Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,930 times











Carbohydrates are sugars that provide the body with energy. There are two types - simple carbohydrates like refined sugars and fruits, and complex carbohydrates like grains. Carbohydrates are digested and absorbed for energy, and the best choices are whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. Disorders can result from too few or too many carbohydrates, such as diabetes, hypoglycemia, and lactose intolerance. Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar is too low and symptoms include shakiness, dizziness, and mood changes.
Presentation on carbohydrates by Christina Cheshire, covering their role, types, and importance.
Carbohydrates defined simply as sugars, the primary energy source for the body.
Carbohydrates provide energy for daily activities and essential organ functions.
Two main types: Simple (monosaccharides) and Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides, starches).
Simple carbohydrates include refined sugars, fruits, and milk; complex carbs include grain products.
Carbohydrates are a major energy source, providing varying lengths of energy for activities.
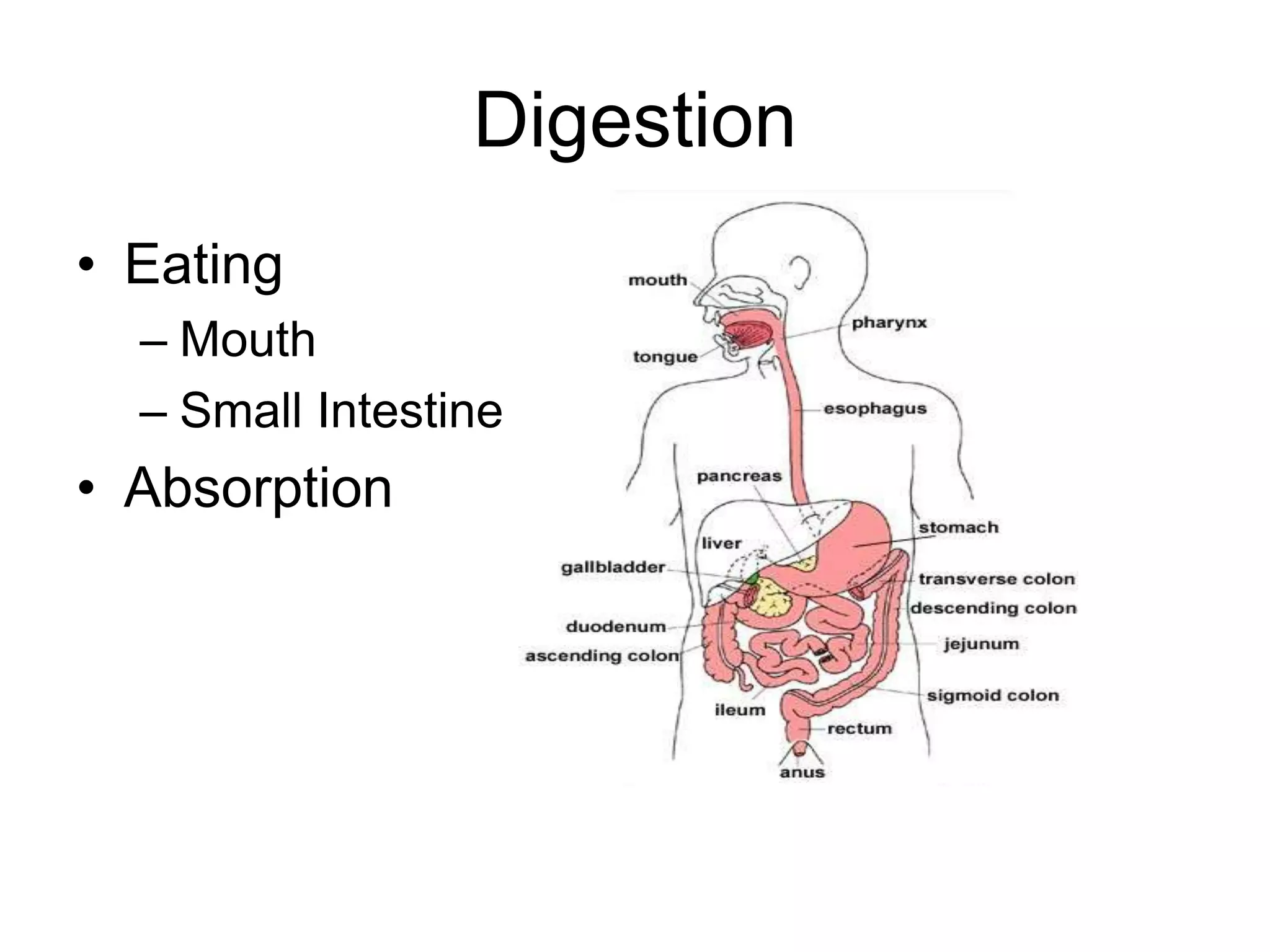
The digestion of carbohydrates occurs in the mouth and small intestine, leading to absorption.
Highlighting the energy benefits of carbohydrates essential for bodily functions.
Best carbohydrate choices include whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and beans to promote health.
Disorders caused by imbalances in carbohydrate intake, including lactose intolerance and diabetes.
Details on hypoglycemia, symptoms, and the necessity for treatment when experiencing symptoms.
Citing resources and references used throughout the presentation on carbohydrates and health.











