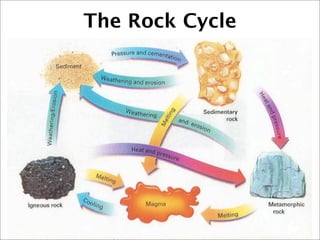
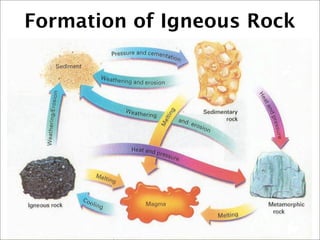
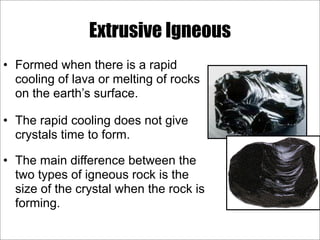
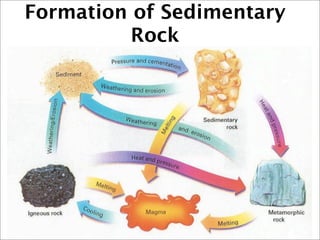
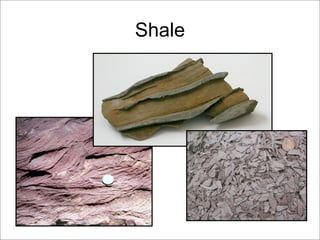
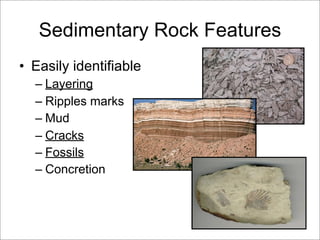
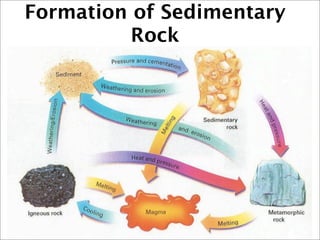
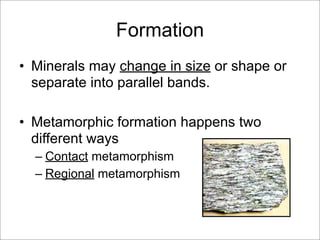
This document discusses the three main types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic - and the rock cycle. It explains that igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks form through compaction or cementation of sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from extreme heat and pressure changing existing rocks. The rock cycle is also summarized, noting that geological forces cause rocks to change forms over time, passing through the different types.