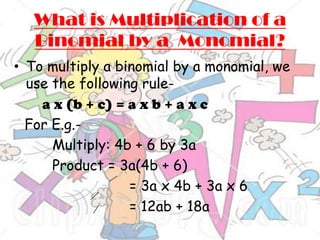
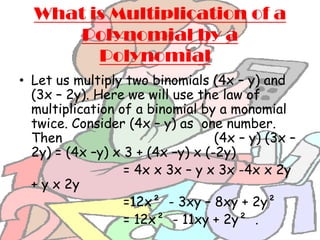
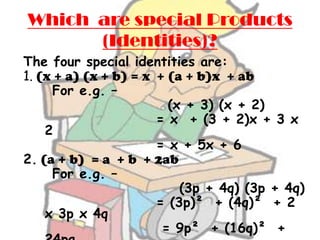
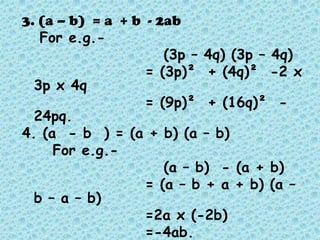The document provides an introduction to algebraic expressions, explaining fundamental concepts such as variables, terms, and the classification of expressions such as monomials, binomials, and trinomials. It details operations involving algebraic expressions, including multiplication and factorization, as well as rules for signs in division. Additionally, it offers historical context about the development of algebra and notable mathematicians who contributed to its evolution.