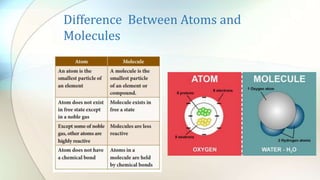
- Elements are pure substances made of one type of atom, while compounds are pure substances made of two or more elements chemically bonded together.
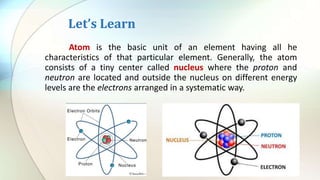
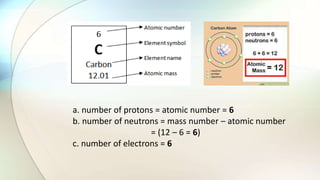
- Atoms are the basic unit of elements and consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons in shells of different energy levels.
- Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge.
- Molecules are the smallest particle of a substance that contains one or more bonded atoms and has the chemical and physical properties of that substance.
- Dalton's atomic theory proposed that matter is made of atoms that cannot be created, destroyed, or converted between elements, and that compounds form from atoms combining in