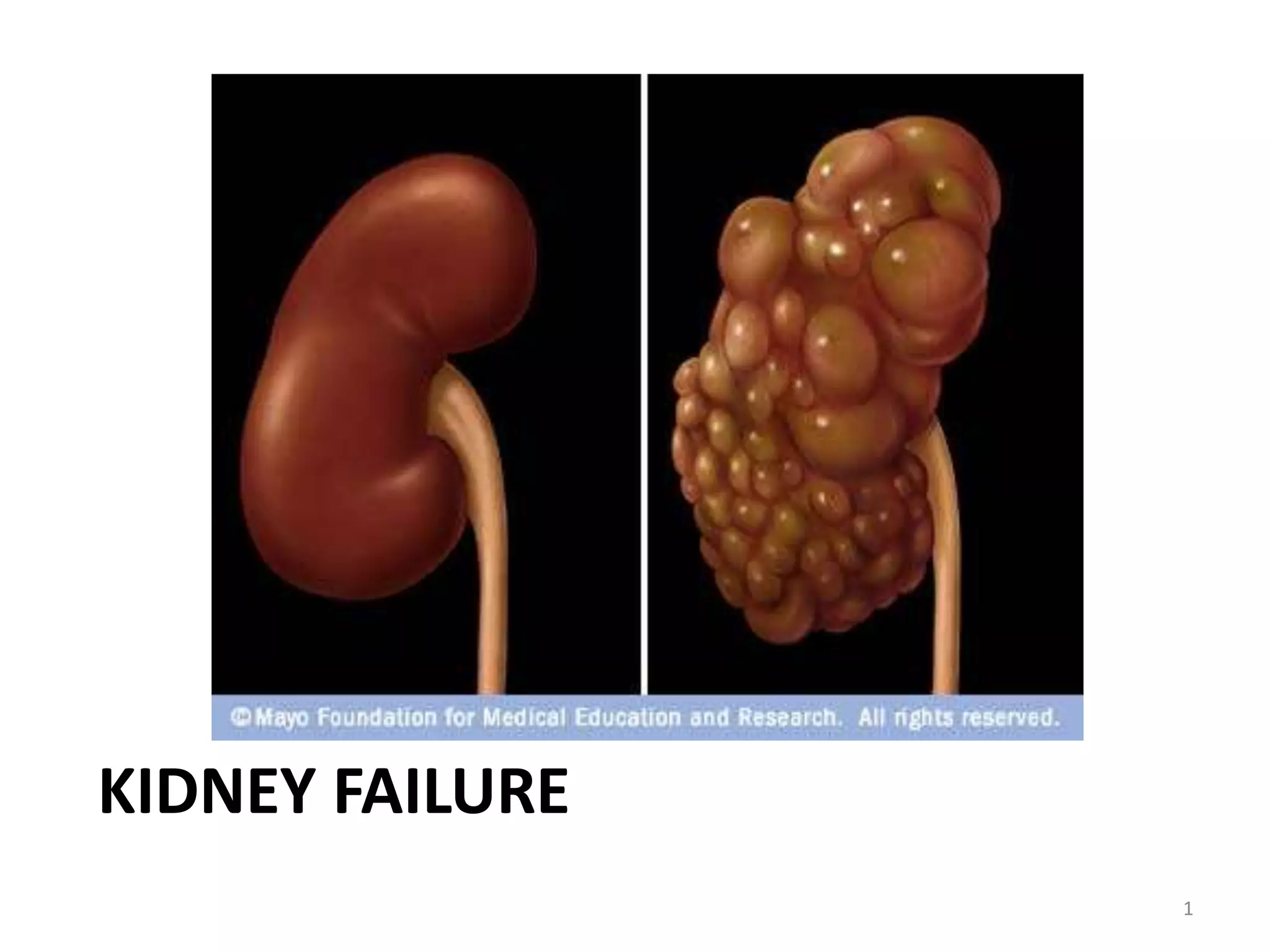
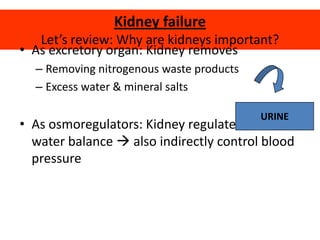
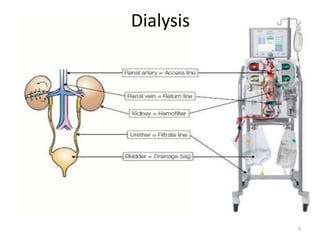
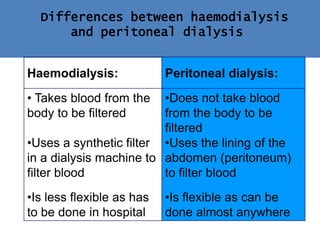
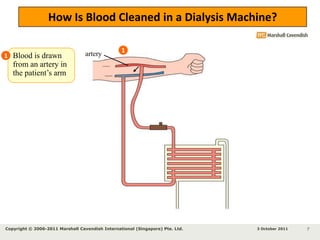
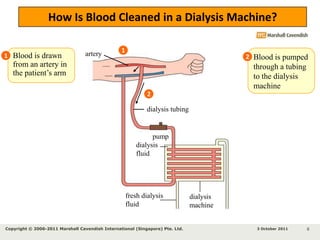
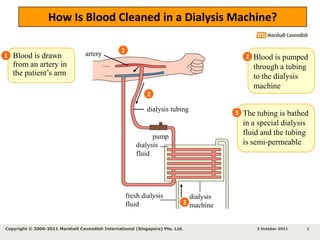
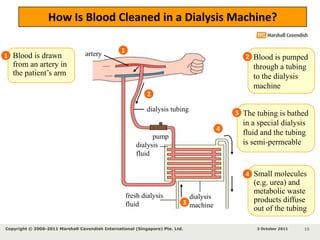
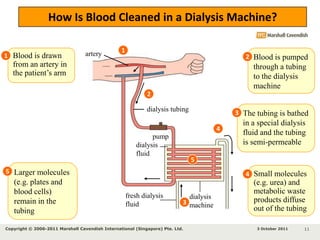
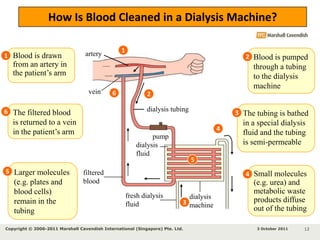
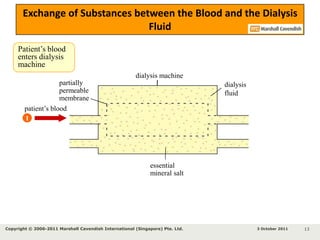
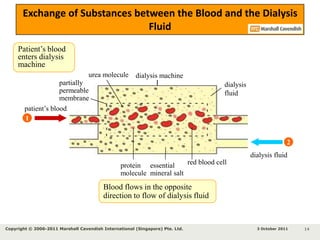
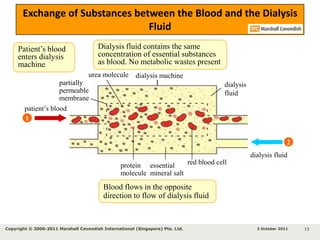
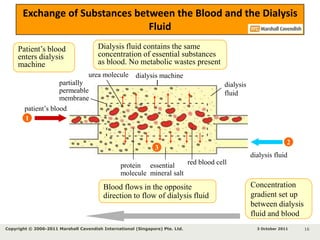
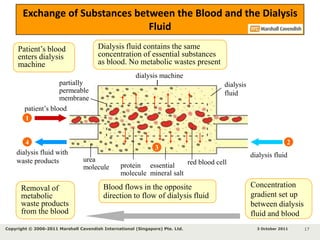
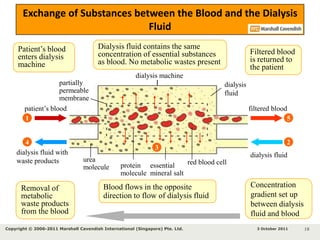
Kidneys are important for removing waste from the blood and regulating fluid and mineral balance. Kidney failure can result from high blood pressure, diabetes, alcohol use, or injuries. Treatment options for kidney failure include kidney transplant, hemodialysis using a dialysis machine, or peritoneal dialysis using a bag and membranes. Hemodialysis involves pumping blood out of the body into a dialysis machine where waste diffuses out of the blood and it is returned cleaned to the body.