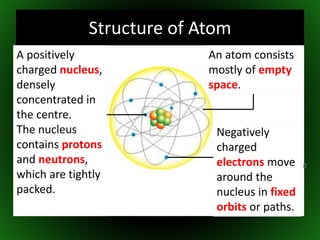
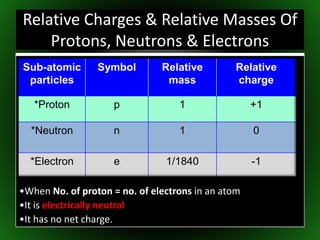
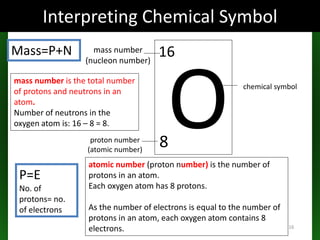
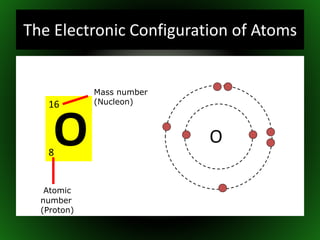
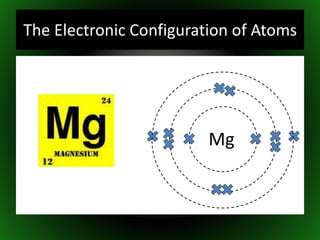
This document provides an overview of atomic structure and isotopes. It begins by recapping atomic structure, including the structure of the atom with electrons orbiting the nucleus, and the relative masses and charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons. It then defines isotopes as atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Examples of different isotopes of oxygen are provided. The document concludes by discussing some uses of radioactive isotopes, such as in food irradiation and carbon dating.