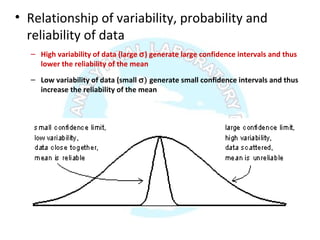
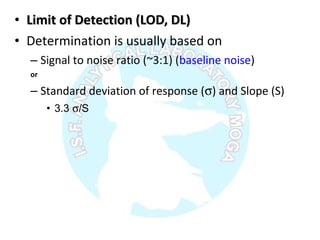
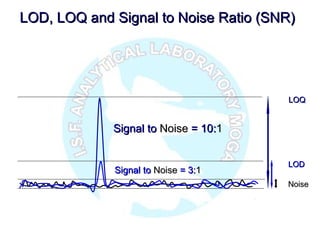
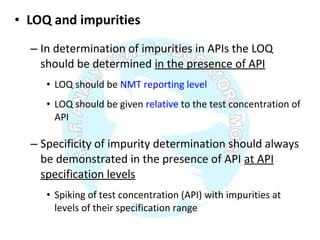
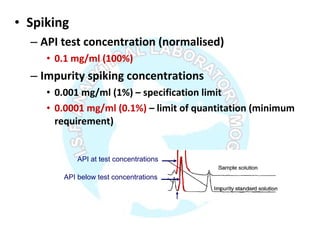
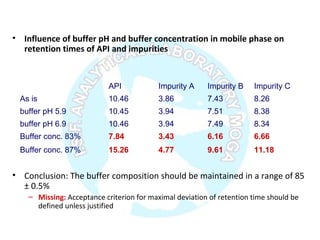
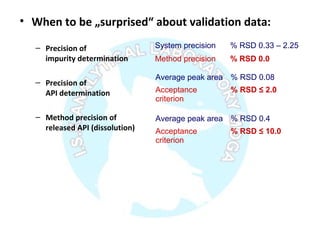
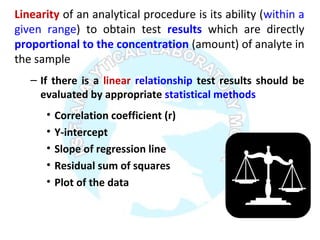
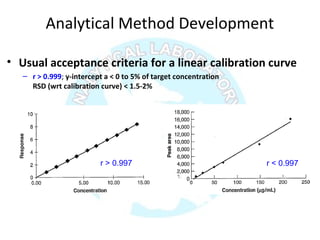
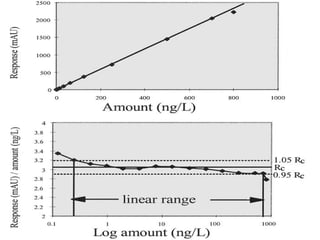
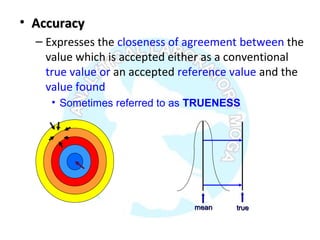
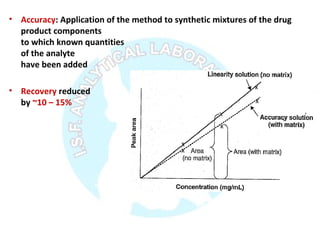
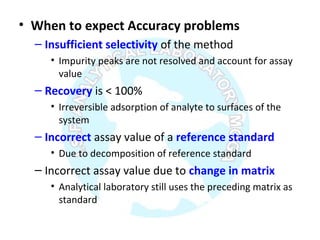
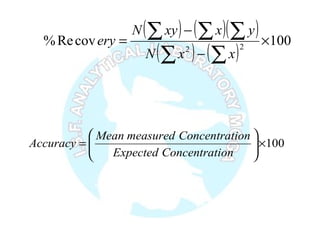
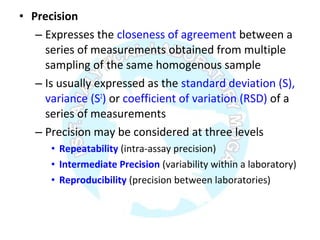
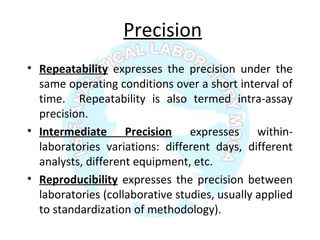
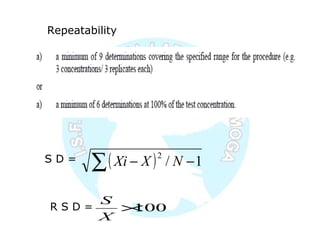
The document is a presentation on analytical method validation, focusing on its importance in ensuring that analytical procedures meet requirements for drug substances and products. It outlines various considerations for validation, including instrument suitability, method specificity, accuracy, precision, and detection limits, along with related guidance documents. Key concepts like robustness, linearity, and system suitability testing are emphasized to ensure reliable and accurate analytical results.





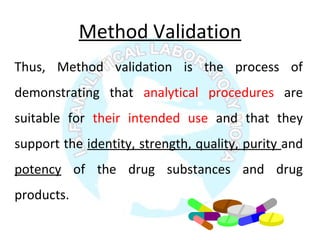




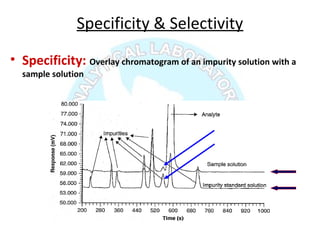

![Regression equation Y = aX + b
Where “a” is the slope of the line and “b” is the
intercept on the y-axis. When X = 0, “a” & “b” will be
according to equation 1.2.
( )∑ ∑
∑ ∑ ∑∑
−
−
= 22
2
xixiN
xiyixiyixi
b
( )∑ ∑
∑ ∑ ∑−
= 22
xixiN
yixixiyiN
a
( )[ ] ( )[ ]∑ ∑∑ ∑
∑ ∑ ∑
−−−
−
=
yiyiNxixiN
yixixiyi
r
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodvalidation-180314102218/85/Analytical-method-validation-15-320.jpg)




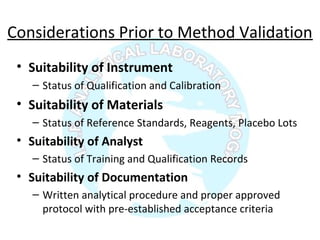
![Numberoftimeseachvalueoccurs
Valuesσ2σ3σ
σ 2σ 3σ
Normal distribution, probability function [P(x)] and confidence
interval [CI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodvalidation-180314102218/85/Analytical-method-validation-29-320.jpg)