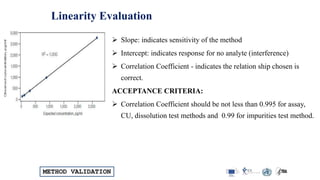
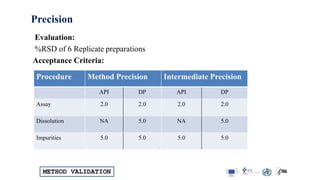
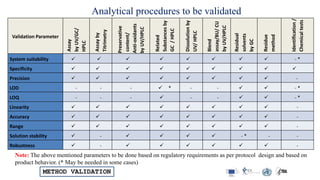
The document outlines the comprehensive process of analytical method validation, detailing its definition, requirements, and parameters such as specificity, precision, linearity, accuracy, and system suitability. It emphasizes the importance of validation in ensuring that analytical procedures are reliable and acceptable per regulatory guidelines like ICH and FDA. Additionally, it discusses acceptance criteria for various validation parameters and the need for revalidation when changes occur in methodologies or products.










![METHOD VALIDATION
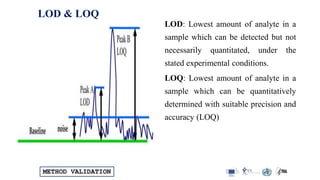
LOD & LOQ
Different approaches suggested by ICH, USP & EP
Several approaches are given in the ICH guidelines for estimating LOD and LOQ
Depending on the procedure : instrumental / non-instrumental
As per ICH and USP, other approaches suggested above are also acceptable.
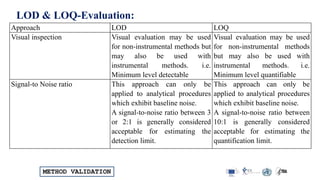
Approach methods LOD LOQ
Visual inspection Minimum level detectable Minimum level quantifiable
Signal to Noise ratio 2:1 or 3:1 10:1
SD of response (σ)& Slope (S) [3:3 x σ] / S] [10.0 x σ] / S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodvalidations-240330110550-59ba2dd8/85/Analytical-Method-Validations-Detailed-Method-Validation-Parameters-16-320.jpg)