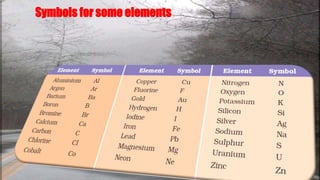
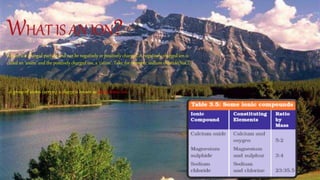
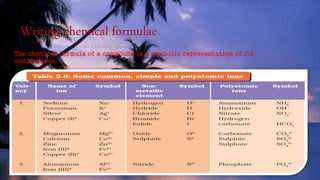
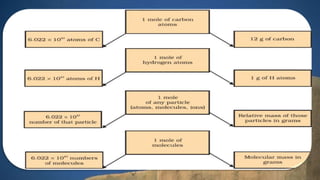
This document discusses the history of atomic theory from ancient Indian and Greek philosophers hypothesizing about the divisibility of matter, to Democritus coining the term "atom" to refer to indivisible particles of matter. It then discusses Antoine Lavoisier establishing the laws of chemical combination including the law of conservation of mass and the law of constant proportions. John Dalton later provided his atomic theory, hypothesizing that all matter is made of atoms which are indivisible, identical for a given element, and combine in simple whole number ratios. The document then discusses concepts like atomic mass, molecules, ions, writing chemical formulas, and introduces the mole concept.