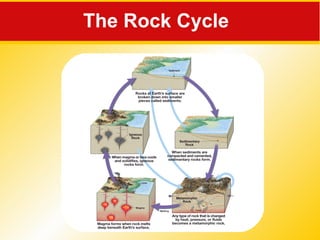
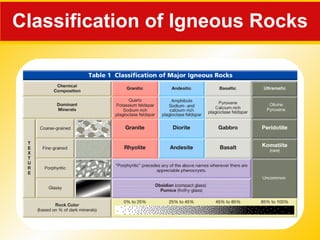
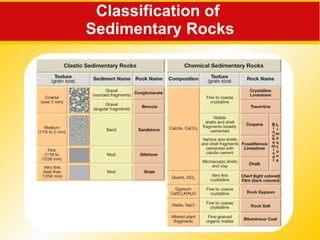
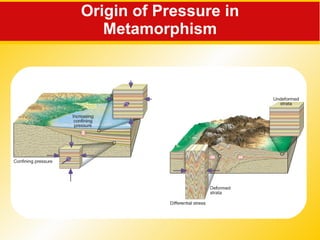
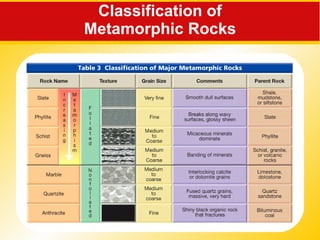
The document discusses the three main rock types - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. It describes the rock cycle which shows how the different rock types are interrelated through geological processes. Igneous rocks form from the cooling of magma, either below ground (intrusive) or on the surface (extrusive). Sedimentary rocks form through the weathering of existing rocks, erosion and deposition of sediments, and compaction and cementation over time. Metamorphic rocks form from the alteration of existing rocks deep underground under high pressures and temperatures.