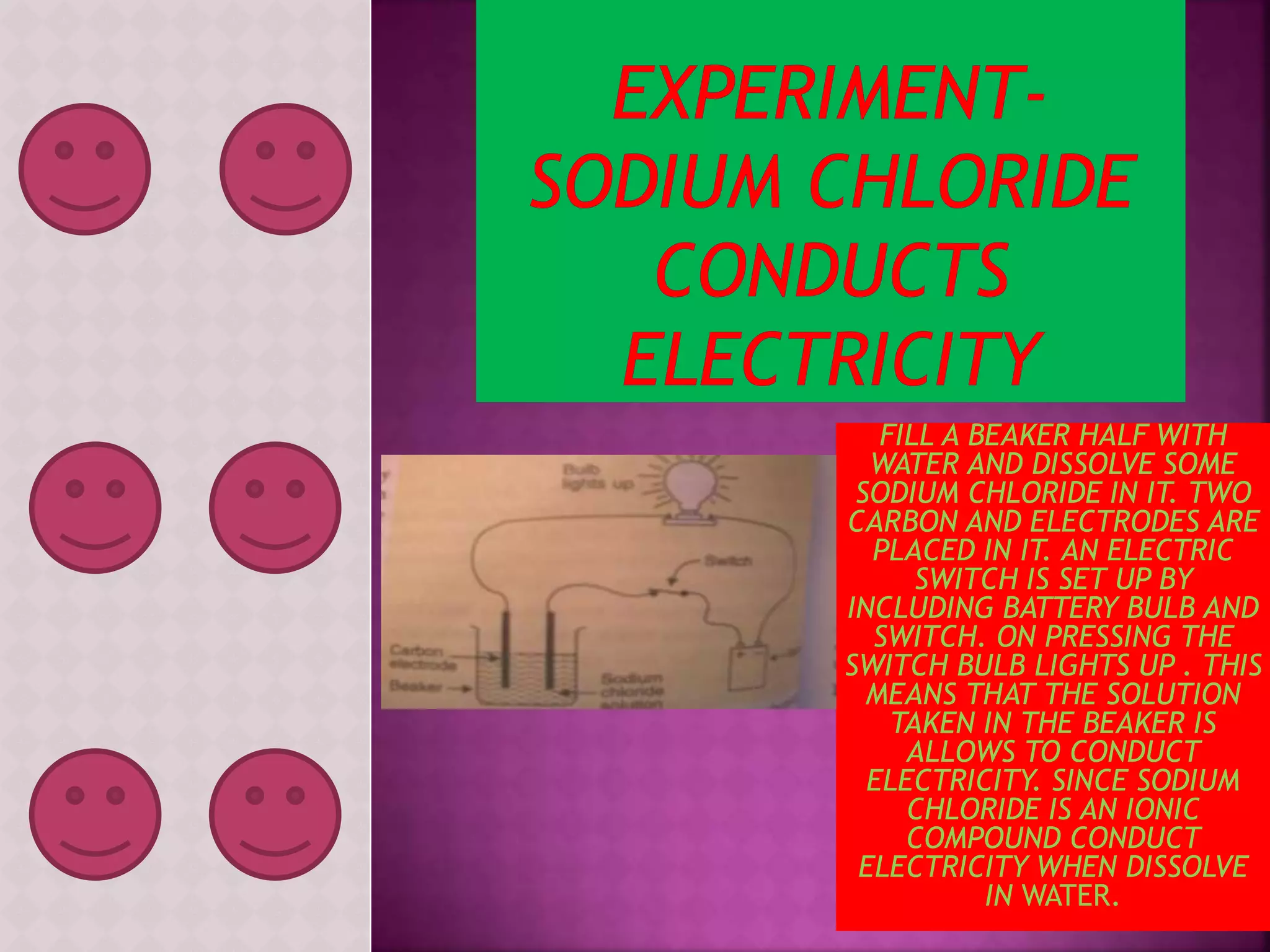
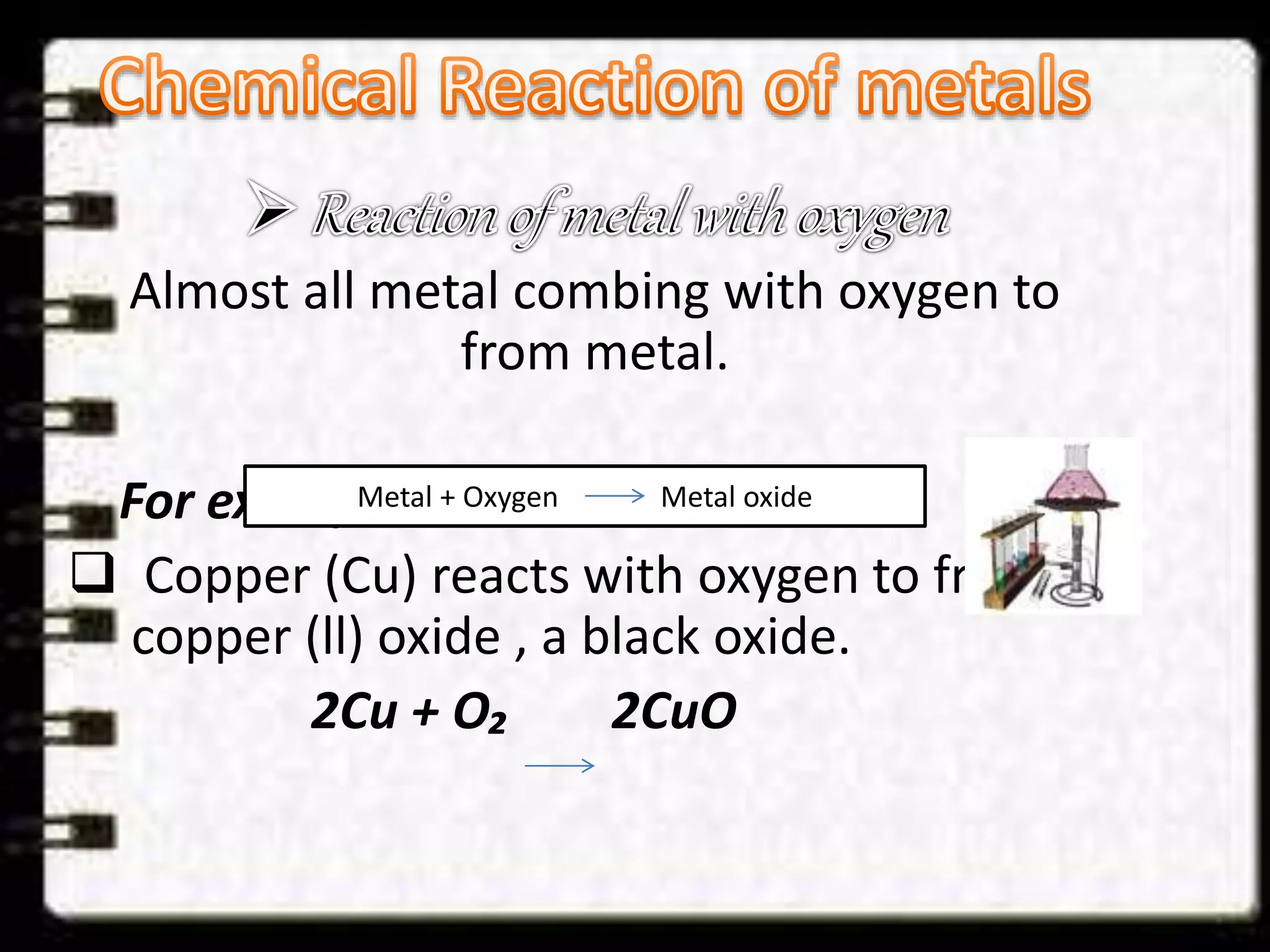
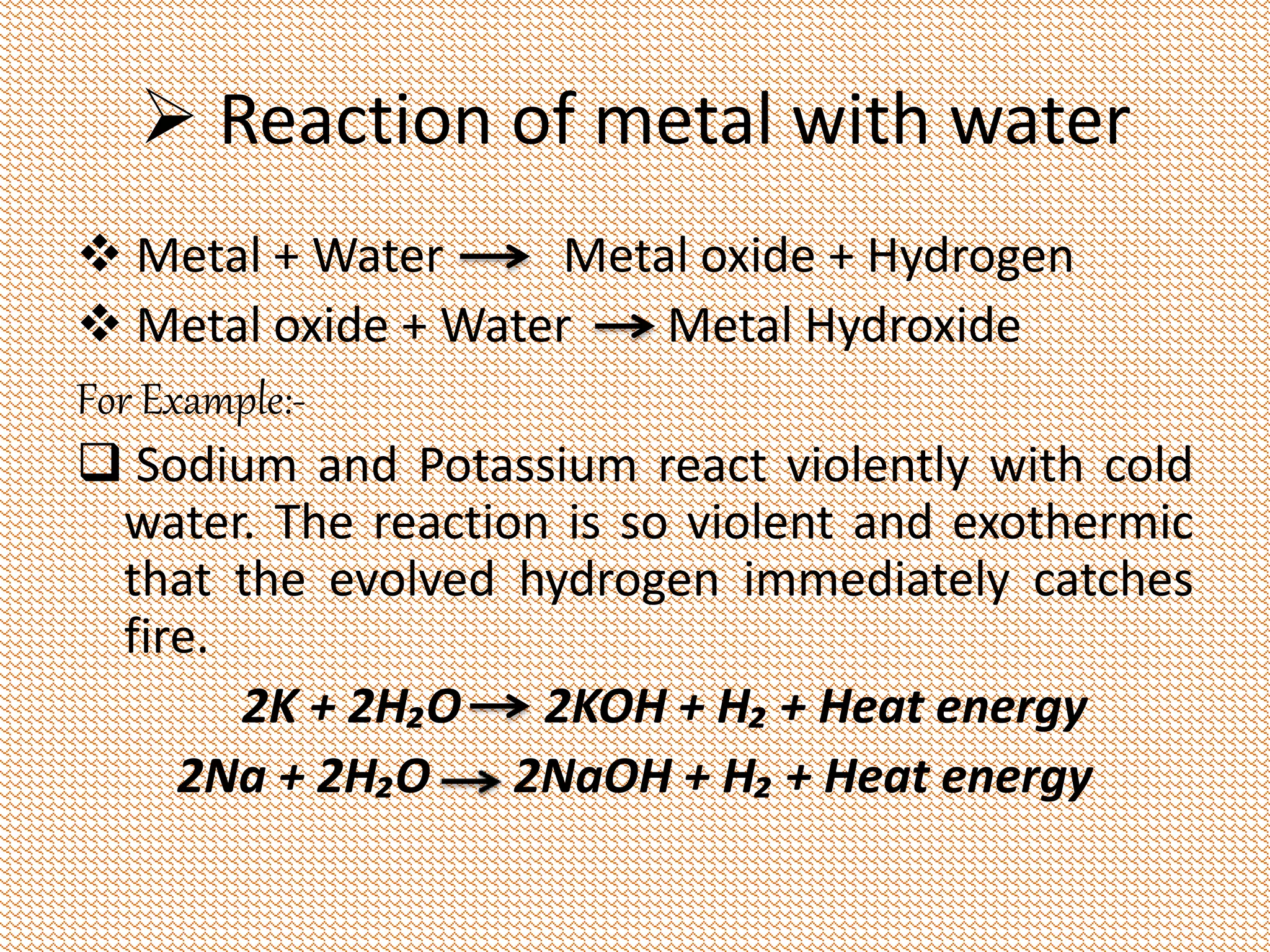
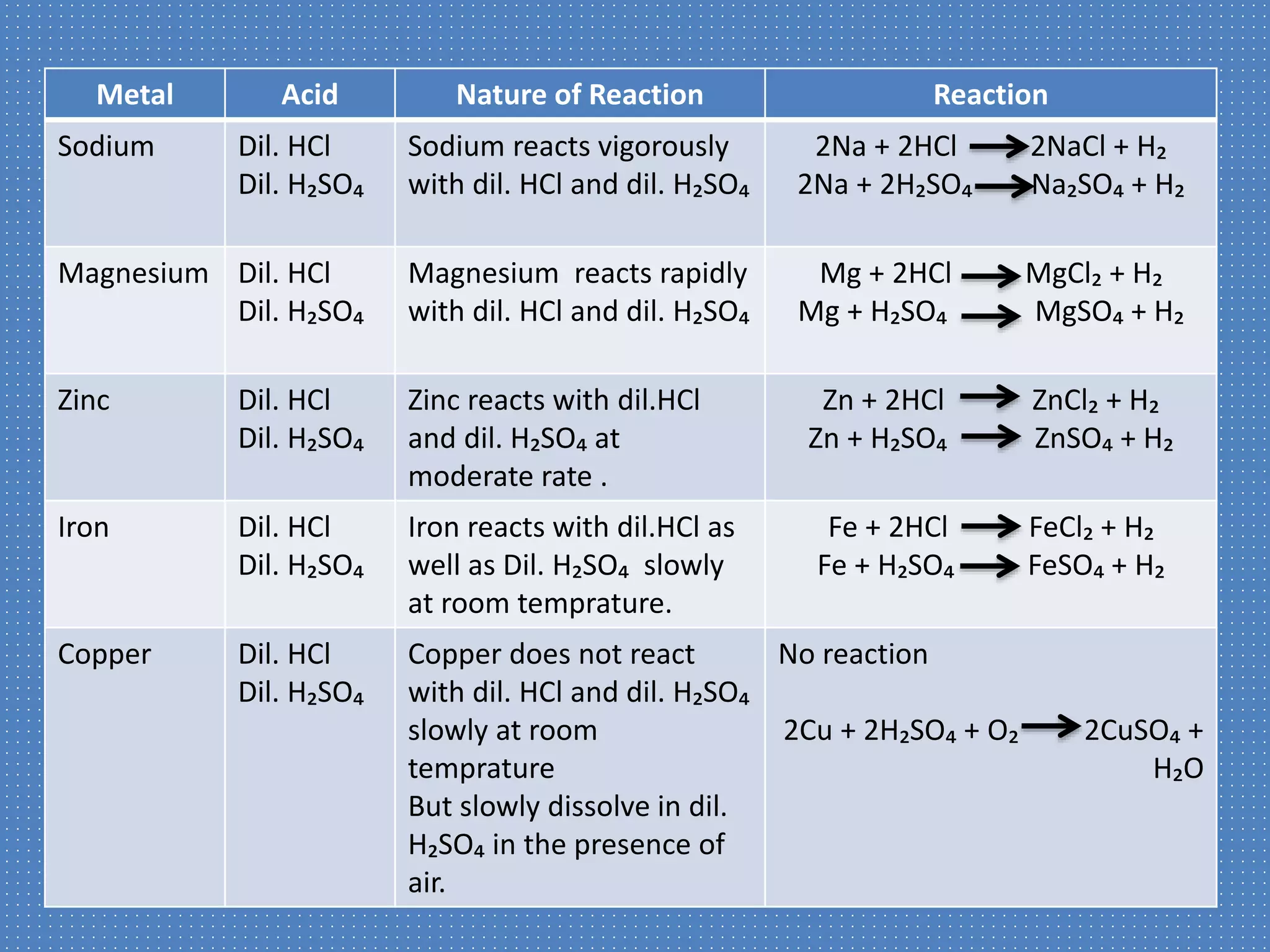
This document discusses a science presentation about the properties and reactions of metals and non-metals. It lists the group members giving the presentation and describes several properties of metals like malleability and conductivity. It then discusses how metals react with oxygen, water, acids, salt solutions, chlorine, hydrogen and how alloys are formed and used. For non-metals, it summarizes their reactions with oxygen, water, acids, salt solutions, chlorine, hydrogen and describes ionic compounds.
















