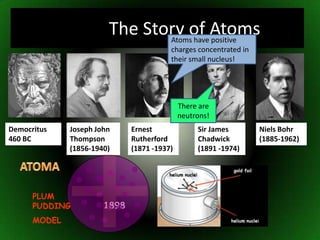
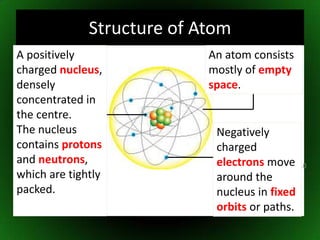
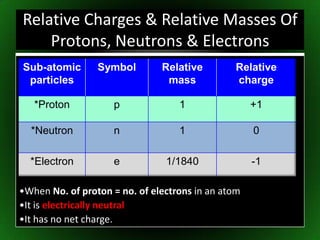
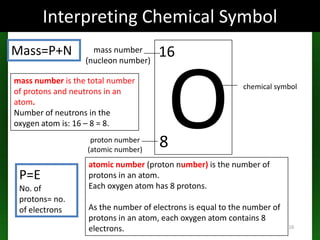
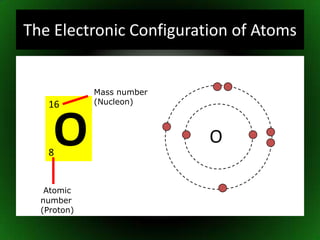
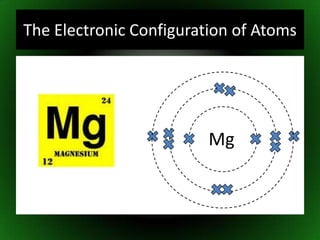
The document discusses atomic structure and isotopes. It recaps atomic structure, including the structure of the atom, relative masses and charges of protons, neutrons and electrons, chemical symbols, and electronic configuration. It then defines isotopes as atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Examples of isotopes of oxygen are provided. Finally, some uses of radioactive isotopes are mentioned, such as in food irradiation, archaeological dating, smoke detectors, and as radioactive tracers.