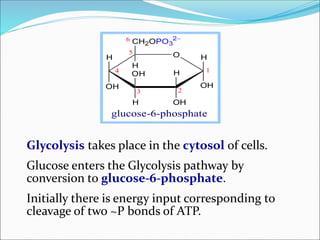
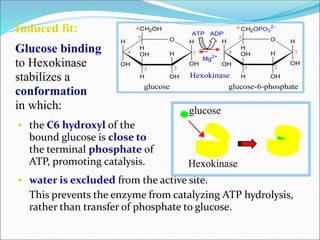
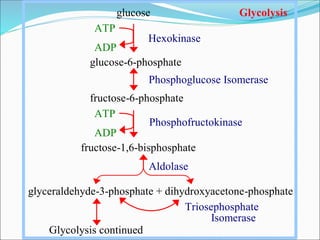
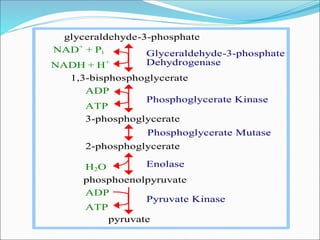
1. Glycolysis is the pathway where glucose is broken down to pyruvate with production of ATP. It takes place in the cytosol of cells.
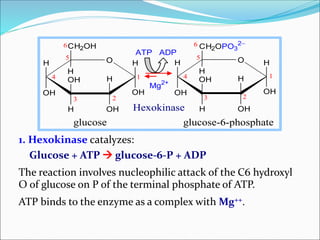
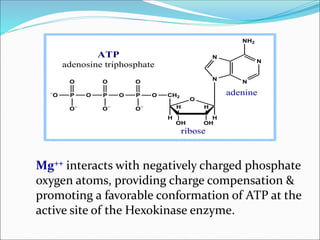
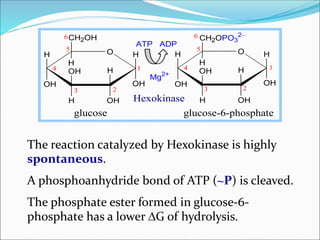
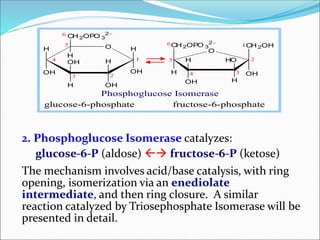
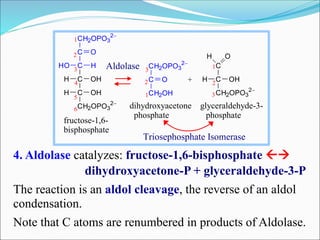
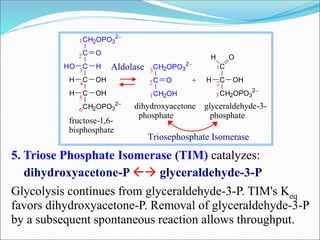
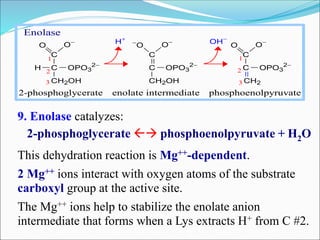
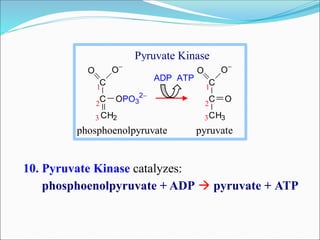
2. Key steps include phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate by hexokinase, isomerization to fructose-6-phosphate, phosphorylation of fructose to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, cleavage to two 3-carbon molecules, conversion of one to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and isomerization, oxidation and phosphorylation to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, substrate-level phosphorylation to form ATP, and generation of pyruvate from phosphoenolpyruvate.


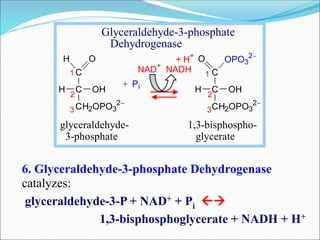
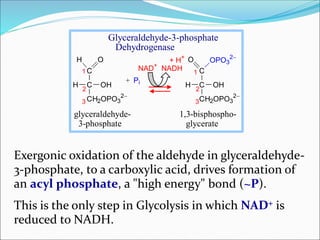
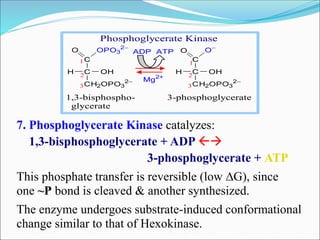
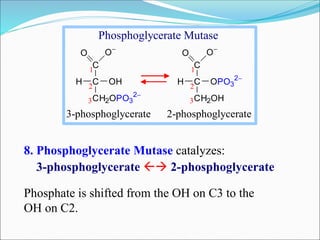
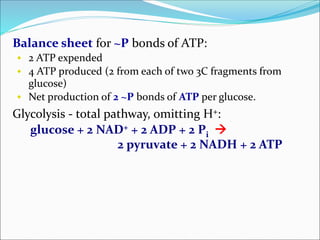
![Inhibition of the Glycolysis enzyme
Phosphofructokinase when [ATP] is high prevents
breakdown of glucose in a pathway whose main role is
to make ATP.
It is more useful to the cell to store glucose as glycogen
when ATP is plentiful.
Glycogen Glucose
Hexokinase or Glucokinase
Glucose-6-Pase
Glucose-1-P Glucose-6-P Glucose + Pi
Glycolysis
Pathway
Pyruvate
Glucose metabolism in liver.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glycolysis-150311120159-conversion-gate01/85/Glycolysis-20-320.jpg)