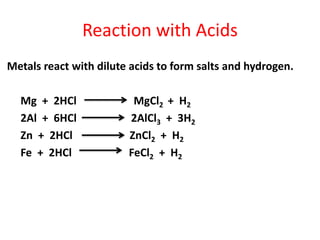
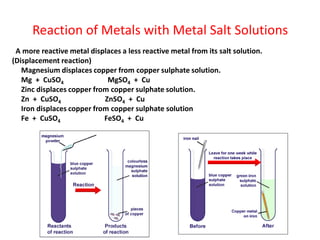
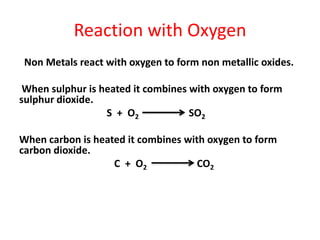
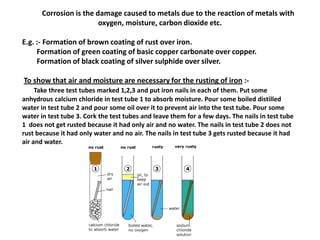
Metals react with oxygen, water, and acids to form metal oxides, hydroxides, or salts. They lose electrons and become positively charged ions. Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metal oxides, gaining electrons and becoming negatively charged ions. Corrosion occurs as metals react with substances like oxygen and water in the air, forming coatings or rust. Corrosion can be prevented by applying protective coatings like oil, paint, zinc plating, or by alloying metals.