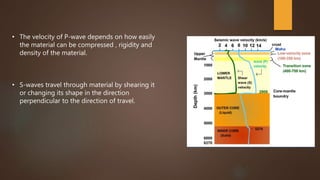
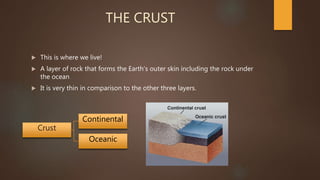
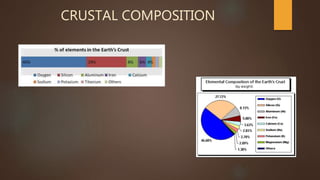
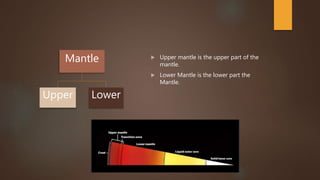
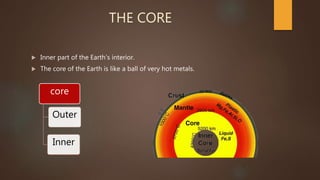
The document summarizes the structure and composition of Earth's interior layers. It describes how seismic waves and samples from deep drilling provide evidence that the Earth has distinct layers, including a crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust varies in thickness and composition between continental and oceanic crust. Below the crust lies the mantle, which makes up over 80% of the Earth's volume and is divided into an upper and lower mantle. The lower mantle and outer core are liquid, while the inner core is solid.