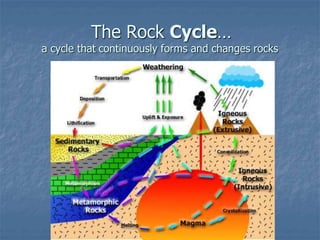
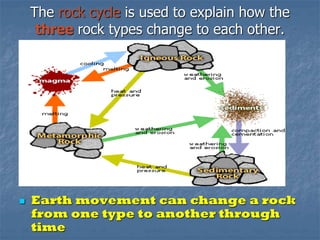
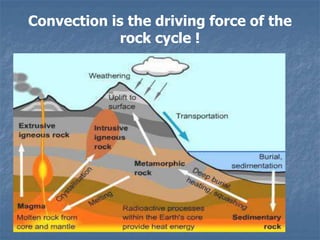
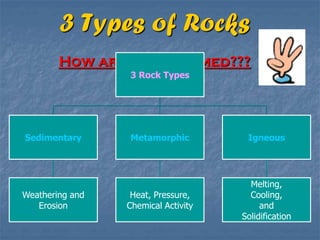
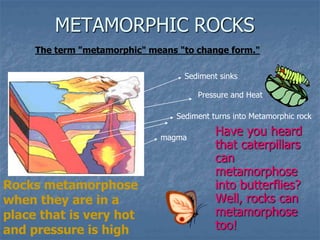
Rocks continuously change forms through the rock cycle. There are three main types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks form from compressed and cemented sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from existing rocks undergoing heat and pressure. Plate tectonics and the rock cycle drive the recycling of Earth's rocks as they change forms over millions of years.