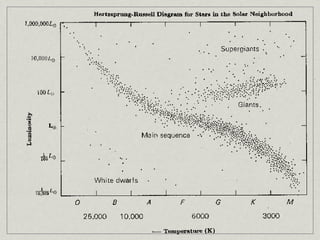
1) Stars begin as clouds of dust and gases called nebulae. Under gravity, the gases condense to form protostars and begin nuclear fusion, becoming main sequence stars like our Sun.
2) As stars age, they expand and become red giants or supergiants after exhausting hydrogen fusion. Further fusion of helium produces carbon.
3) When further fusion is no longer possible, the star collapses into a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole in a supernova explosion, depending on the star's original mass.