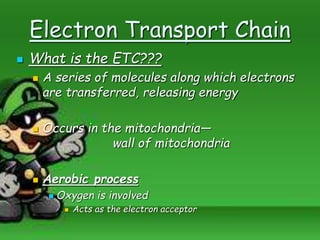
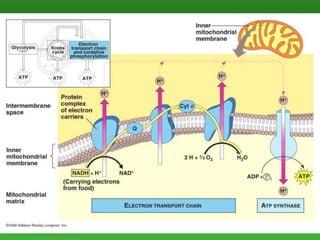
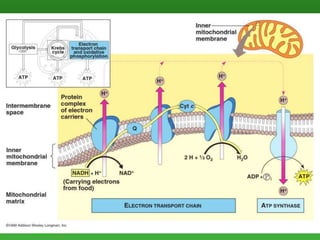
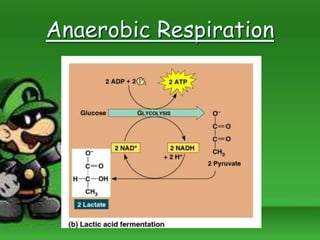
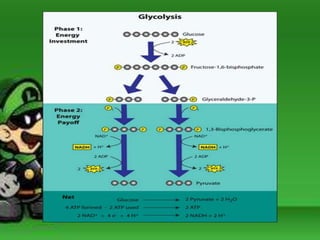
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down food molecules in the presence of oxygen to extract energy. It involves glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down pyruvate and produces more ATP and electron carriers. In the electron transport chain, electrons are passed through protein complexes, pumping protons across a membrane and producing most of the ATP through chemiosmosis. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen as the final electron acceptor to produce the most energy. Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen through fermentation.