Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
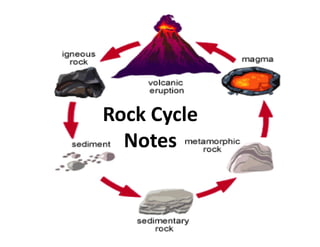







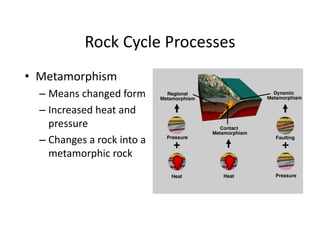

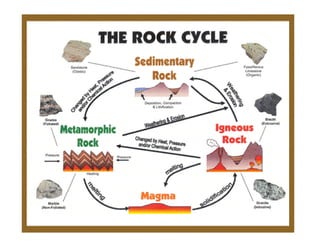
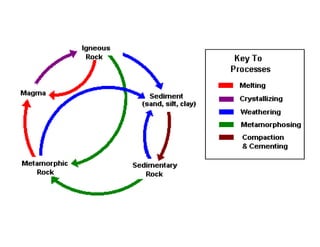
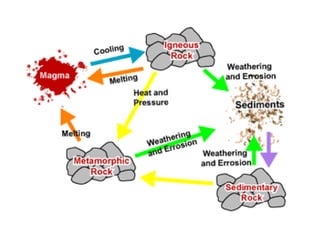


The document discusses the rock cycle, which describes how rocks constantly change form through various natural processes. Rocks can be broken down by weathering into sediments and then transported by erosion. These sediments may be deposited, compacted, and cemented to form sedimentary rocks. Increased heat and pressure can metamorphose sedimentary and igneous rocks. Melting of rocks forms magma that cools and solidifies into new igneous rocks. This cyclic process results in rocks continuously changing their shape and composition over geological time.













