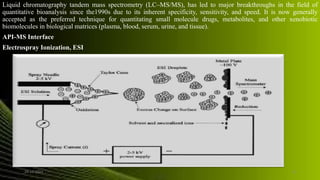
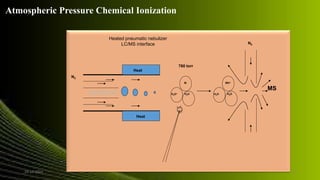
The document outlines the bioanalytical method development process, which is essential for the quantitative determination of drugs and their metabolites in biological materials. It emphasizes the importance of method validation to ensure reliability and accuracy in drug analysis, particularly in pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic studies. Techniques such as LC-MS/MS are highlighted for their specificity and sensitivity in bioanalytical applications, including drug development and clinical chemistry.
![Bioanalytical Method Development
Mr. Sagar Kishor savale
[Department of Pharmacy (Pharmaceutics)]
avengersagar16@gmail.com
24-12-2015 1
Department of Pharmacy (Pharmaceutics) | Sagar savale](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioanlyticalmethoddevelopment-151225053601/75/Bioanlytical-method-development-1-2048.jpg)