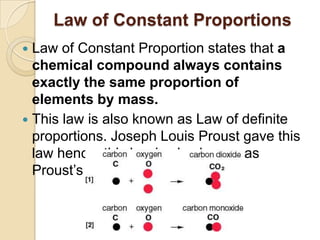
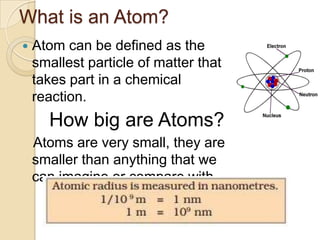
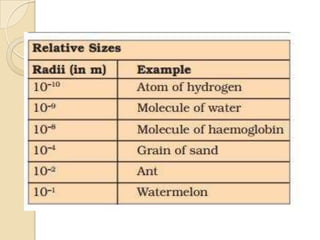
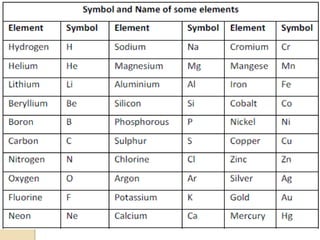
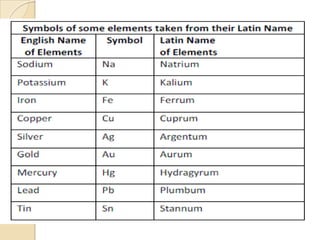
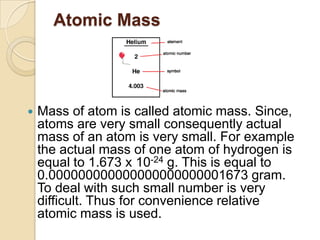
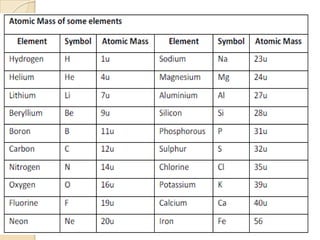
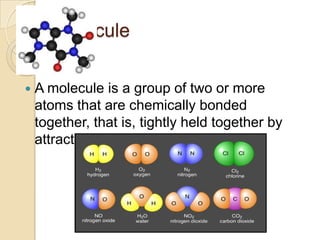
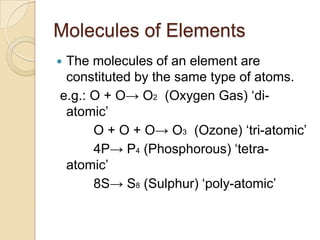
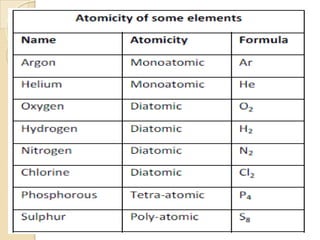
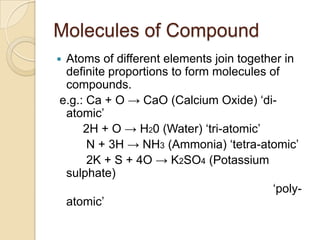
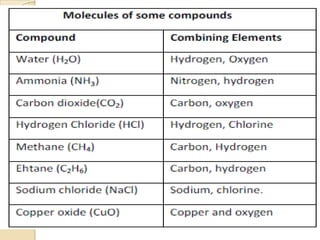
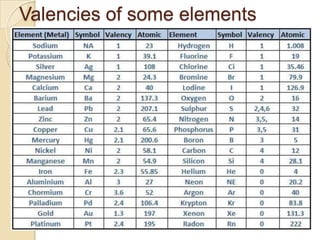
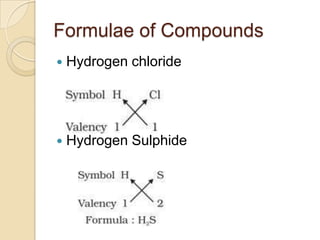
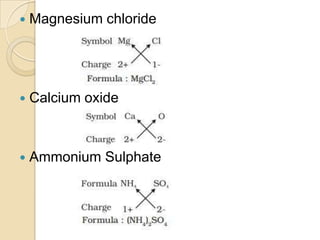
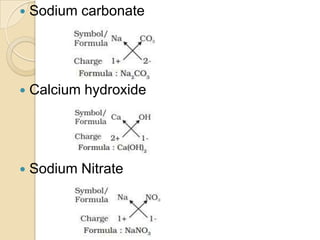
This document discusses the history and development of atomic theory. It describes how ancient Indian and Greek philosophers first proposed that matter is divisible into smaller particles. Democritus named these indivisible particles "atoms." Later, scientists like John Dalton and Antoine Lavoisier established laws of chemistry, including the law of conservation of mass and the law of constant proportions, which supported the atomic theory. Dalton further proposed that elements are made of atoms that combine in whole number ratios. The document defines key concepts like molecules, ions, chemical formulas, and moles. It provides examples of atomic structure and molecular formulas of common compounds.