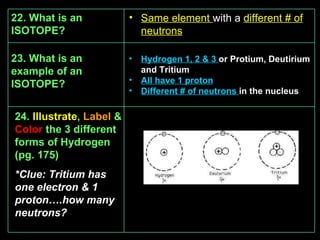
This document provides an overview of atomic structure including the basic particles that make up atoms and their properties. It discusses that atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged and found in the nucleus. Neutrons have no charge and are also found in the nucleus. Electrons are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons determines what element an atom is. Atoms can gain or lose electrons to become ions with positive or negative charges. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.