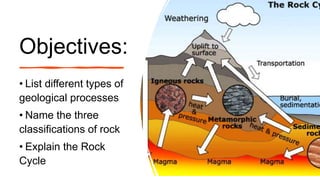
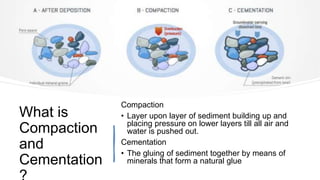
The document explains the rock cycle, detailing geological processes that transform rocks among three classifications: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. It covers key processes such as weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation, melting, cooling, solidification, and metamorphism. Additionally, it provides descriptions and examples of each type of rock and their formation processes.


















![Resources:
A. DeWitt (Dec. 09, 2008) The Rock Cycle [PowerPoint] SlideShare
https://www.slideshare.net/guest74968e/the-rock-cycle-presentation-
834378
C. Reich Little(Sep. 25, 2017) Rockcycle 2017 [PowerPoint]
SlideShare https://www.slideshare.net/mariejajaroa/rock-cycle-
57878723
Mojavehack (Feb. 26, 2015) 5.0 Rocks and Rock Cycle [PowerPoint]
SlideShare https://www.slideshare.net/mojavehack/50-rocks-and-rock-
cycle
R. Brindley (Sep. 27, 2011) The Rock Cycle and Rocks [PowerPoint]
SlideShare https://www.slideshare.net/rebelbrindley/the-rock-cycle-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/therockcycle-220821201709-80721245/85/The-Rock-Cycle-pptx-21-320.jpg)