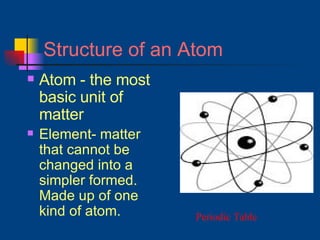
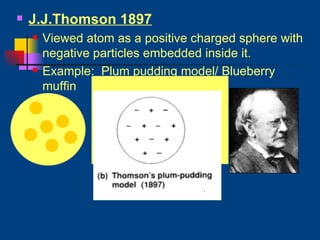
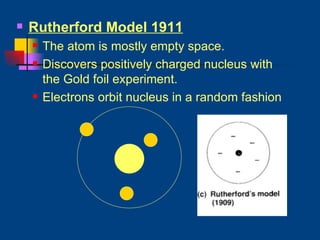
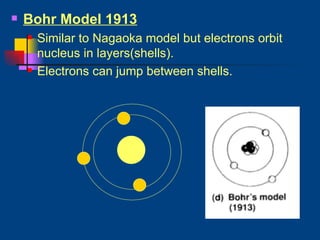
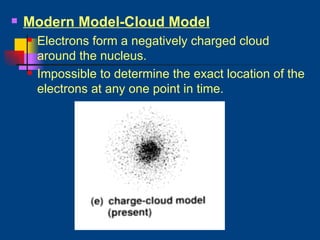
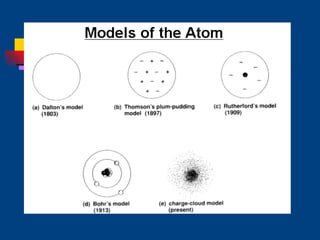
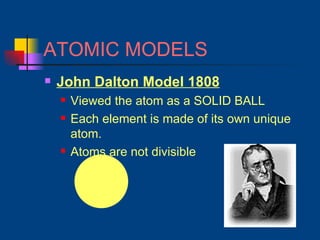
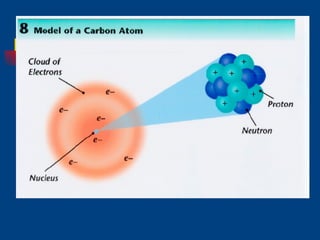
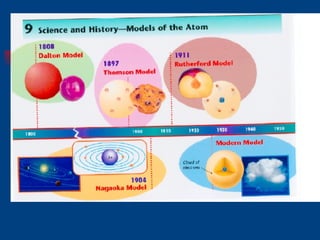
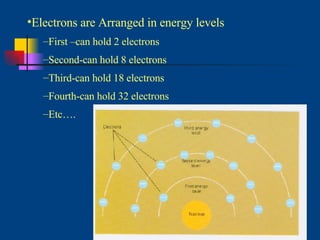
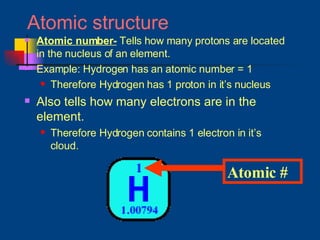
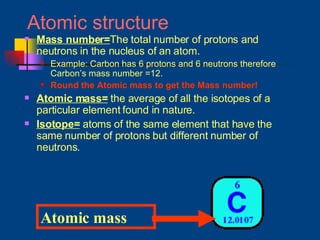
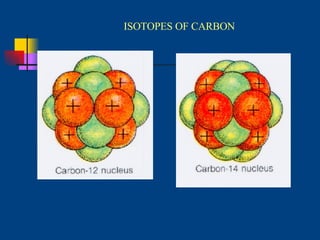
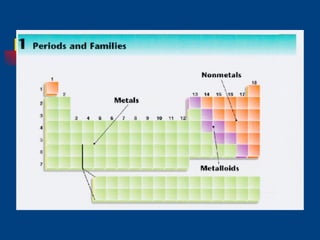
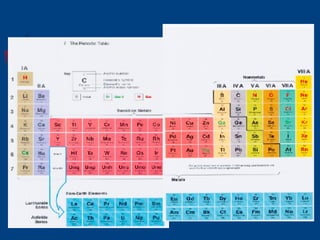
The document discusses atomic structure and the periodic table. It explains that atoms are the basic unit of matter and are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The number of protons determines the element. The periodic table organizes the elements and provides information about atomic structure like atomic number and mass. It also describes the historical models of the atom including those proposed by Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr.