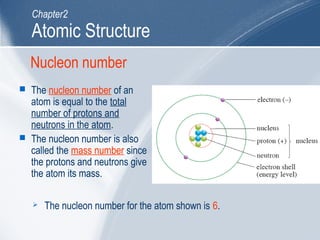
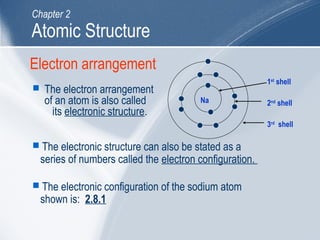
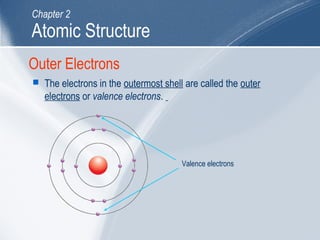
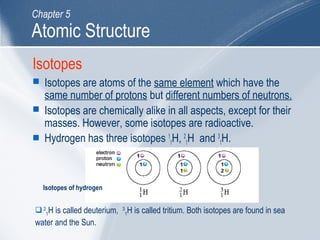
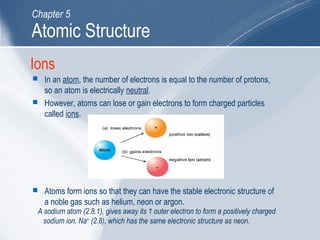
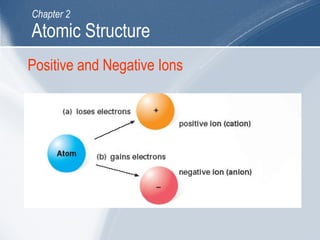
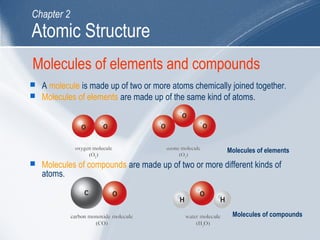
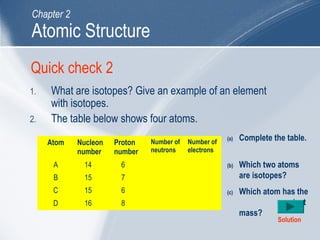
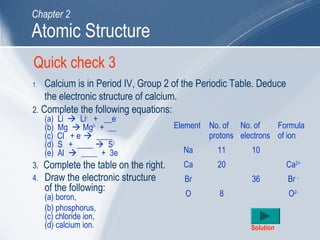
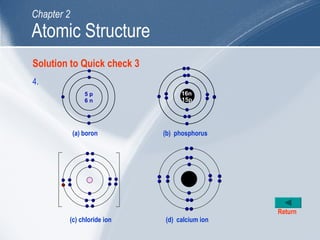
The document outlines key learning outcomes and concepts about atomic structure, including describing the structure of atoms with atomic numbers 1 to 20, defining terms like atomic number and mass number, explaining electron configuration and outer electrons, and distinguishing between isotopes, ions, and molecules of elements and compounds. It also provides illustrations of atomic structure and examples of applying atomic structure concepts.