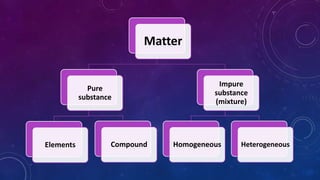
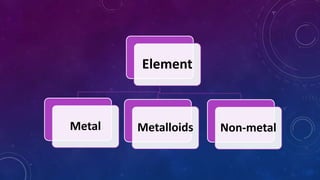
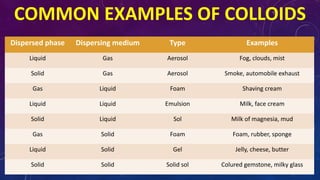
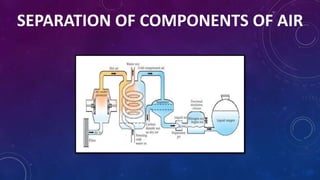
The document discusses the classification of matter, explaining the differences between pure substances, mixtures, and their respective types such as elements, compounds, homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. It details various methods for separating mixtures, like filtration, distillation, and chromatography, along with examples of each method. Additionally, it outlines physical and chemical changes in matter, emphasizing their characteristics and differences.