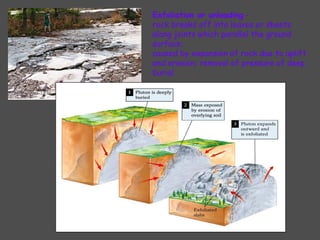
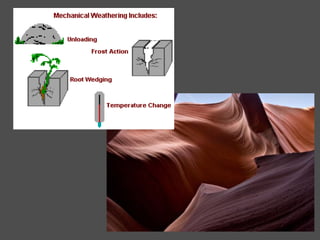
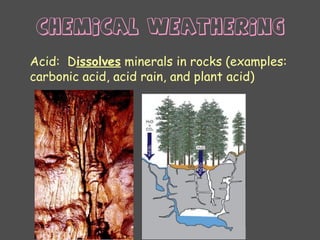
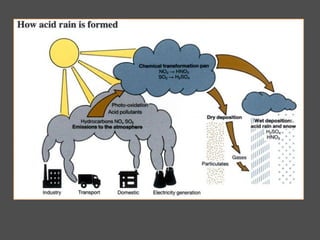
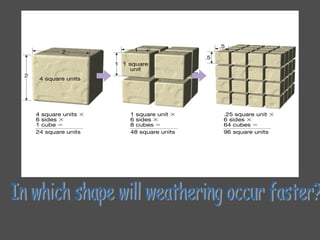
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks and materials at the Earth's surface through mechanical and chemical processes. Mechanical weathering causes no chemical change and includes temperature fluctuations, frost action, root growth, and abrasion by water and wind. Chemical weathering alters the composition of minerals and includes dissolution by water and acids, oxidation, and hydrolysis. The rate of weathering depends on factors like composition, cracks/holes, climate, topography, air pollution, and exposure time. Both mechanical and chemical weathering work together to slowly break down rocks over very long periods of time.