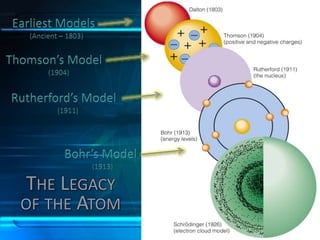
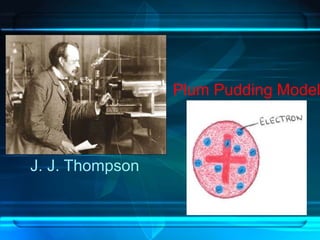
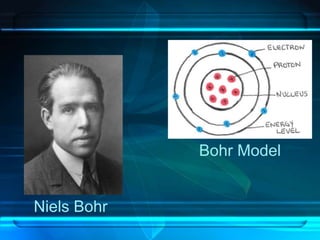
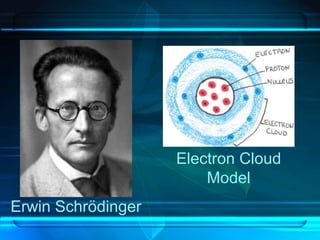
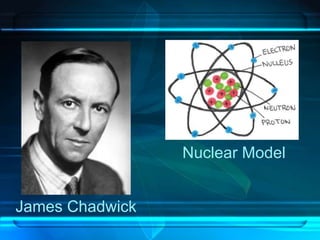
This document discusses the development of atomic theory from ancient Greece to modern times. It begins with Democritus' idea in 400 BC that matter is made of indivisible atoms. John Dalton expanded on this in 1803 with his Billiard Ball Model, proposing atoms as tiny invisible particles that make up elements. Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus in 1911 and protons in 1920 with his Planetary Model. Niels Bohr proposed fixed electron energy levels around the nucleus in 1913. Modern atomic theory incorporates Erwin Schrodinger's 1926 Electron Cloud Model and James Chadwick's 1932 discovery of neutrons in the nucleus.