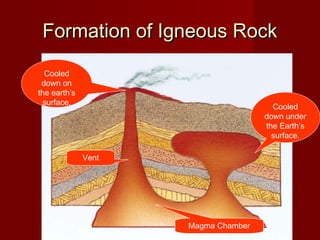
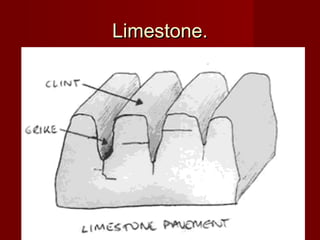
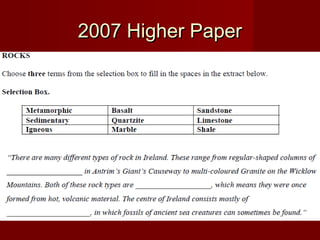
The document discusses different types of rocks, categorizing them into igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic based on their formation processes. Igneous rocks like granite and basalt are formed from cooled lava and magma, sedimentary rocks like limestone and sandstone arise from compressed organic materials, and metamorphic rocks such as marble and quartzite evolve from other rock types due to heat and pressure. Each type of rock has unique characteristics and examples along with various uses, particularly in construction and natural resource extraction.