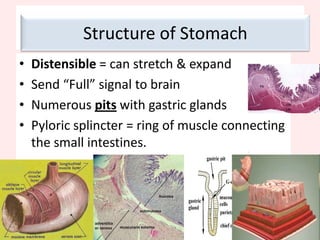
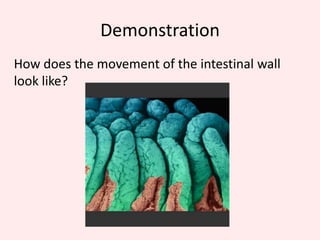
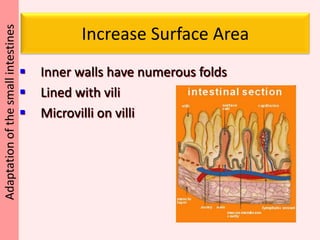
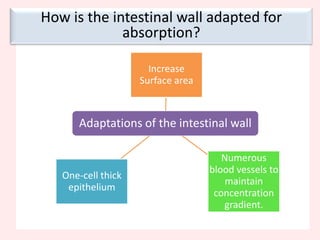
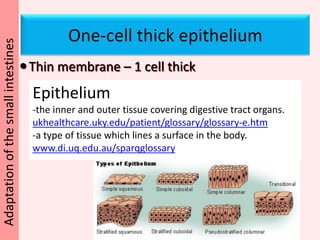
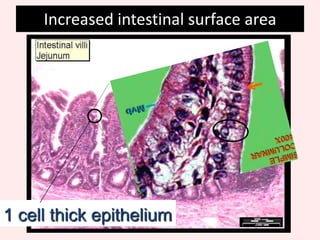
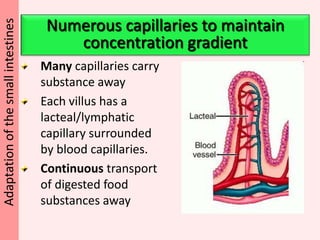
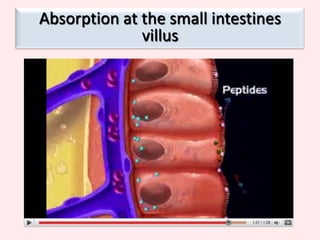
The document discusses the mammalian digestive system, examining the esophagus, stomach, and small intestines, and the adaptations that allow the small intestines to efficiently absorb nutrients. It describes how the villi and microvilli in the small intestines increase surface area for absorption and how a thin epithelium, capillaries, and concentration gradients aid absorption. Key nutrients like glucose and amino acids are absorbed and transported via the hepatic portal vein to the liver to be redistributed and utilized throughout the body.