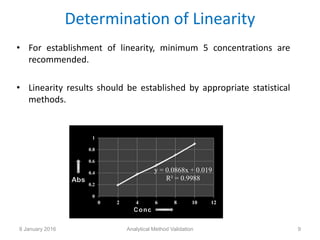
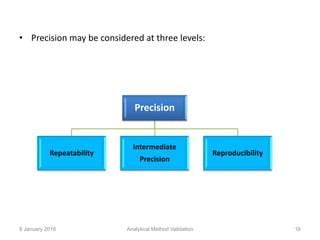
Validation is defined as establishing documented evidence that a process will consistently produce results meeting pre-determined specifications. Key aspects of analytical method validation include accuracy, precision, specificity, limit of detection/quantitation, linearity, range, robustness, and system suitability. Validation demonstrates a method is suitable for its intended use and ensures consistent, reliable results are obtained in compliance with regulations.