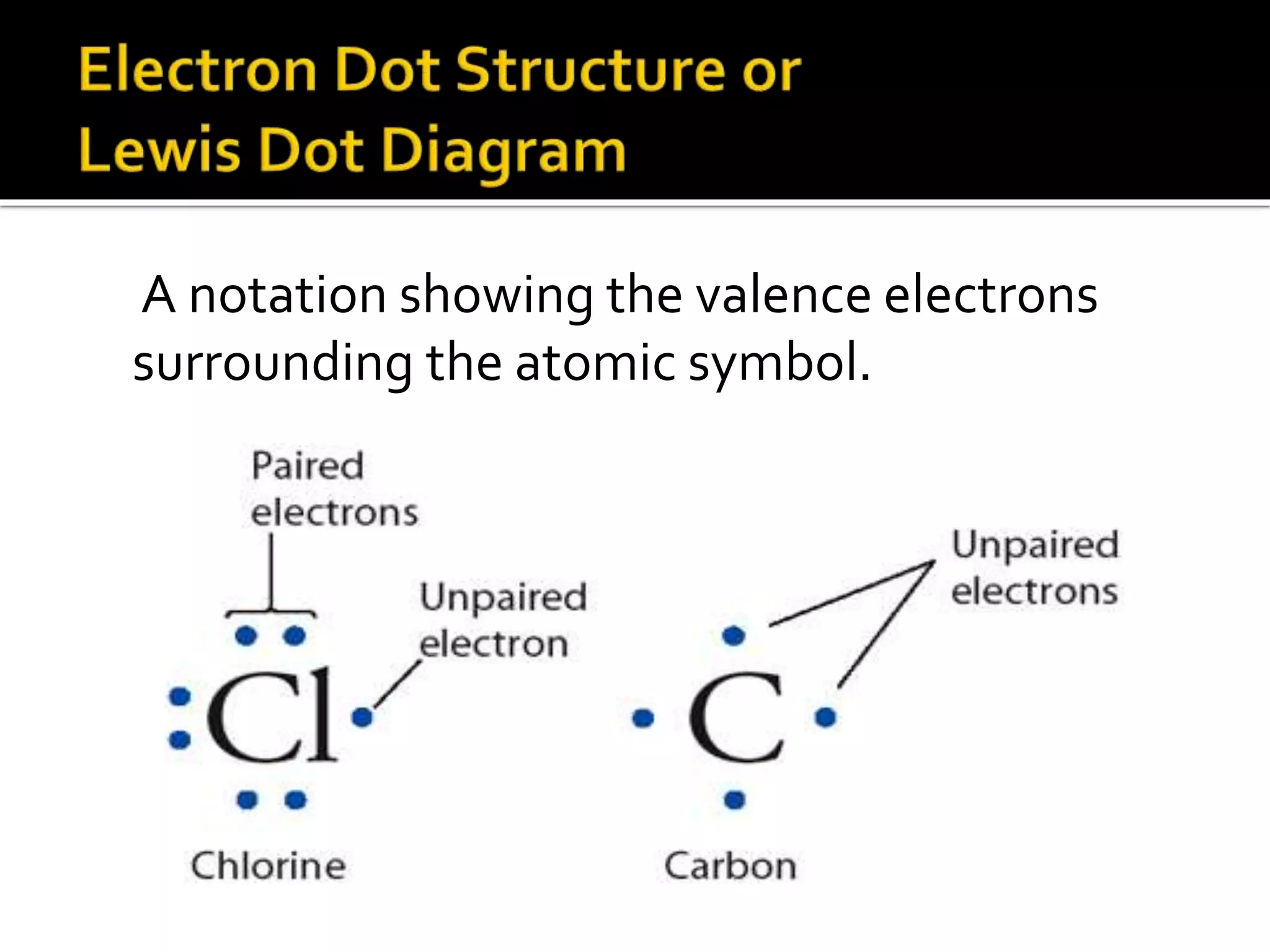
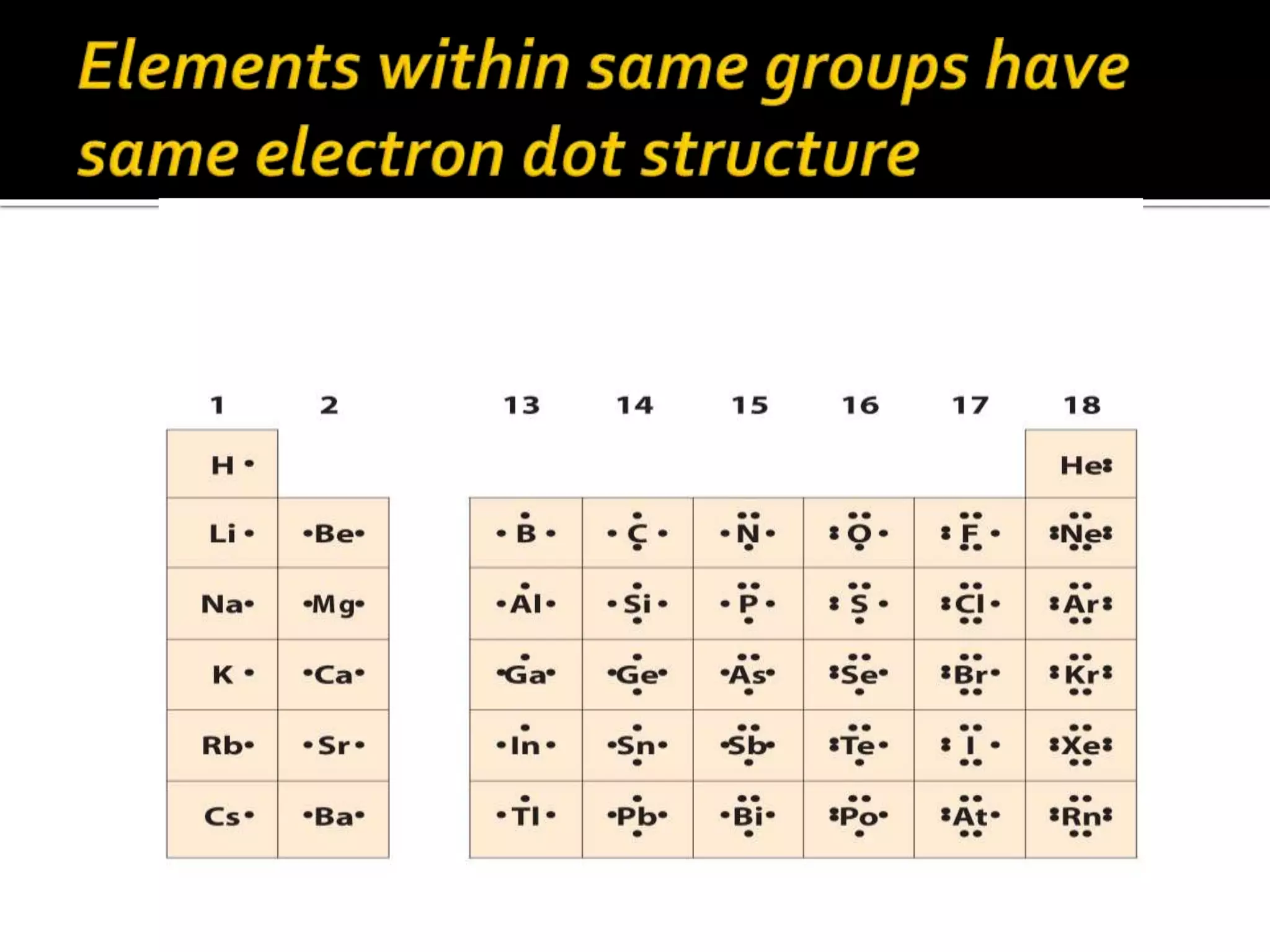
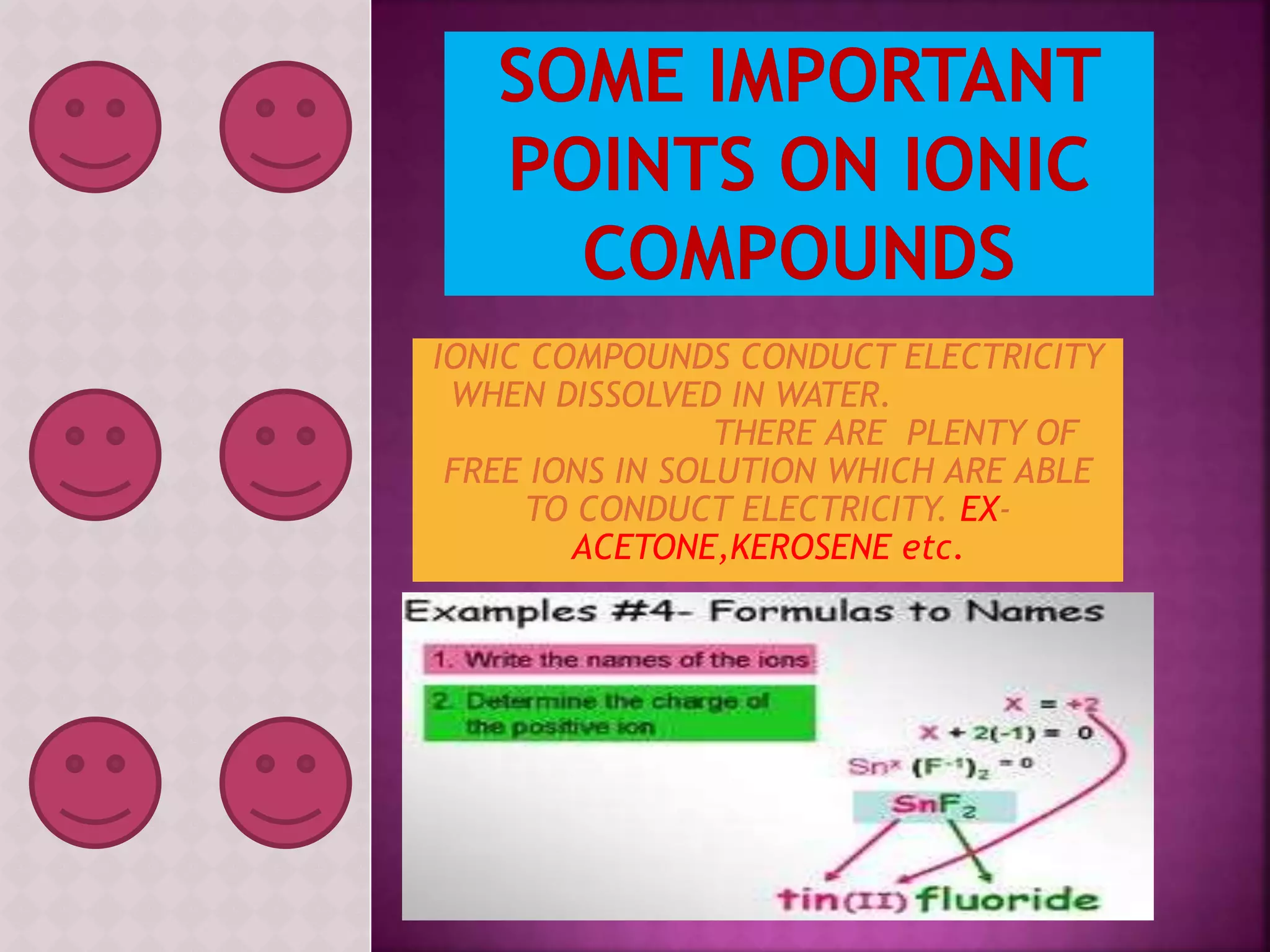
![Ionic compounds
The compounds containing ionic bonds
are called ionic compounds.Theyare
formed by transfer of electrons from one
atom to another . Ionic compounds are
made up of positively charged
ions[cataions]+ and negatively charged
ions [anions].Ionic compounds are
also known as Electrovalent
compounds.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactionofmetalwithoxygen-141008012927-conversion-gate02/75/Reaction-of-metal-with-oxygen-20-2048.jpg)